2-Pituitary tumours Z
- Headache
- Visual field defect (Bitemporal hemianopia) Optic nerve dysfunction
- Colour deficit
- Visual deterioration
- Optic atrophy
- MRI scan + Neuro referral
3-Thyroid eye disease (TED)
-
Patient may be
-
Euthyroid
-
Hypothyroid
-
Hyperthyroid :-40% of patients with Graves disease get eye signs
-
4-8% loose vision
-
TED is the commonest cause of proptosis (unilateral or bilateral) in adults Z
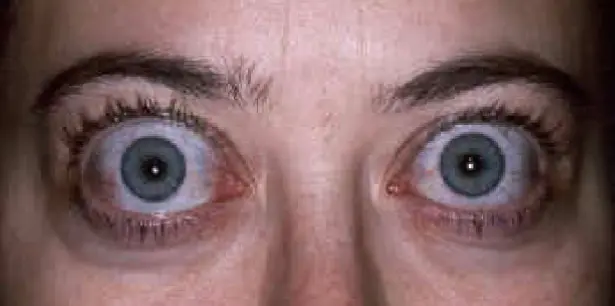
THYROID EYE DISEASE
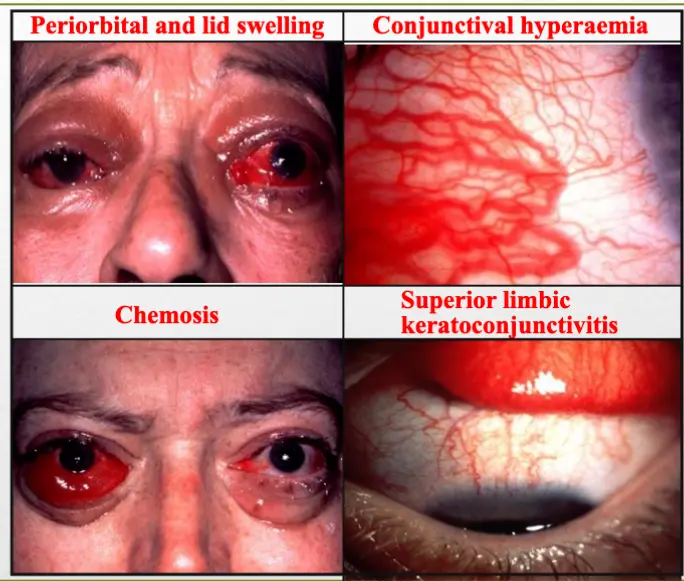
- Soft tissue involvement
- Periorbital and lid swelling
- Conjunctival hyperaemia
- Chemosis
- Superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis
- Eyelid retraction
- Proptosis
- Optic neuropathy
- Restrictive myopathy
Soft tissue involvement
1- Signs of eyelid retraction Occurs in about - first sign to appear Z
- Unilateral/Bilateral lid retraction
- Lid lag in downgaze
- Unilateral/Bilateral or no proptosis
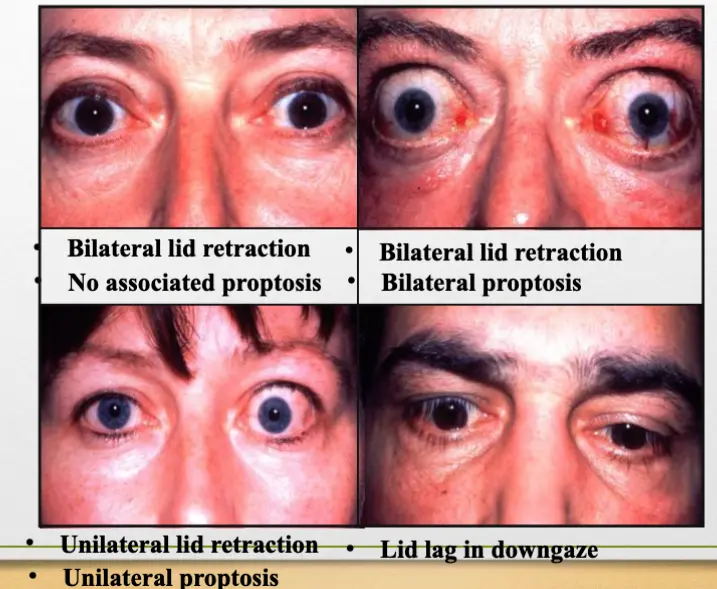
2- Proptosis
- Occurs in about
- Uninfluenced by treatment of hyperthyroidism
Axial and permanent in about May be associated with choroidal folds
Treatment options
- Systemic steroids
- Radiotherapy
- Surgical decompression
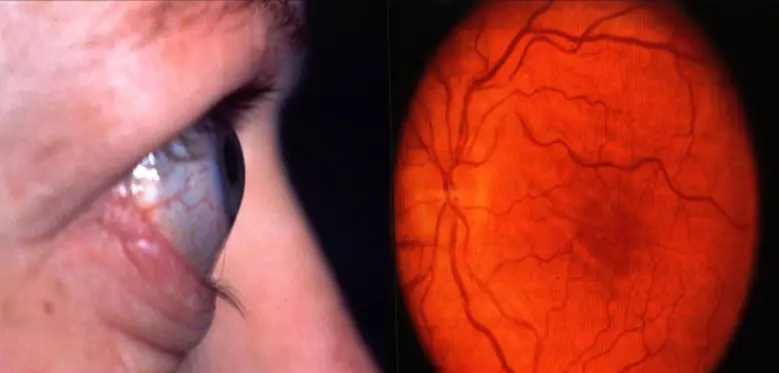
3- Optic neuropathy
- Occurs in about 5%
- Early defective colour vision
- Usually normal disc appearance
Caused by optic nerve compression at orbital apex by enlarged recti
Often occurs in absence of significant proptosis
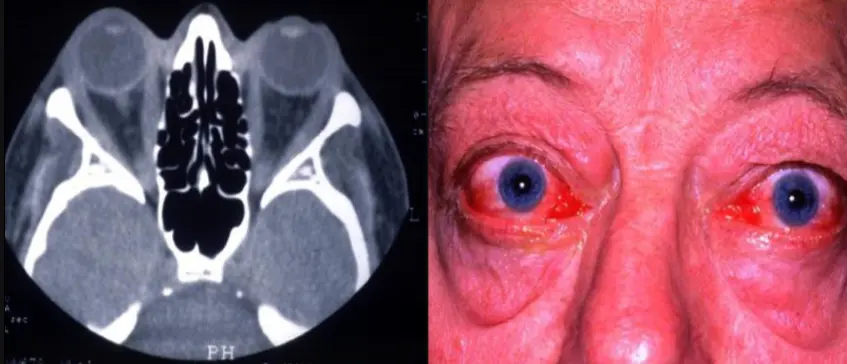
4- Restrictive myopathy
- Occurs in about
- Due to fibrotic contracture

- Elevation defect - most common - IR - first muscle effected (restrictive myopathy fibrosis)
- Adduction defect - less common - MR
- Depression defect - uncommon - SR
- abduction defect rare - LR
Treatment Z
- Control thyroid status (medical/ surgical)
- Lubricants
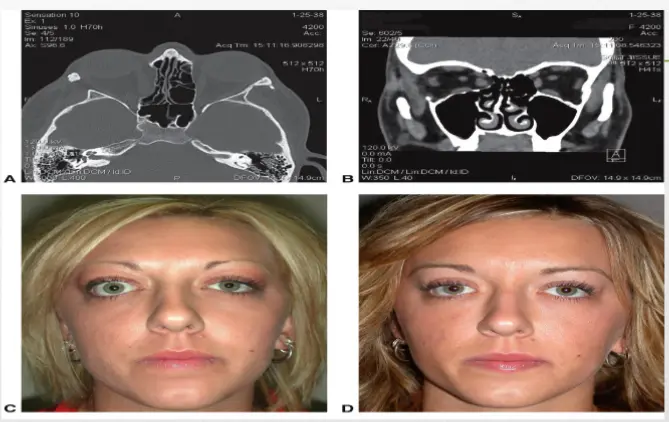
- Orbital decompression surgery
- Muscle surgery/ prism in glasses
- Lid surgery
Orbital decompression

Other endocrine disorders affecting eyes:
| Gland | Disorder | Ocular manifestations |
|---|---|---|
| Hypothalamus | Suprasellar tumours | Optic atrophy, Papilloedema |
| Parathyroids | Hyper/ Hypoparathyroidism | Conjunctival & corneal calcification, cataract |
| Adrenals | Pheochromocytoma Addison’s disease Cushing’s disease | Hypertensive retinopathy hyperpigmentation Cataract, exophthalmos |