Melanoma
Arise from epidermal melanocytes Skin is most common site also seen in mucosa, retina, and leptomeninges
- Incidence tripled in last 4 decades
- All ages affected, median age 53
Etiology
Cumulative and prolonged UVB and/or UVA exposure
UVA exposure from tanning beds increases risk for melanoma
Risk Factors
- Numerous nevi (common or atypical)
- Atypical nevi
- Family or personal history of melanoma
- Immunosuppression = SCC
- Intermittent intense sun exposure
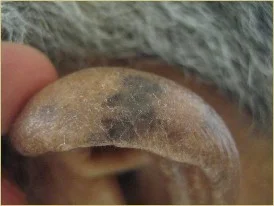
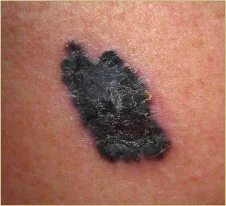
Clinical Presentation
-
Typically appears as a pigmented papule, plaque or nodule.
-
Demonstrates any of the ABCDES
- It may bleed, be eroded or crusted
- Patients may give history of change
-
Majority located in sun-exposed areas, but also occur in non-sun-exposed areas, such as the buttock
- Also occur on mucous membranes (mouth, genitalia)
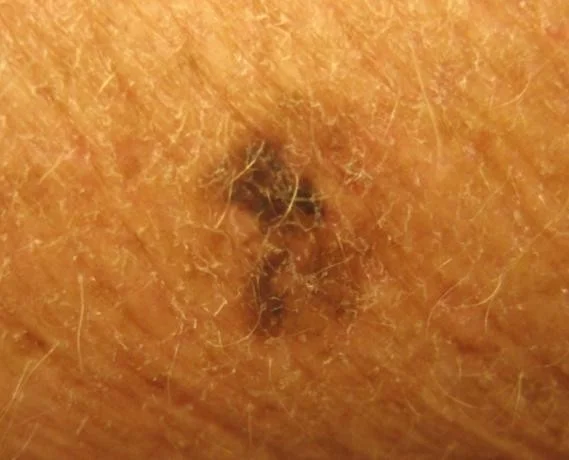
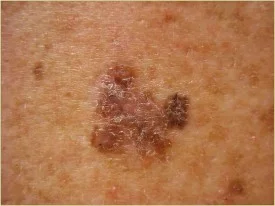
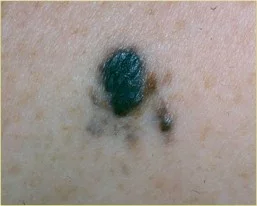
The ABCDEs of Melanoma
The ABCDEs of Melanoma Suspicious moles may have any of the following features:
- ASYMMETRY
- With regard to shape or color
- BORDER
- Irregular or notched
- COLOR
- Very dark or variegated colors
- Blue, Black, Brown, Red, Pink, White
- DIAMETER
- >6 mm, or “larger than a pencil eraser”
- Diameter that is rapidly changing
- EVOLVING
- Evolution or change in any of the ABCD features