Inspection
- Visual Acuity
- Refraction
- Intraocular pressure
- Alignment & Motility
- Pupillary Response
- Fundoscopic Exam
- Visual Fields
Inspection (External Appearance)
- Inspects external ocular (eye) structures (lids, conjunctiva, iris, cornea, pupils)
- Gently moves eyelids up and down to obtain a better view
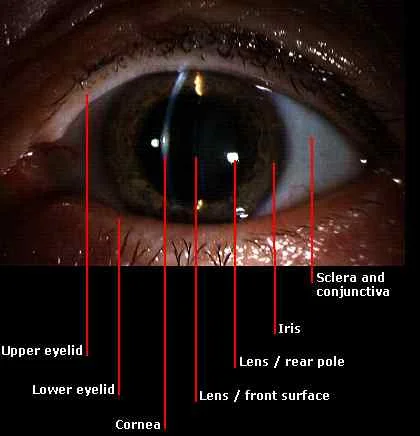
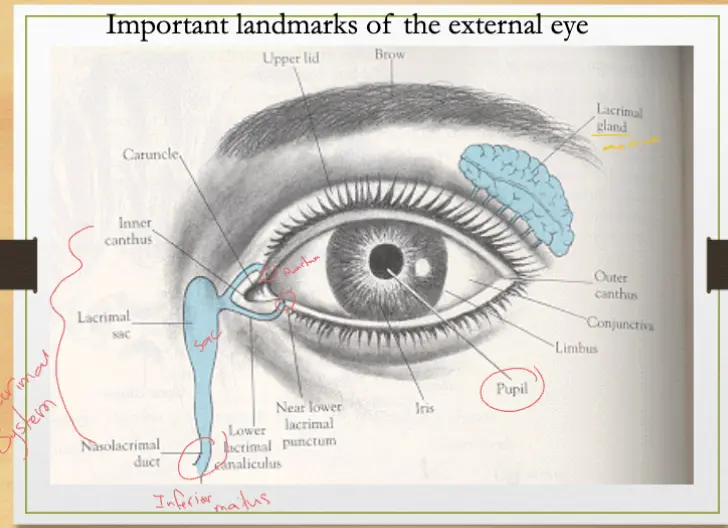
Important Landmarks of the External Eye
Structures to Inspect
- Position and alignment of eyes
- Orbit
- Eyelids & Eyebrows
- Lacrimal Apparatus
- Conjunctiva, sclera, cornea
Facilitate Visualization
- Move lower lid down, ask pt to look up
- Move upper lid up, ask pt to look down
- Compare symmetry, use your ruler
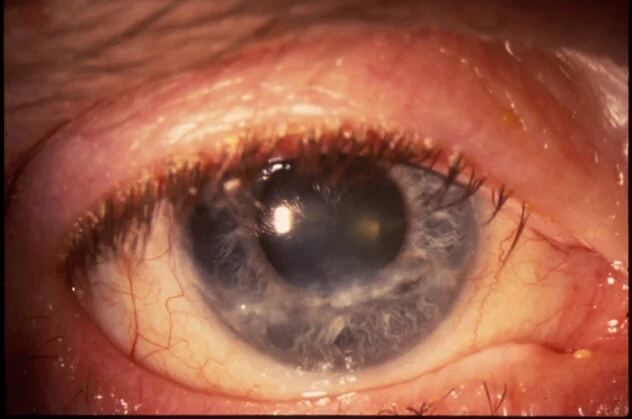
Blepharitis
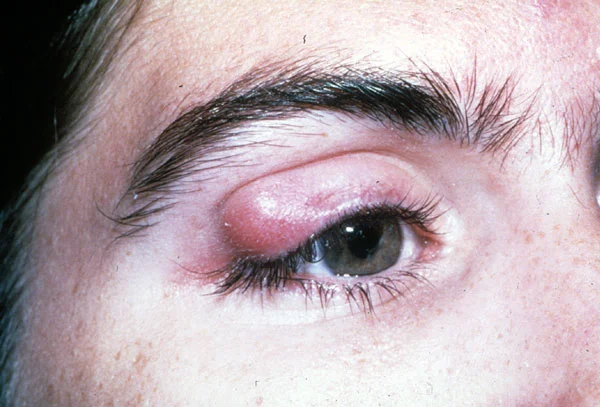
Chalazion
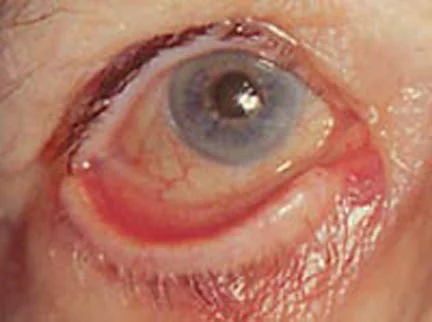
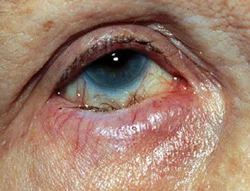
Ectropion
Entropion
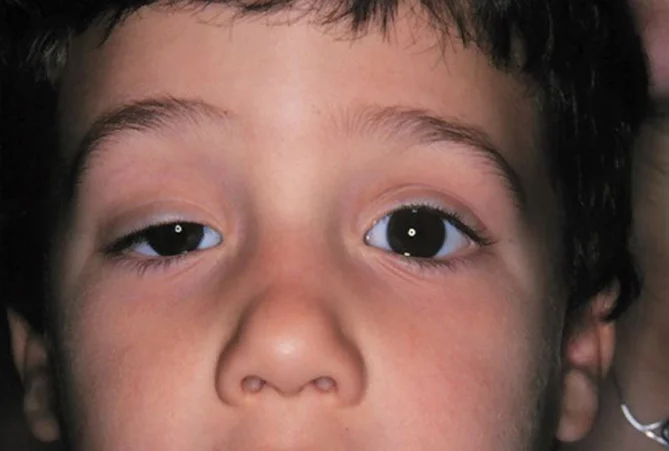
Ptosis
- 3yrs
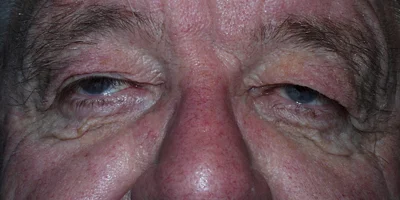
Dermatochalasis
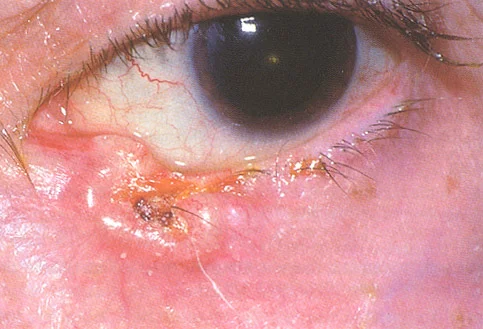
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
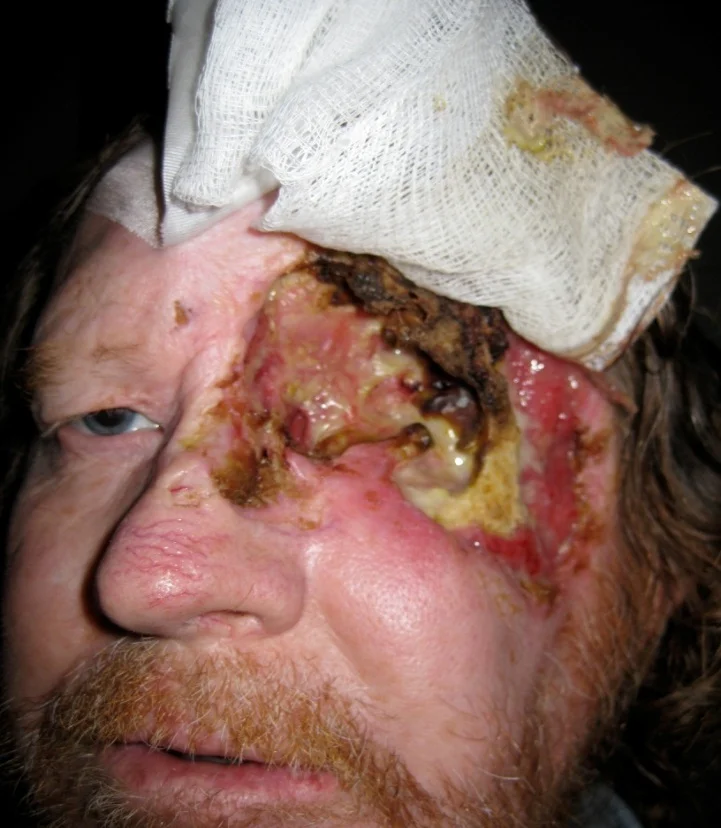
Pre-Septal Cellulitis
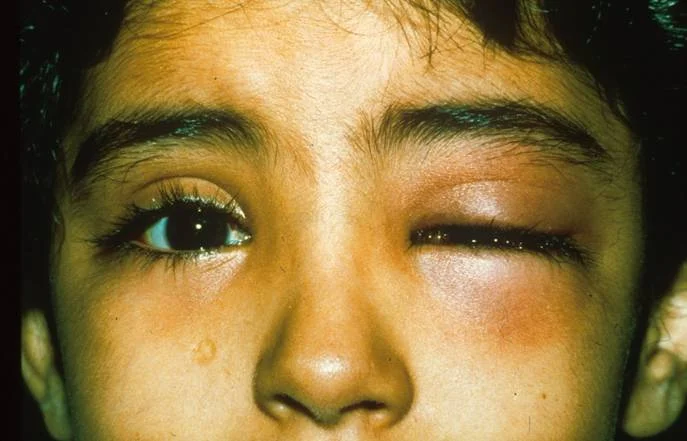
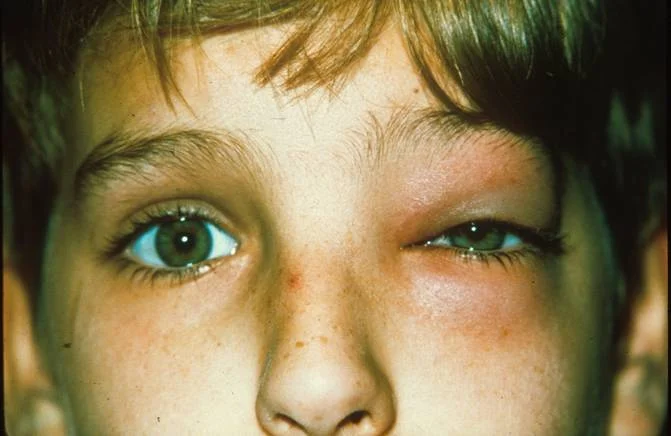
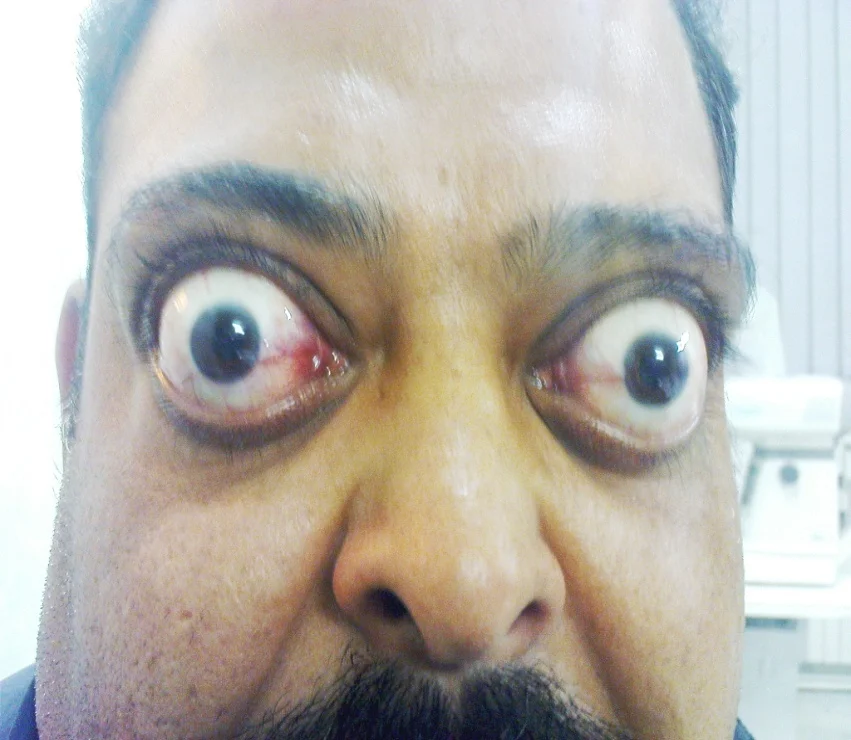
Exophthalmos
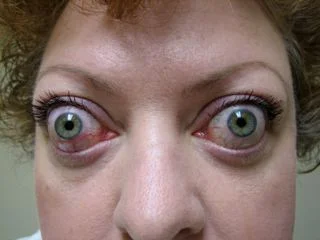
Proptosis
Thyroid
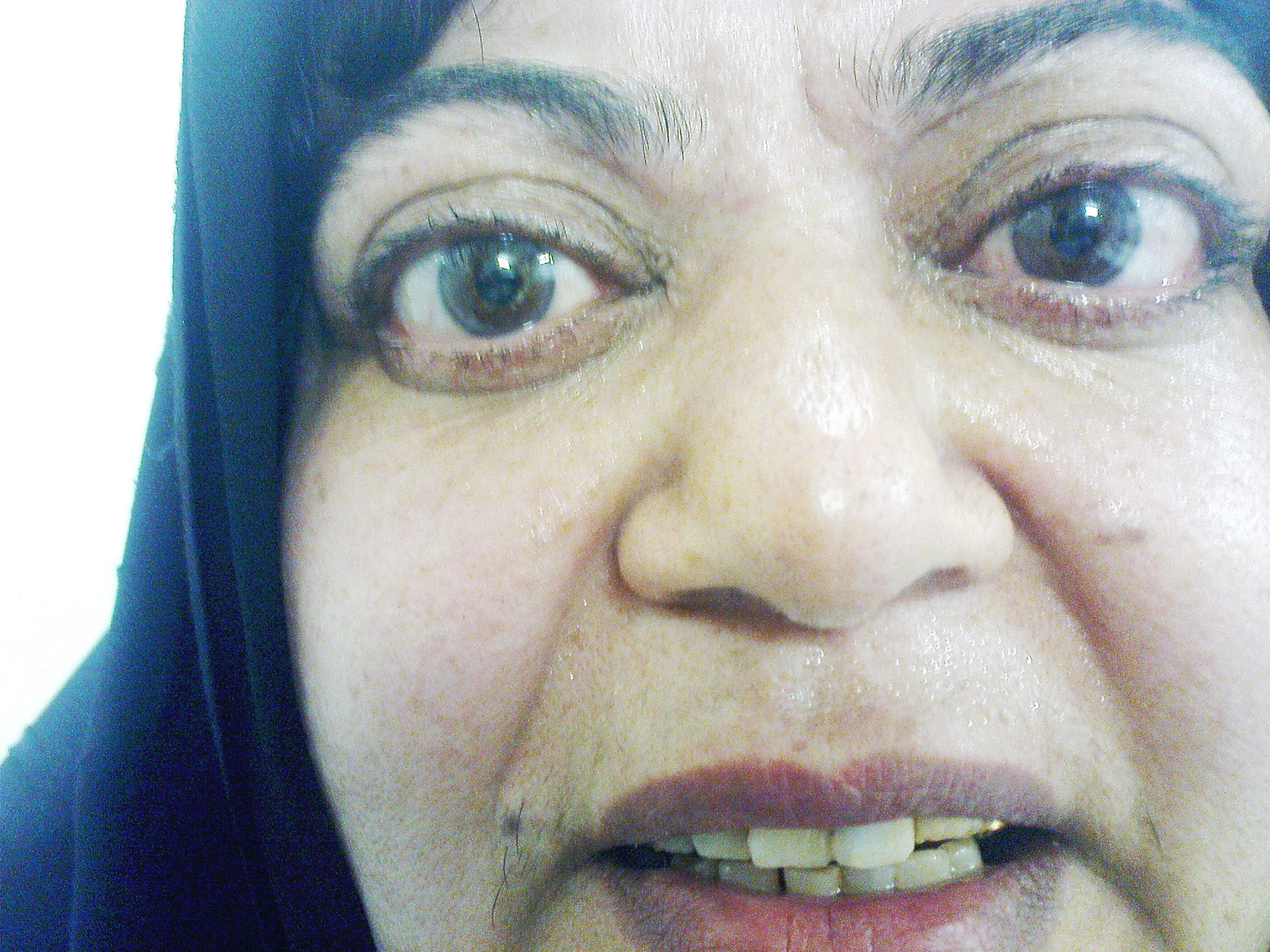
Exophthalmos
Thyroid Eye Disease Exopthalmos
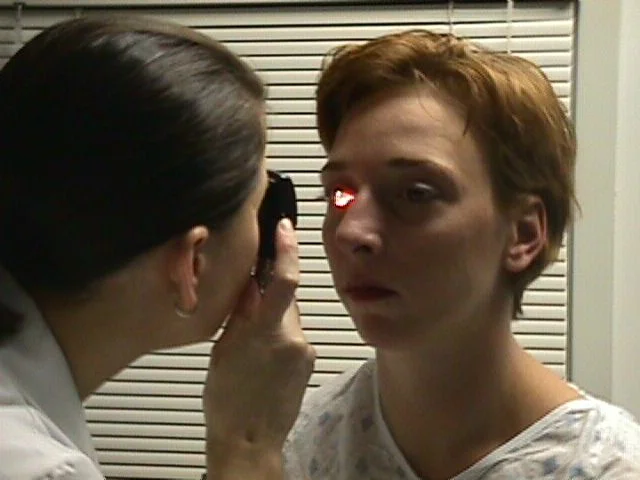
Inspecting the Anterior Structures
Using Ophthalmoscope
- Rotate the lens progressively towards the positive diopters to around +10 to +12 to visualize the anterior aspects of the eye

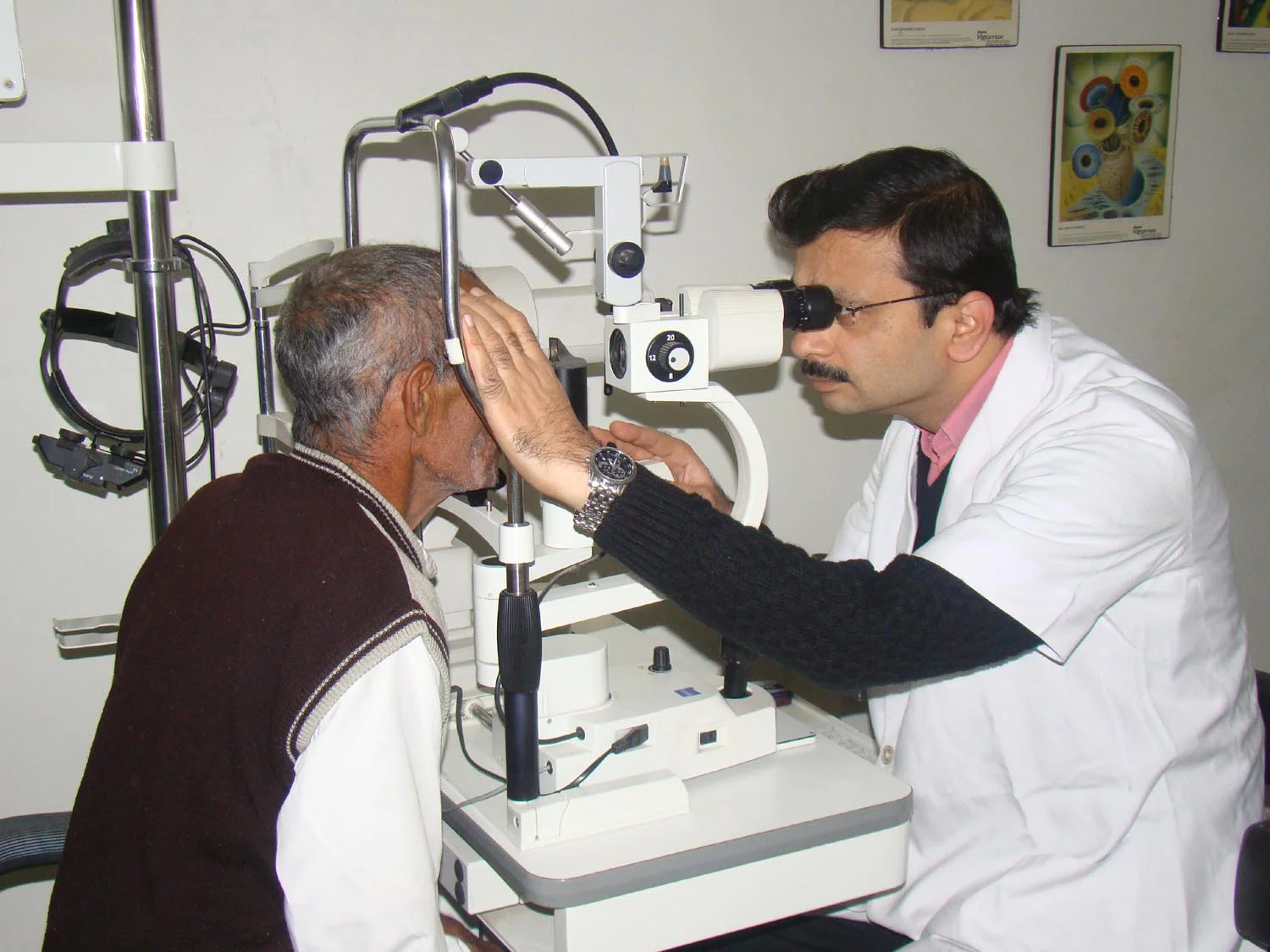
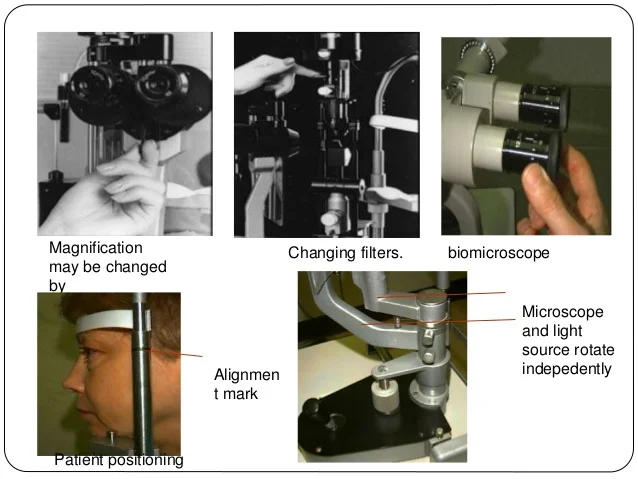
Using Slit Lamp (Biomicroscopy)
-
Magnification may be changed by
-
Changing filters. Biomicroscope
-
Microscope and light source rotate independently
-
Patient positioning
-
Alignment mark
- Interior Segment: Anterior segment
- Magnification
- Lens