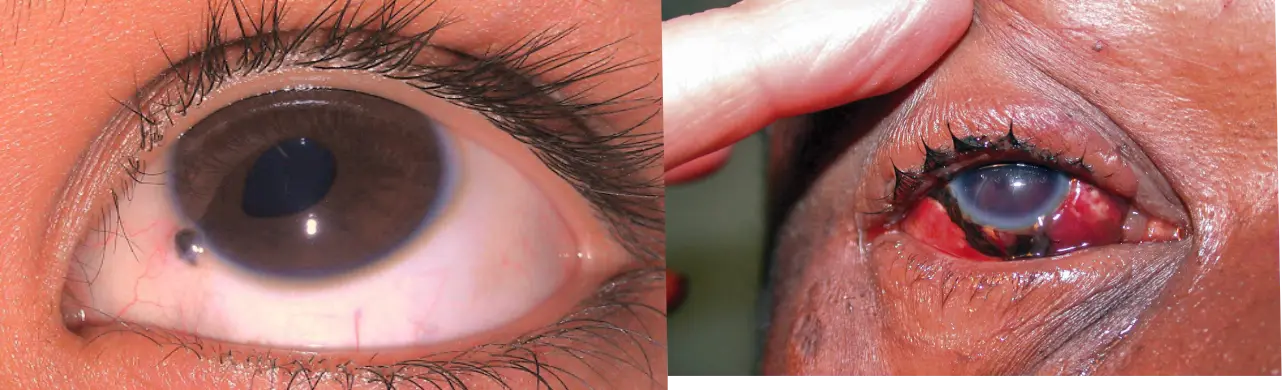
1- Bulbar Conjunctiva: (Covers the sclera) 2- Palpebral Conjunctiva: (Lines the inner surface of the eyelids) 3- Conjunctival Fornix: (The junction/fold between the bulbar and palpebral conjunctiva)
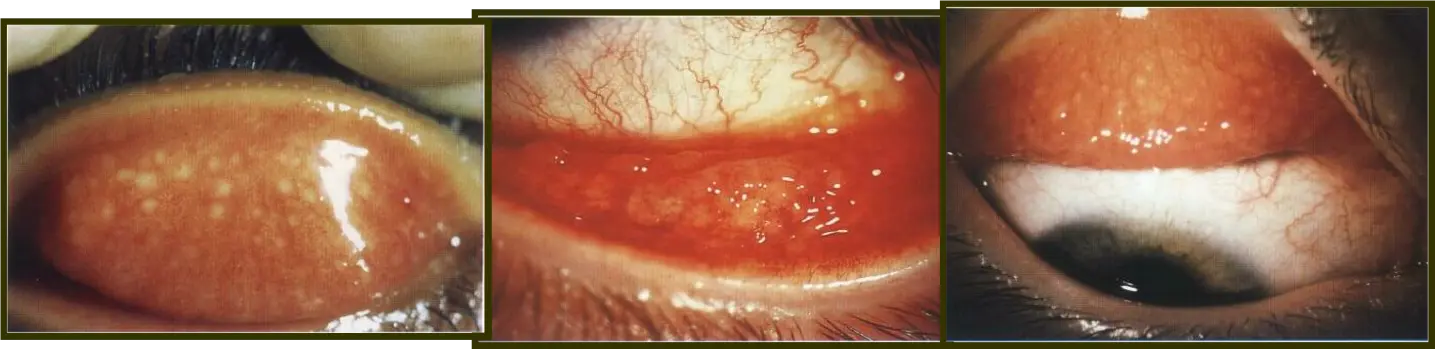
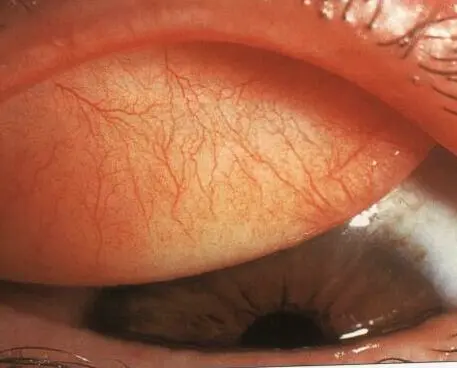
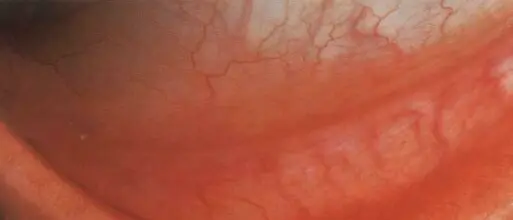
Conj. follicles
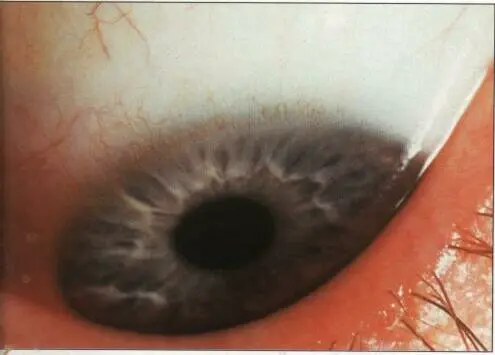
Conj. papillae
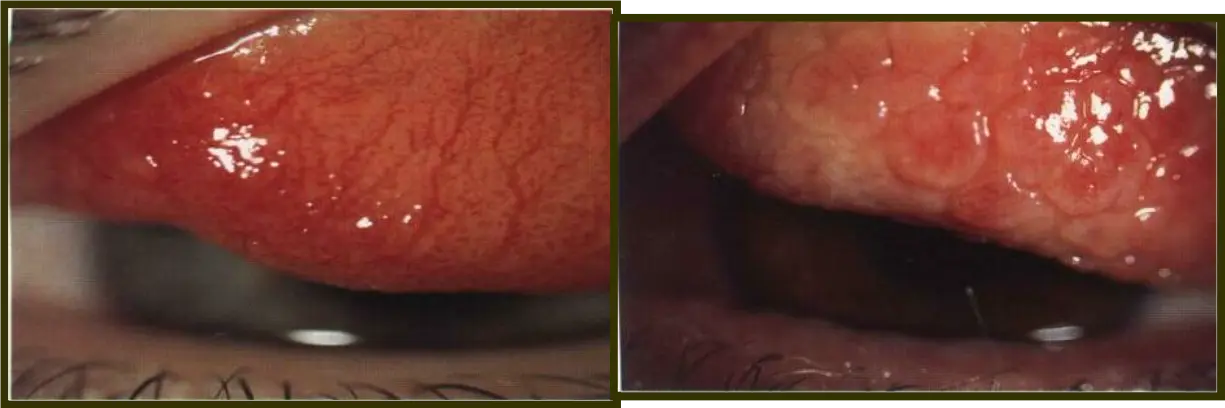
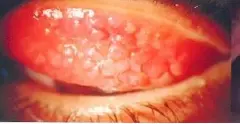 Giant (cobblestone) papillae
Diagnosis: Giant palpebral conjunctivitis
What is the cause: Wearing contact lens, - Chronic allergy
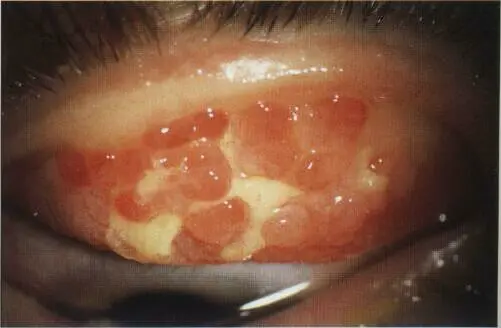
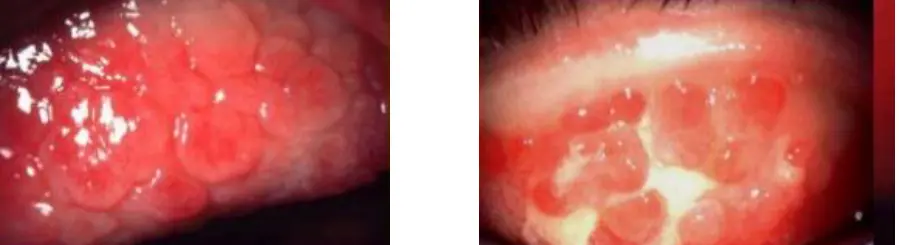
Giant (cobblestone) papillae
Diagnosis: Giant palpebral conjunctivitis
What is the cause: Wearing contact lens, - Chronic allergy
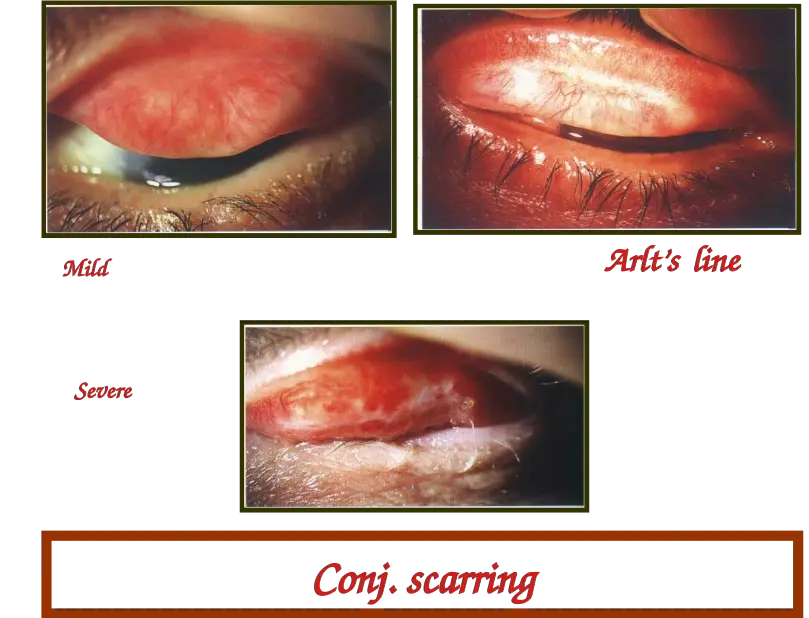
Conj. Scarring Y
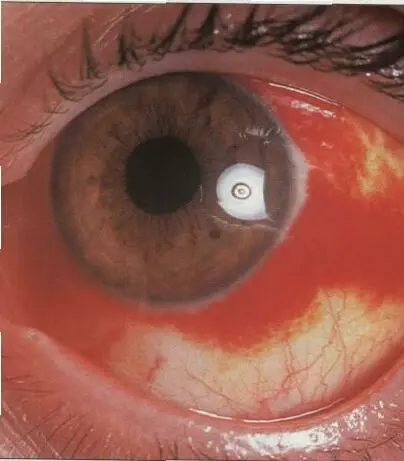

Subconjunctival hemorrhage
Young male after gym training discovered redness in eye.
Causes:
- Truama,
- Spontaneously (rupture due severe cough, constipation, lifting heavy objects)
- Systemic Hypertension
- Coagulation diseases
Treament:
- No specific treatment only assurance to patient, leave the hemorrhage would resolve its own in two weeks
- ask for medical assessment for hypertension, liver diseases
its never IOP doesnt lead to it
Symblepharon Y
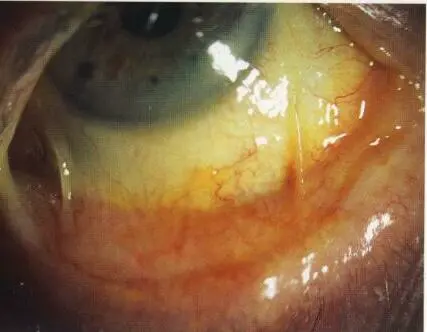
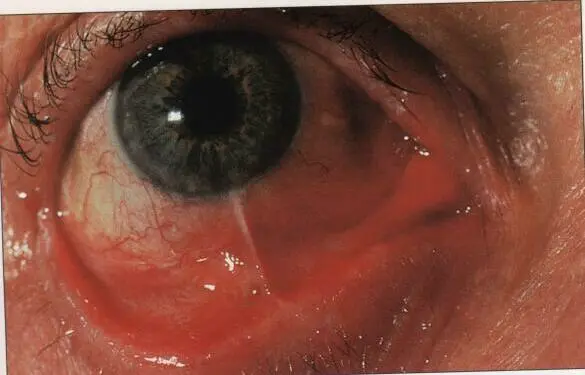
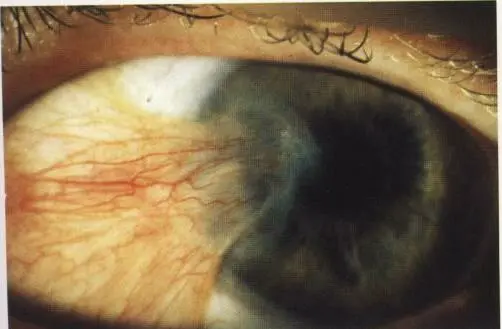
Pinguecula
Cause: Hyaline degeneration of conjunctiva
Sign: Yellowish, grayish elevation near limbus never crosses cornea, usually triangular shape
Risk Factors:
- Exposure to sun rays, hot weather
Treatment:
- Assurance
- Lubricants
- Decrease exposure to sun rays with sunglasses
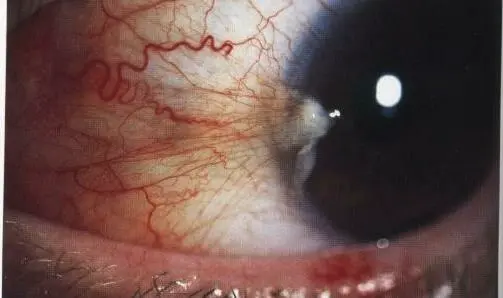
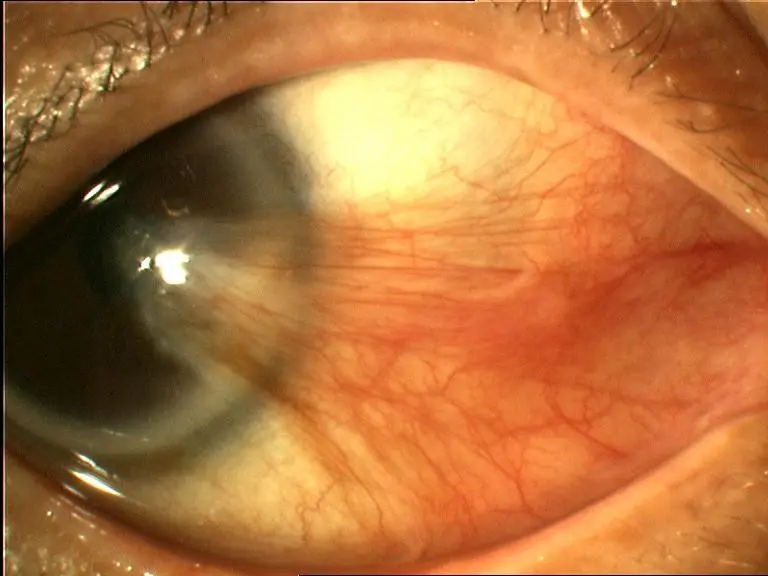
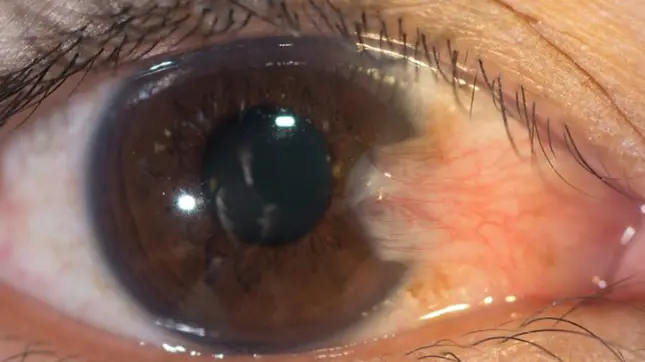
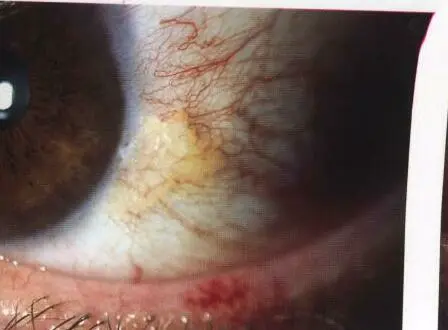
Pterygium (wing)
Cause: Fibrovascular growth of conjunctiva, triangular shape near limbus, and creeps may crosses cornea
Risk Factors:
- workers, farmers
Treatment:
- Assurance
- Lubricants
- Decrease exposure to sun rays with sunglasses
- If it crosses to the cornea, Surgical removal is indicated (cosmetic and effects vision by covering pupil or compression may result in astigmatism)
Pterygium (recurrent)
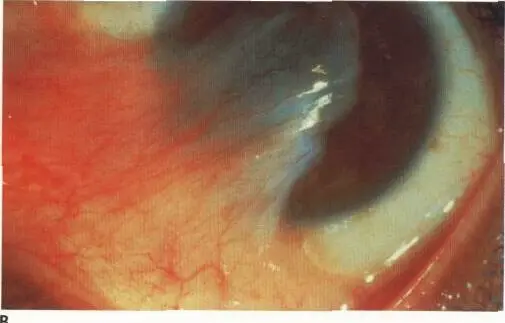
Bitot’s spot Y
Foamy surface with chalky avascular appearance
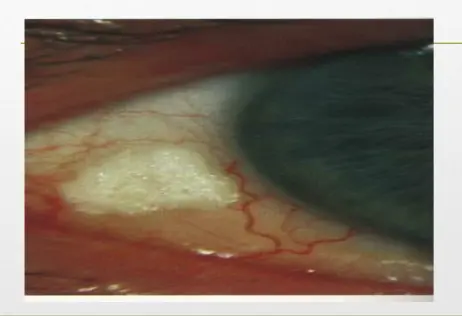
Conjunctiva navus Y
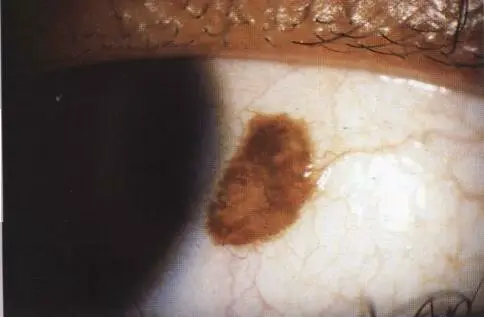
Conj. cyst Y
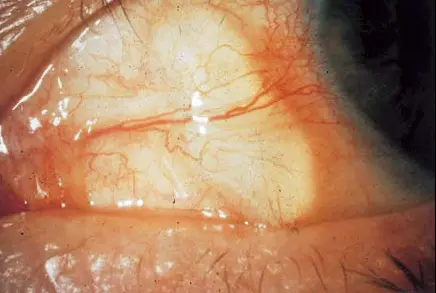
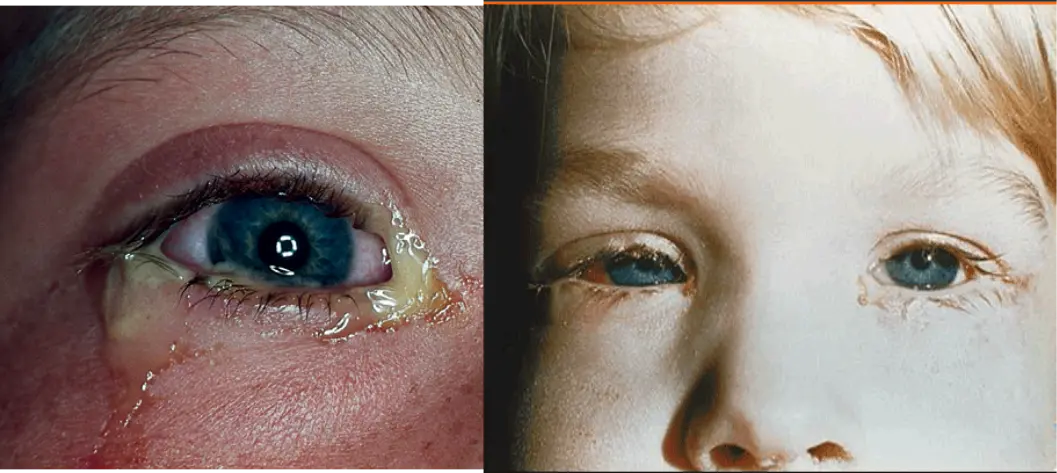
Conjunctivitis
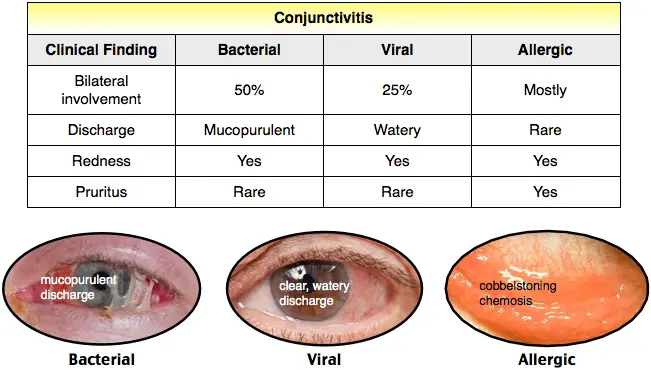
- Viral; LN
- Allergic; Itching
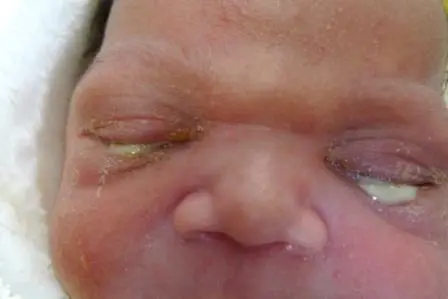
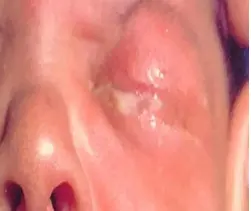
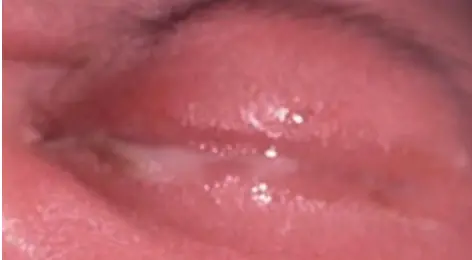
Neonatal Conjunctivitis
Cause:
- Neisseria gonorrhea
- Chlamydia
Treatment:
- Before starting, child’s conjunctiva swab, mother’s cervical, and vaginal
- Eye lid hygiene
- Topical & Systemic antibiotics
Scleritis. Y
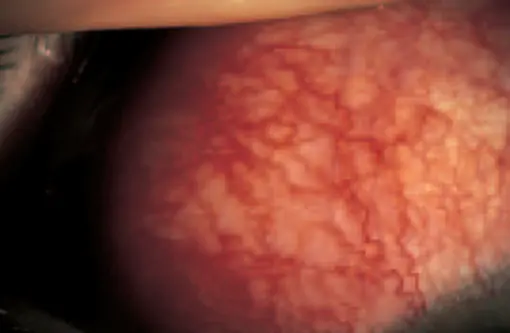
Episcleritis. Y
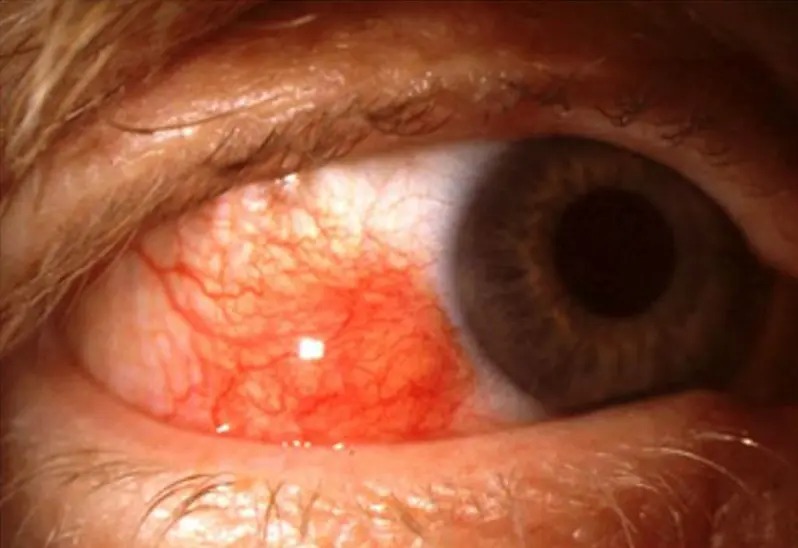
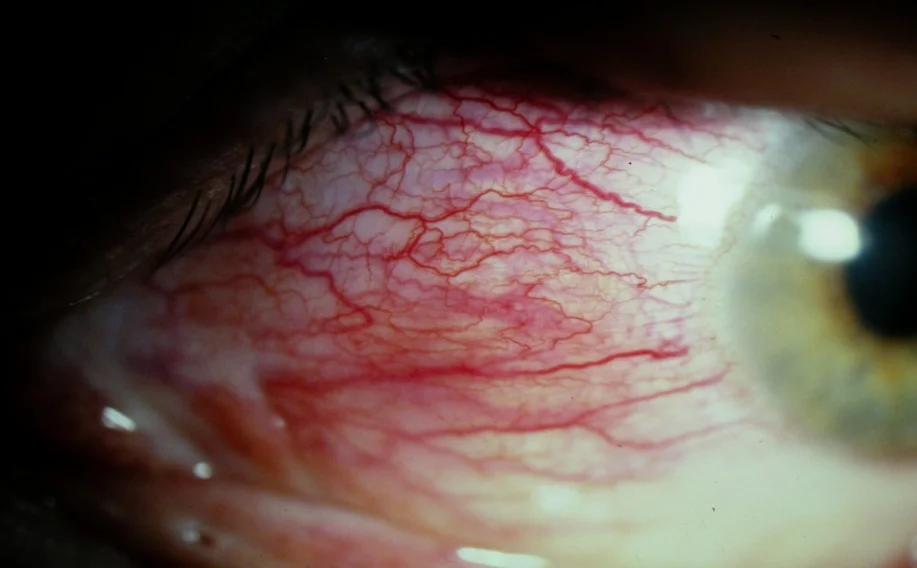
 #Y
#Y
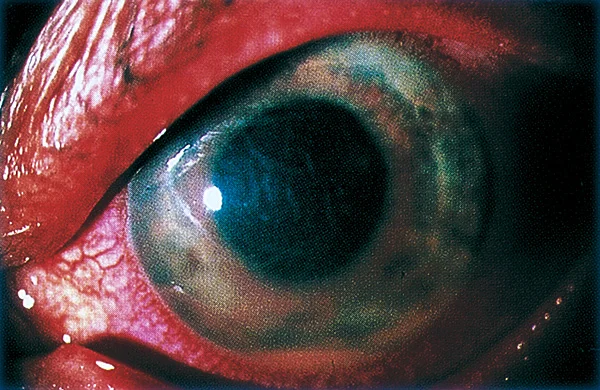

Iritis
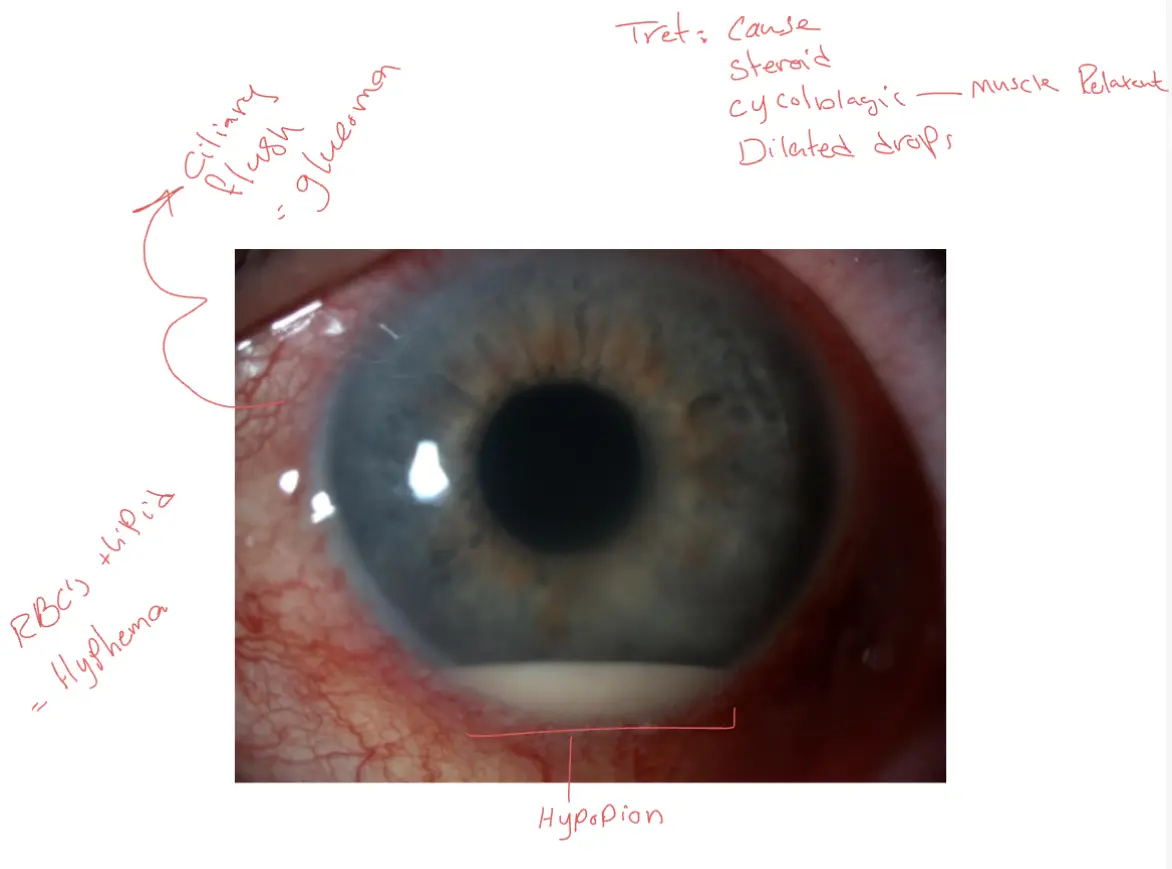
Uveitis
- Inflammation of the uveal tissue (iris, ciliary body, or choroid), retina, blood vessels, optic disc, and vitreous can be involved.
Etiology; Bilateral
- Idiopathic 90%
- Inflammatory diseases
- HLA B27, Ankylosing spondylitis, IBD; UC, Reiter’s syndrome, Psoriatic arthritis
- Sarcoidosis, Behcet’s, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Syndrome Z
- Infectious
- Herpes virus
- Toxoplasmosis
- Tuberculosis
- Syphilis
Management
- Identify possible cause
- Topical steroid; muscle relaxant
- Topical cycloplegic; ciliary spasm
- Systemic immunosuppressive medication
- Steroid
- Cyclosporine
- Methotrexate
- Azathioprine
- Cyclophosphamide
- Immunomodulating agents ±
- Infliximab (Anti-TNF)