Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Malignant neoplasm of germinative basal layer of epidermis and hair follicles
- Rarely metastasize (<0.025%) but can cause extensive tissue damage
- BCC/SCC ratio is 4:1
Types
- Nodular
- Superficial
- Morpheaform; solid - hard
- Pigmented
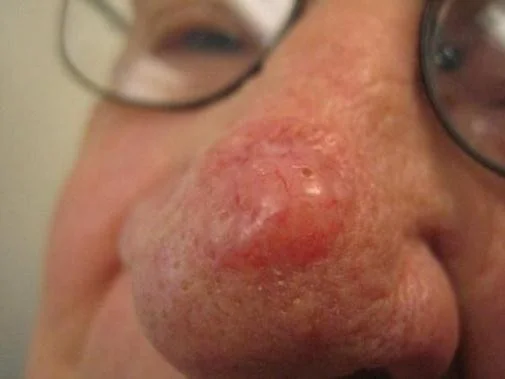
Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Most common variant
- Pearly, waxy papule, nodule, or plaque
- Superficial telangiectasia - small dilated blood vessels
- Frequent superficial ulceration
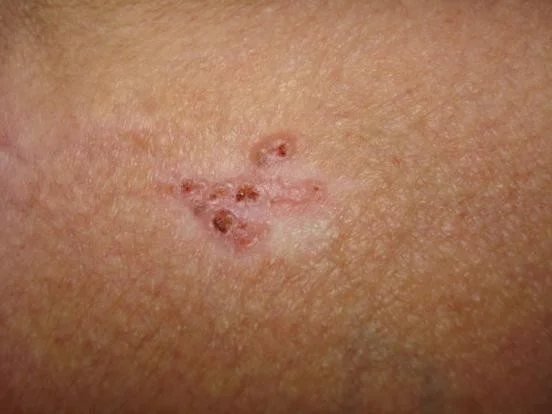
Morpheaform Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Scar-like plaque
- whitish dermal plaque with atrophy
- More extensive subclinical spread
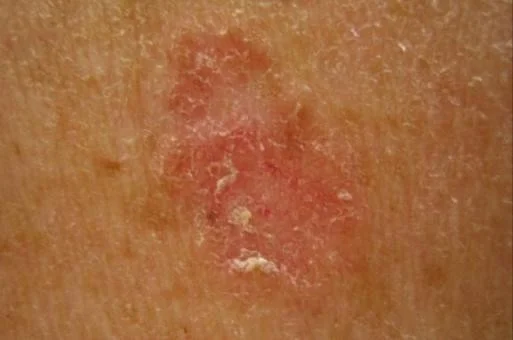
Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Red scaly plaque, mimics superficial dermatitis
- Most common on the trunk and extremities
- Seen with chronic arsenic and areas of radiation damage
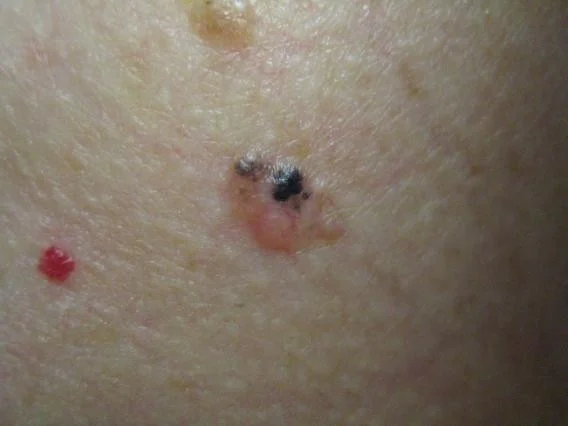
Pigmented Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Dark brown or blue pearly papule
- Mimics dysplastic nevus or nodular melanoma
- Seen with darker skin types
Pigmented BCC
Epidemiology
- 95% Caucasians
- 95% between ages 40-79 years old
- 85% head and neck
- Nose most common site, approximately 30% of all tumors