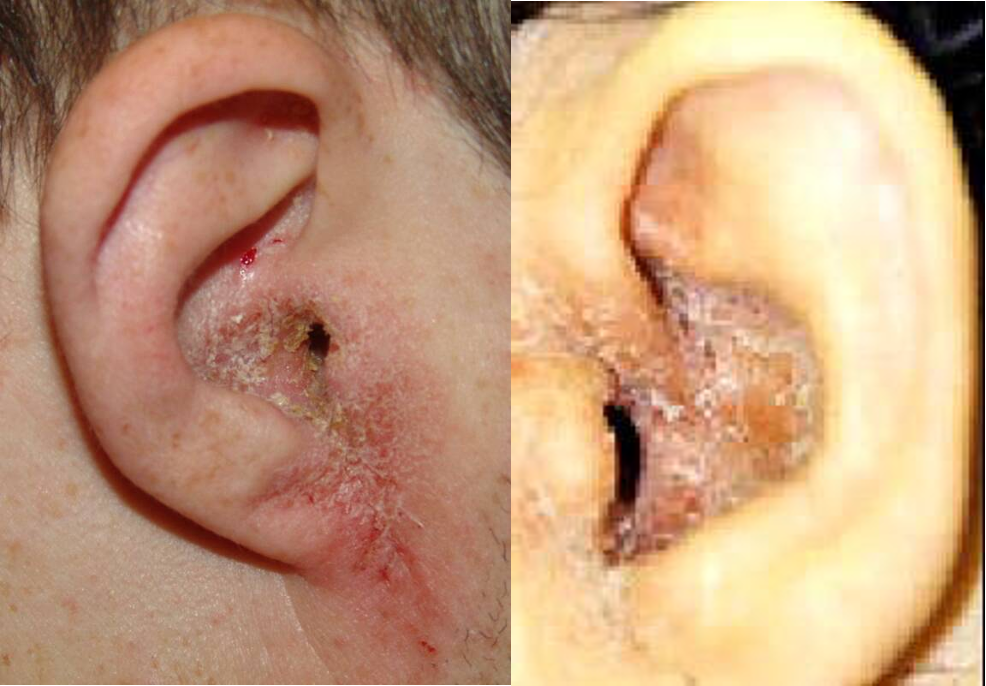
Otitis Externa
Definition:
Inflammation of meatal skin which may spread to involve the pinna and epidermal layer of the tympanic membrane
Risk Factors:
- Hot and humid climate
- Swimming
- Trauma to meatal skin
Pathogens:
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Proteus mirabilis
- Staphylococci
- Streptococci
Causes of Otitis Externa
Infective:
- Bacterial: Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas, others
- Fungal: Aspergillus niger, Candida albicans
- Viral: Herpes zoster
Reactive:
- Eczematous
- Seborrheic
Presentations:
- Earache
- Discharge
- Hearing loss
- Itching
Physical Examination:
- Tenderness
- Narrow EAC
- Discharge
- Debris
- Lymphadenopathy
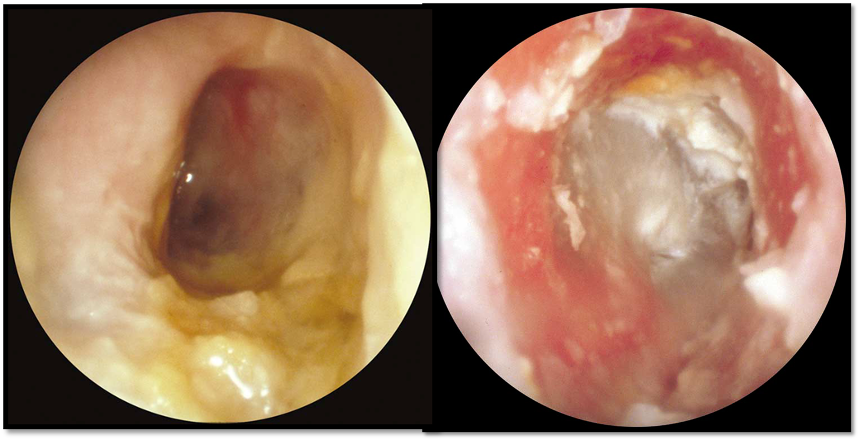
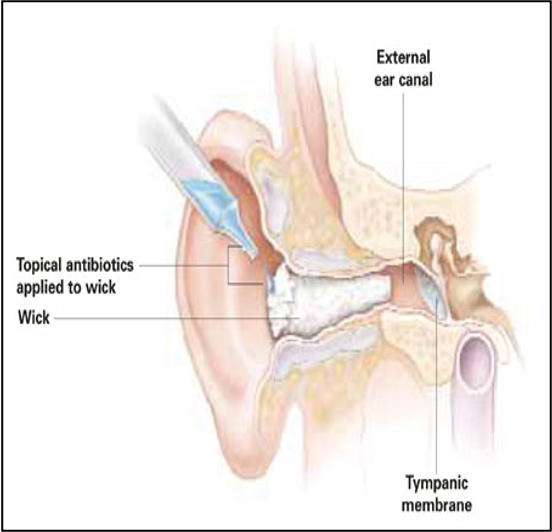
Management:
- Ear cleaning (CS) and wicks
- Antibiotics (Topical +/- Oral)
- Analgesia
- Patient instructions (Avoid instrumentation, Keep ear dry)
- Local steroid
Complications:
- Necrotizing (malignant) otitis externa (skull base osteomyelitis)
Clinical Types of Otitis Externa
- Localized O.E (Furuncle)
- Diffuse infective O.E.
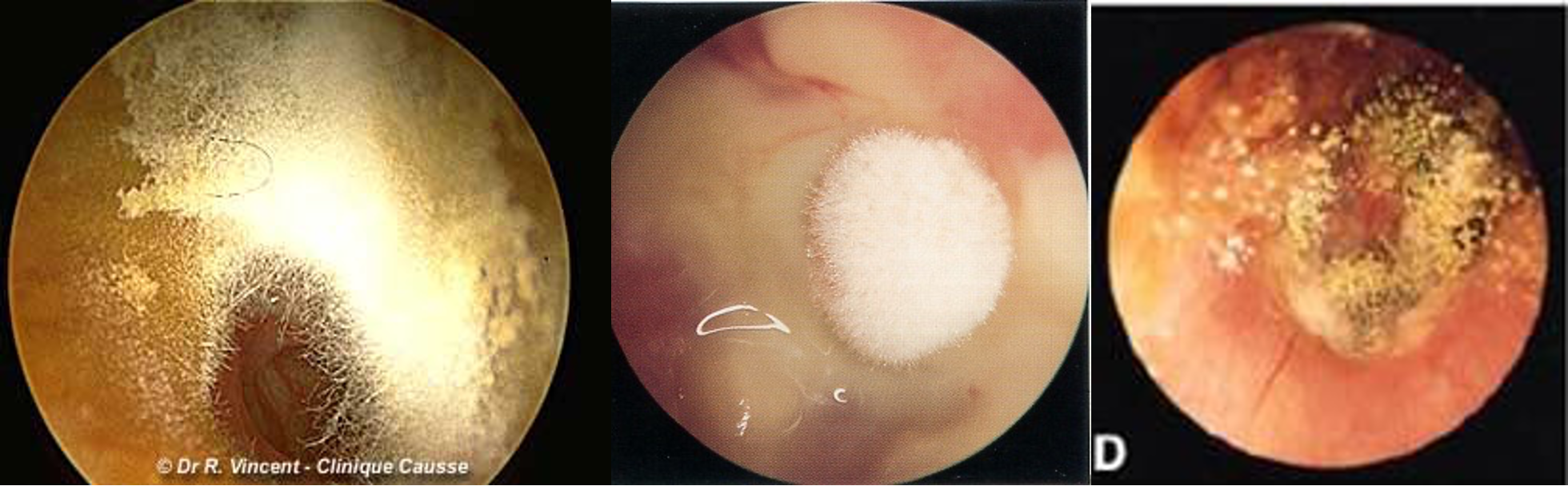
- Otomycosis
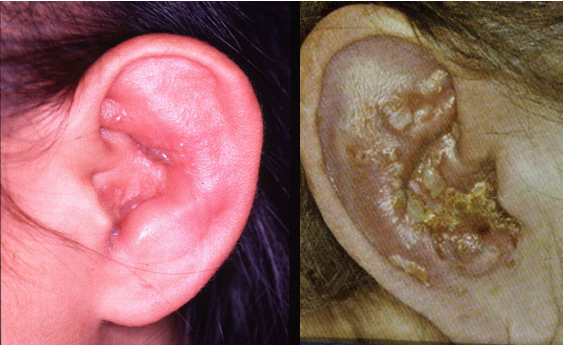
- Herpetic O.E.
- Eczematous and seborrheic O.E.
Localiced/ diffused infective
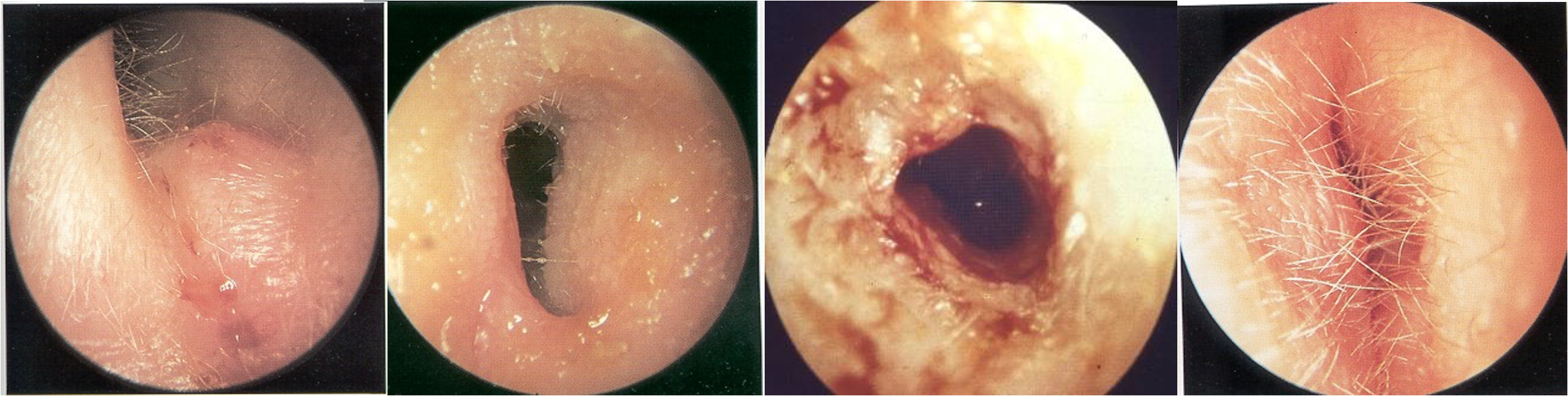
Otomycoosis
Herpetic O.E.
Eczematous and seborrheic O.E.