Management of Prolonged Labour
Diagnosis
History should include:
- Age.
- parity.
- Duration of labour.
- Partograph abnormality.
- Duration of ROM(amount & colour of liquor).
- Antenatal records and complications
- Previous prolonged labour: * fetal death, * instrumental delivery. * caesarean sections.
Examination
-
General exam.
- Features of maternal distress.
-
Abdominal exam (Revise):
- Frequency and intensity of uterine contractions.
- Presentation.
- Engagement.
- Estimated fetal weight
Retraction ring (bandl’s ring) is seen and felt between upper & lower segment (site of uterine rupture).
Obstructive Labor

Vaginal Examination
- Vaginal exam:
- Dry hot vagina.
- Cervical dilatation.
- Fetal presentation and position, station.
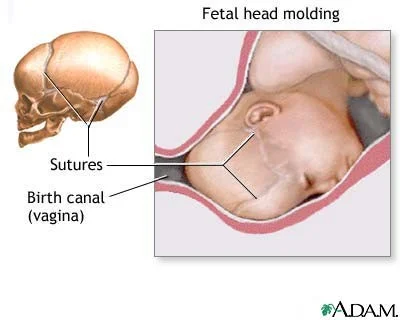
- Excessive caput and moulding.
Treatment of Poor Progress
-
Treatment of poor progress in the 1st stage of labour :
- Good hydration.
- Pain relief.
- Empty bladder.
- Cross match blood.
- Emotional support.
-
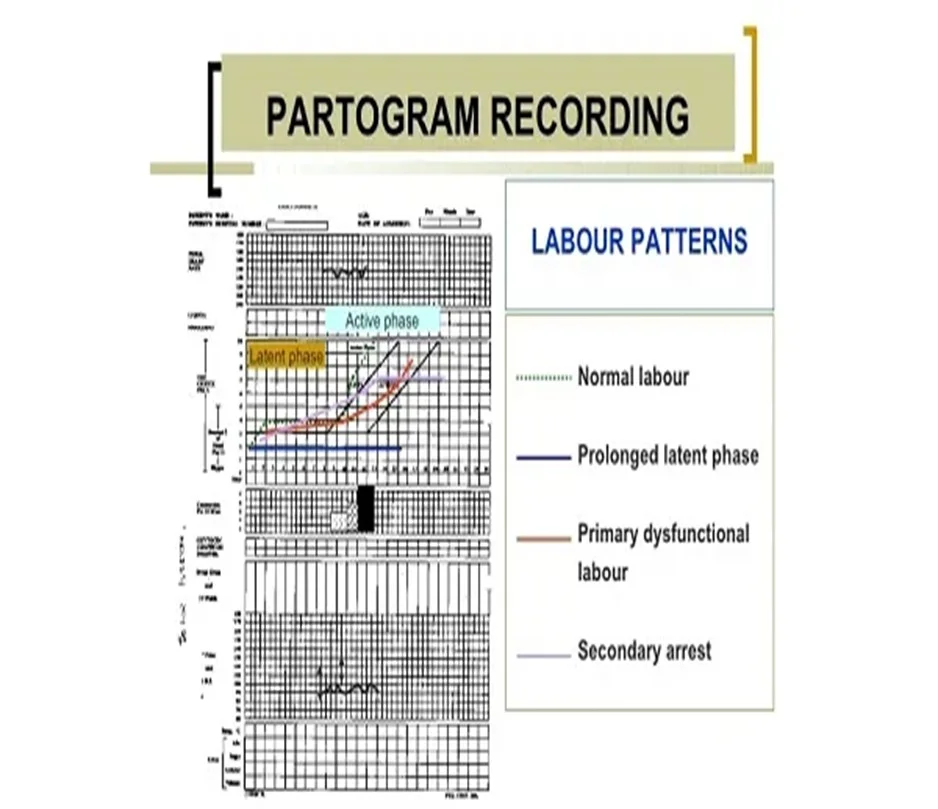
When poor progress in labour is suspected : Repeat vaginal examination every 2(rather than 4 hours ) & plot on partograph

In the 2nd Stage of Labour
- Rehydration.
- Intravenous oxytocin for inefficient uterine cont.
- Instrumental birth can be considered.
- Caesarean delivery if :
- Instrumental birth attempt is unsuccessful.
- or if obstructed labour present.
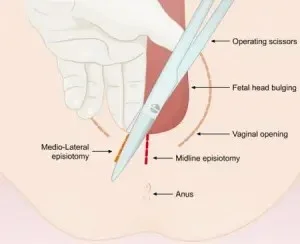
- Episiotomy for a resistant perinium.

Treatment of CPD
- Oxytocin must never be used in a multiparous woman where CPD is suspected.
- A Caesarean section is indicated in cases of CPD with elements of obstructed labour