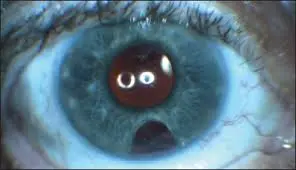
Peripheral iridectomy
- A part of the iris near its root is removed.
- The pupil remains round.
Iridectomy
Iridotomy
Sector iridectomy Y
- A part of the iris from the pupil to ciliary border is removed.

Visual iridectomy Y
- A small part of the iris near the pupil but not reaching to ciliary border is removed.
- Its site is different (better down)
Japanese iridectomy Y
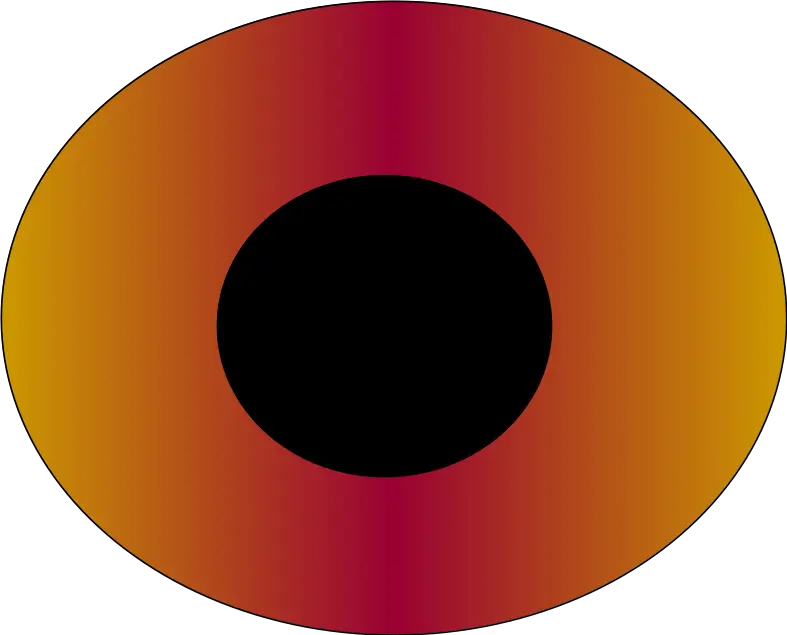
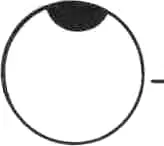
Drawn up pupil
- Pupil is not central ¬ rounded .
- Iris tissue is present all round the pupil.
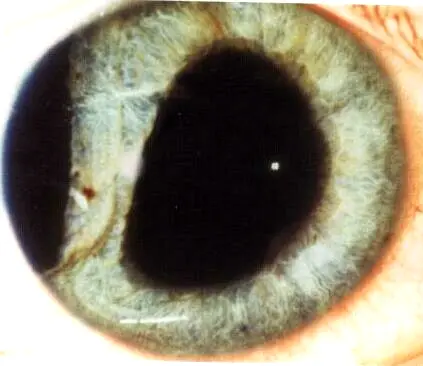
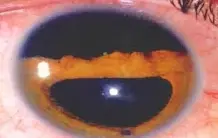
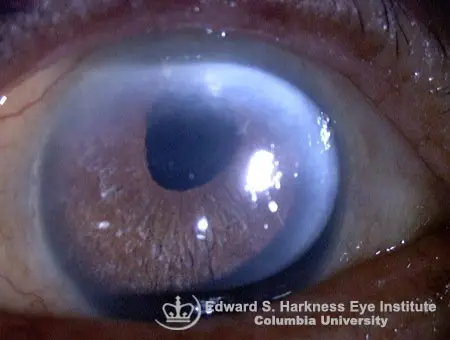
Iridodialysis
- D-shaped pupil
- Loss of the peripheral area of the iris.
Cause:
- Trauma
- Iatrogenic
Complication:
- Diplopia
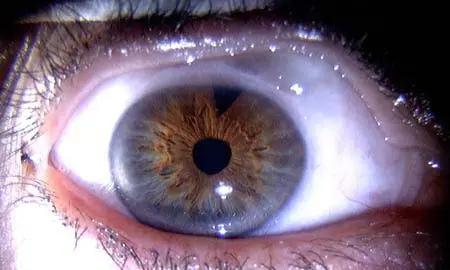
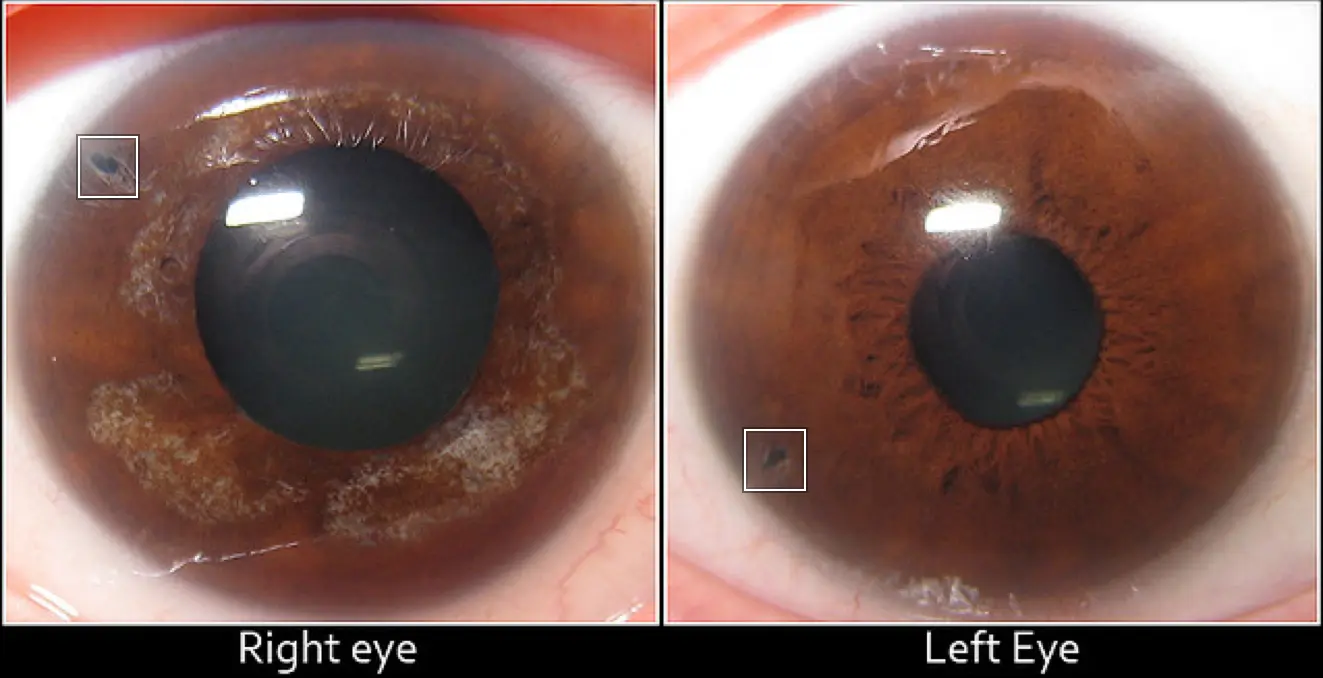
Iris coloboma Y
- Defect is present in the iris
- Commonly bilateral and lower
- Due to failure of fetal cleft closure.
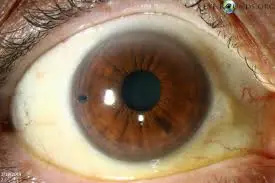
Posterior synechiae Y
Adhesion ( ) the iris and ant lens capsule
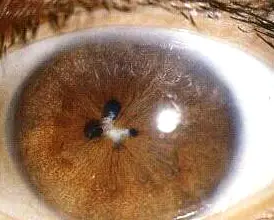
Posterior synechiae Y
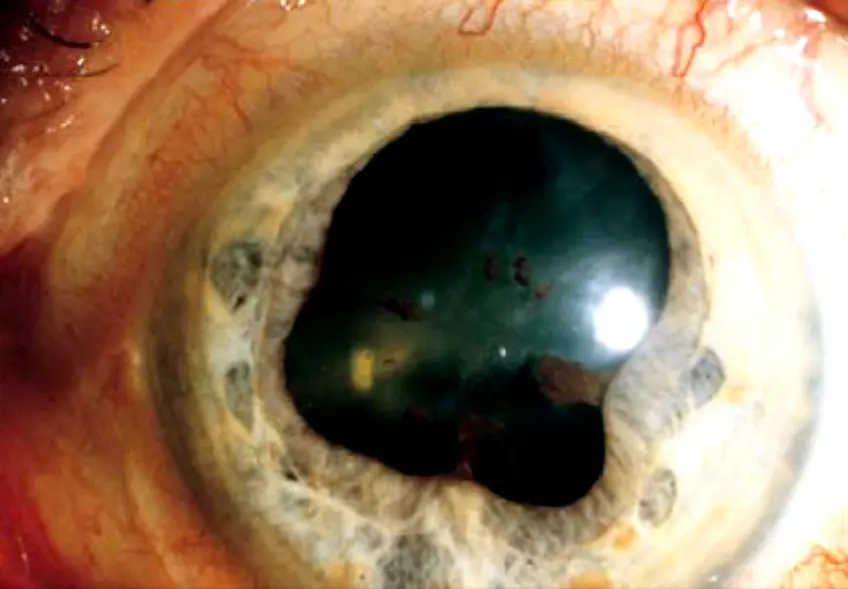
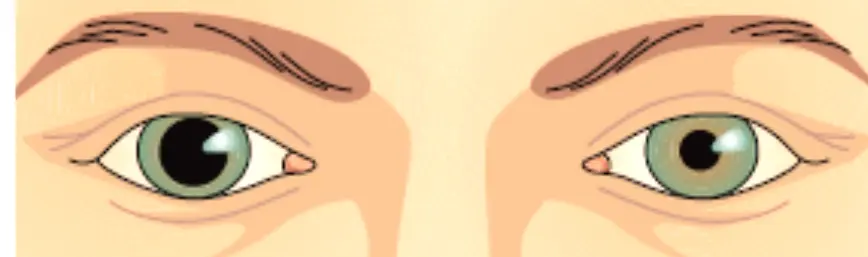
Anisocoria (unequal pupil)
Unilateral horner most common
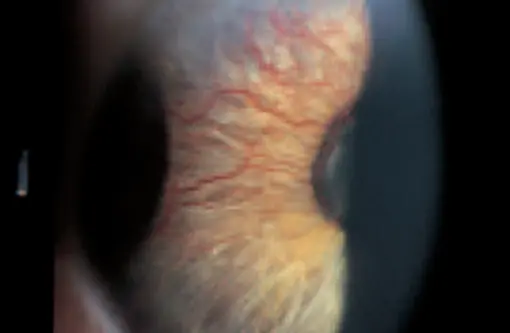
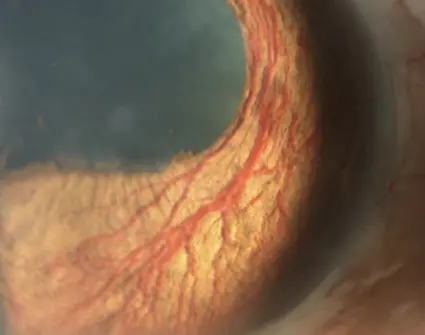
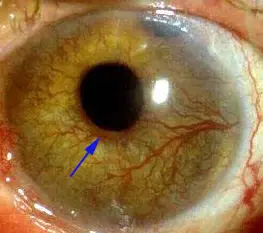
Rubeosis iridis (Abnormal Iris Vessels)
Causes:
- Ischemic central retinal vein occlusion (ICRVO)
- PDR
Complications:
- Rupture of blood vessels leading to hyphema
- Neovascular glaucoma
Treatment:
- Panretinal photocoagulation (PRP) for proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) + valve implantation
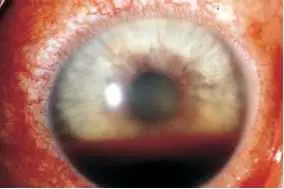
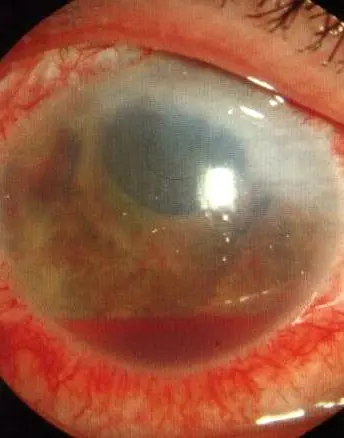
Hyphema (Blood in the anterior chamber) Z
Causes: resulting to blood in anterior chamber
- Trauma
- Rupture of abnormal iris vessels
(NEVER select HYPERTENSION)
Complications:
- Secondary glaucoma with elevated IOP
- Recurrent bleeding
- Corneal blood staining
- least common is corneal fistula
Treatment:
-
Hospital admission
-
Semi-sitting position & Rest
-
Promote blood resorption
-
Antiglaucomatous eye drops treatment for elevated IOP
-
Follow up with the patient with level of Hyphema and IOP
-
Surgery indicated only in (if total/subtotal Hyphema, resistance treatment, persistent IOP) - aspiration of blood from anterior chamber and glaucoma surgery
-
Avoid aspirin or any drugs that increase bleeding
Hypopyon Y
Pus in Ac
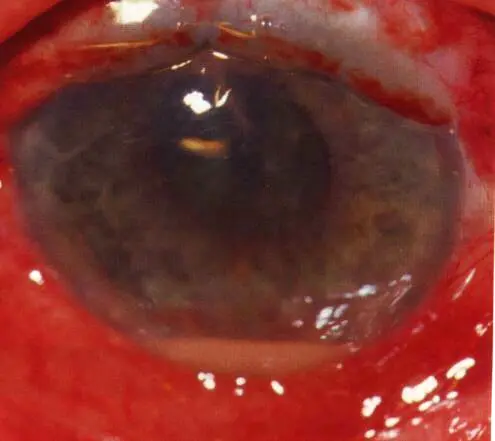
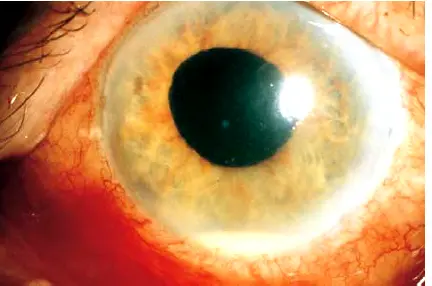
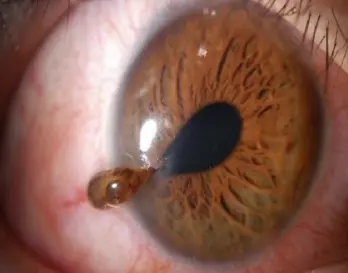
Iris prolapse
Management: Return it back and do repair surgery