Definition:
- Chronic otorrhea (>3 months) through perforated TM.
Pathogens:
- Mixed infections: Gram-negative bacilli (Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, Proteus, E. coli), Staphylococcus, anaerobes.
Presentation:
Types of CSOM:
| Feature | Tubotympanic (Safe) | Atticoantral (Unsafe) |
|---|
| Discharge | Profuse, mucoid, odourless | Scanty, purulent, foul smelling |
| Perforation | Central | Attic or marginal |
| Granulations | Uncommon | Common |
| Polyp | Pale | Red and fleshy |
| Cholesteatoma | Absent | Present |
| Complications | Rare | Common |
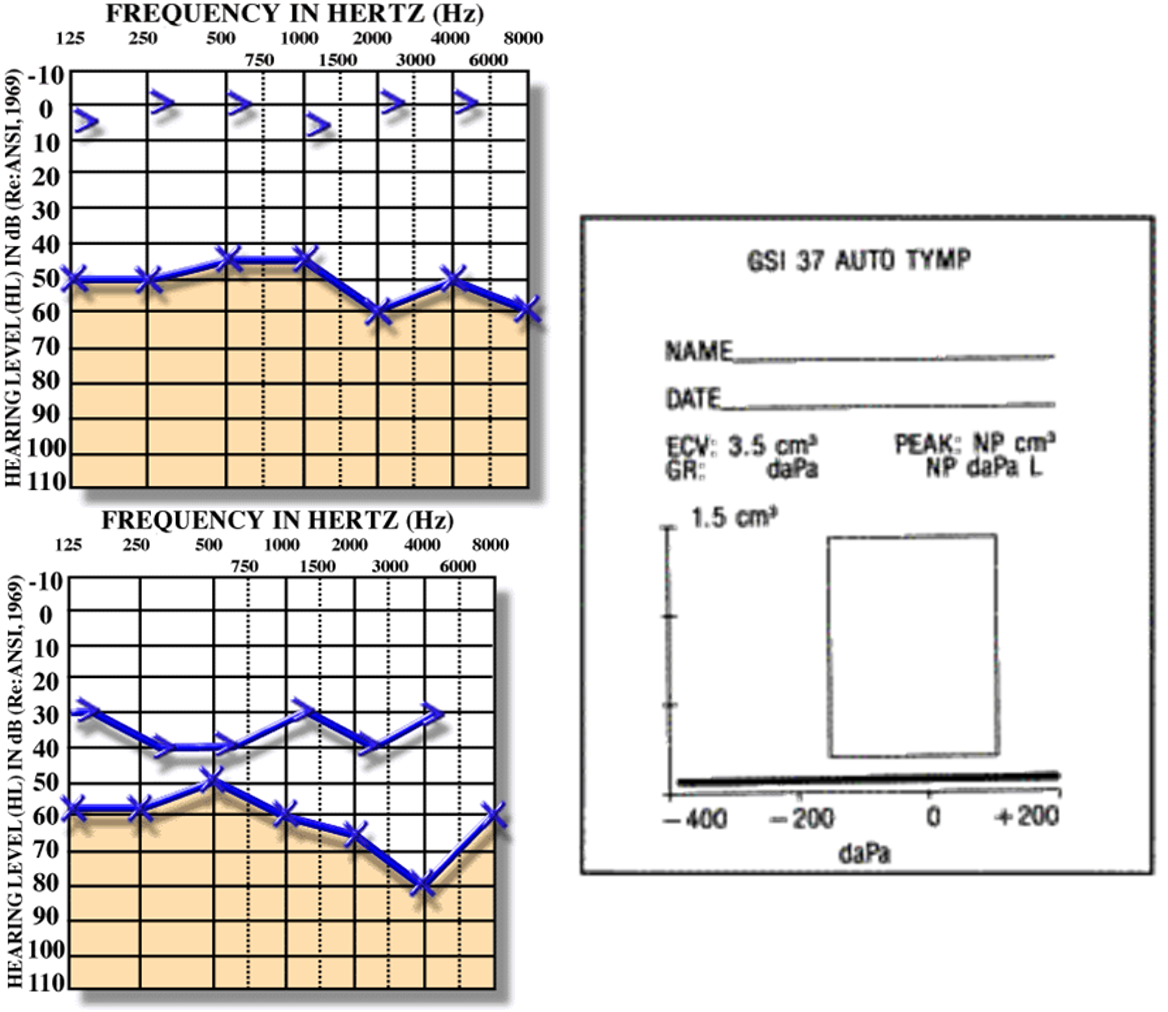
| Audiogram | Mild to moderate conductive deafness | Conductive or mixed deafness |
| ![[Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media-20250116104541382.webp | 520]] | |
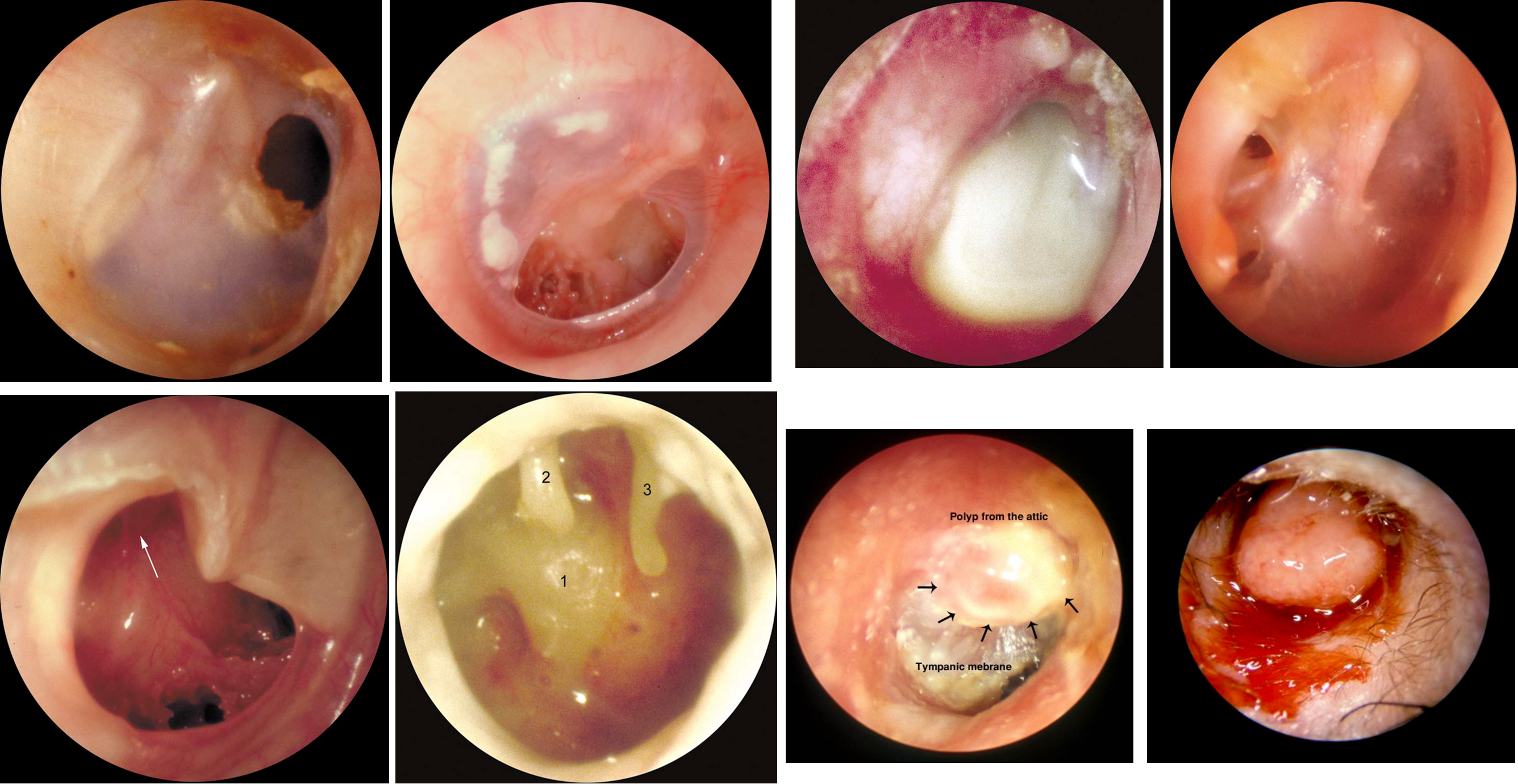
Types of Perforations in CSOM:
- Central perforation (anterior)
- Subtotal perforation
- Total perforation with destruction of the fibrous annulus
- Attic perforation
- Posterosuperior marginal perforation
Approach to CSOM
- History & Clinical Examination
- Audiology
- Radiology (CT)
Management:
- Water precaution, aural toilet, antibiotics, surgery (tympanoplasty, mastoidectomy).