BIOPSYCHOSOCIAL MODEL DIAGNOSIS & CLASSIFICATION IN PSYCHIATRY
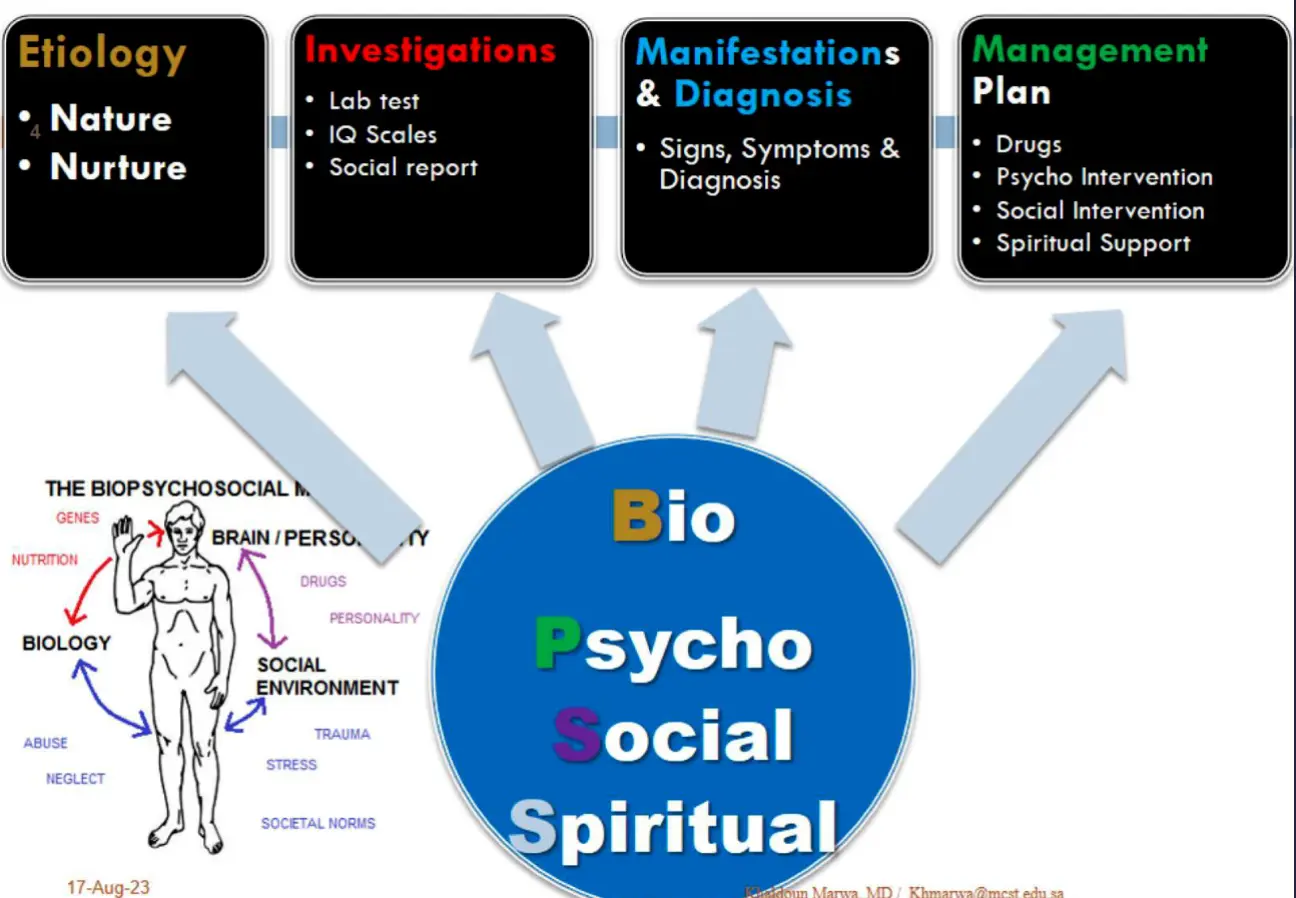
Etiology
- Nature
- Nurture
Investigations
- Lab test
- IQ Scales
- Social report
Manifestations & Diagnosis
- Signs, Symptoms & Diagnosis
Management Plan
- Drugs
- Psycho Intervention
- Social Intervention
- Spiritual Support
Types of Classification
- Categorical Classification:
-
Grouping disorders into separate entities according to symptom – pattern, course and outcome.
-
It includes hierarchal categories:
- Organic mental disorders then functional psychotic disorders (e.g. Schizophrenia) then neurotic disorder (e.g. generalized anxiety disorder) then personality disorders.
-
Also it includes built-in hierarchy of significance within the disorders themselves.
e.g.: Anxiety symptoms occur commonly with depressive disorder.
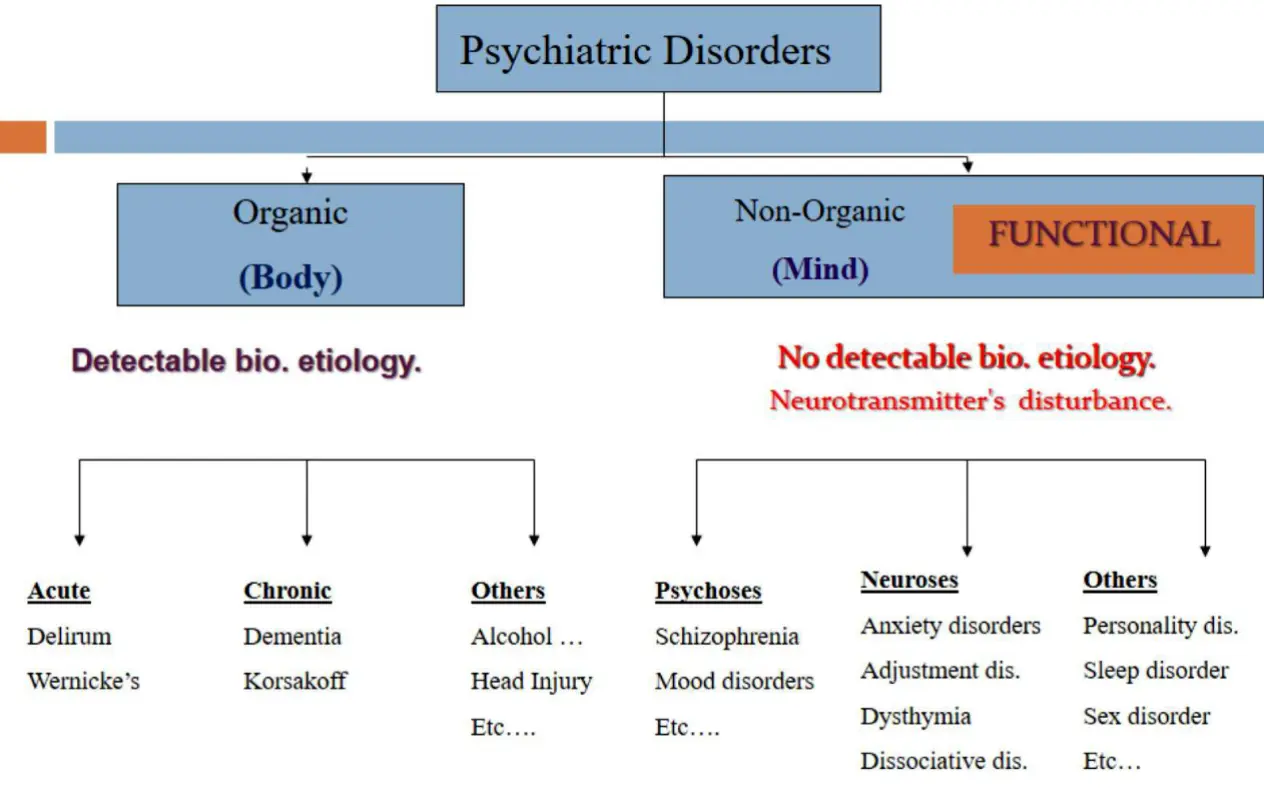
Psychiatric Disorders
-
Organic
(Body)
Detectable bio. etiology.- Acute
- Delirium
- Wernicke’s
- Chronic
- Dementia
- Korsakoff
- Others
- Alcohol …
- Head Injury
- Etc…
- Acute
-
Non-Organic
(Mind) functional No detectable bio. etiology.
Neurotransmitter’s disturbance.- Psychoses
- Schizophrenia
- Mood disorders
- Etc…
- Neuroses
- Anxiety disorders
- Adjustment dis.
- Dysthymia
- Dissociative dis.
- Others
- Personality dis.
- Sleep disorder
- Sex disorder
- Etc…
- Psychoses
Clues for Diagnostic Categories .. 6 Gates
Organic
- Organic
- Dementia
- Alzheimer’s type, vascular dementia, dementia due to a general medical condition, substance induced persisting dementia,
- Delirium
- Dementia
- Drugs
- Stimulants
- Opioid
- Cannabis
- Alcohol
- others
Psychosis
- .
- Schizophrenia
- Schizoaffective
- Psychotic due to medical condition,
- substance-induced psychotic
- Mood
- Depressive dis
- Bipolar disorder
- dysthymia dis
- cyclothymia dis
- mood dis due to a general medical condition
- Substance-induced mood disorder
Neurotic
- Anxiety, Stress
- Anxiety dis
- Stress related dis
- Substance-related dis
- Personality
- Custer A
- Custer B
- Custer C

Cues Suggestive of Organic Etiology
Disturbance of:
- Consciousness
- Cognitive Functions
- a. Attention and concentration
- b. Orientation: time, place & person
- c. Memory: immediate, recent and remote
- Vital Signs
Presence of: Z
- Visual hallucinations
- Neurological signs e.g. Dysarthria
- Physical illness HTN, DM, …
- Old age
delirium medical issue, due electrolyte, fever, sol’s, inflammation
Primary VS Secondary Psychiatric Disorders
| Feature | Primary Psychiatric Disorders | Secondary Psychiatric Disorders |
|---|---|---|
| Etiology | Multi-factorial | One diagnosable systemic medical disease, CNS disease, or substance |
| Examples | - Schizophrenia | - Depression due to SLE |
| - Major depressive disorder | - Psychosis due to amphetamine | |
| In Medicine | Like Essential hypertension | Like secondary HTN due to renal artery stenosis |
| Clues Suggestive of Being | ||
| Primary | - Normal consciousness & vital signs | - Disturbance of consciousness or vital signs |
| - Presence of: | - Presence of: | |
| 1. Auditory hallucinations | 1. Non-auditory hallucinations (e.g. visual) | |
| 2. Soft neurological signs | 2. Hard neurological signs | |
| 3. Young age onset | 3. Physical illness | |
| 4. Old age onset |
Broad Classification of Psychiatric Disorders
| Feature | PSYCHOSIS | NEUROSIS… |
|---|---|---|
| Insight & Reality Testing | Impaired insight & reality testing | Intact insight & reality testing |
| Judgment | Impaired judgment | Good judgment |
| Quality of Symptoms | Abnormal quality of symptoms | Abnormal quantity of symptoms |
| Psychotic Features | Presence of active/positive psychotic features (e.g., delusions, hallucinations) and negative features (e.g., poverty of thoughts & speech, lack of ambition, initiation, and restricted affect) | No psychotic features |
| Examples | E.g., schizophrenia | E.g., anxiety disorders |
| Severity | Refers broadly to severe forms of mental disorders. | Generally less severe than psychosis. |
| Examples | 1. Organic mental diseases | 1. GAD (Generalized Anxiety Disorder) |
| 2. Schizophrenia | 2. OCD (Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder) | |
| 3. Affective disorders | 3. Phobic disorders | |
| 4. Panic disorder | ||
| Characteristics | Greater severity | Symptoms are closer to normal experience e.g., anxiety |
| Lack of insight | ||
| Patient’s inability to distinguish between subjective experience and reality e.g., hallucinations, delusions. |
Positive Psychotic Features
Major disturbances in:
- A: Mood e.g., extreme euphoria.
- B: Behavior e.g., disorganized behavior.
- C: Thinking e.g., delusions, FOI.
- Perception e.g., hallucination.

Negative Features
- A: Restricted affect.
- B: Lack of ambition, initiation, & self-neglect.
- C: Poverty of thoughts & speech.
- Poor self-care & hygiene.
Summary
- Diagnosis in psychiatry is based mainly on clinical features.
- There are 2 main systems of classification; ICD & DSM.
- Multiaxial Record.
- Organic vs. Functional.
- Cues suggestive of organic mental disorder.
- Psychosis vs. Neurosis.
- Positive vs. Negative features.