Induction of Labour
Definition and Indications
- IOL is the planned initiation of labour prior to its spontaneous onset.
- performed when the risks to the fetus and/or the mother of the pregnancy continuing outweigh those of its end.
- chance of success (determine by parity & favourable cervix).
- How to assess the cervical favourability?
- By Bishop score.
- if the risks of the process to the mother and/or fetus are acceptable.
Indications for Induction
- Prolonged pregnancy (usually offered after 41 completed weeks).
- PROM.
- Pre-eclampsia and other maternal hypertensive disorders.
- FGR.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Fetal macrosomia.
- Deteriorating maternal illness.
- Unexplained antepartum haemorrhage.
- Twin pregnancy continuing beyond 38 weeks.
- Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy.
- Maternal isoimmunization against red cell antigens.
- ‘Social’ reasons.
Modified Bishop’s Score
Assessment Criteria


Methods of Induction
Mechanical and Surgical Methods
- Mechanical :
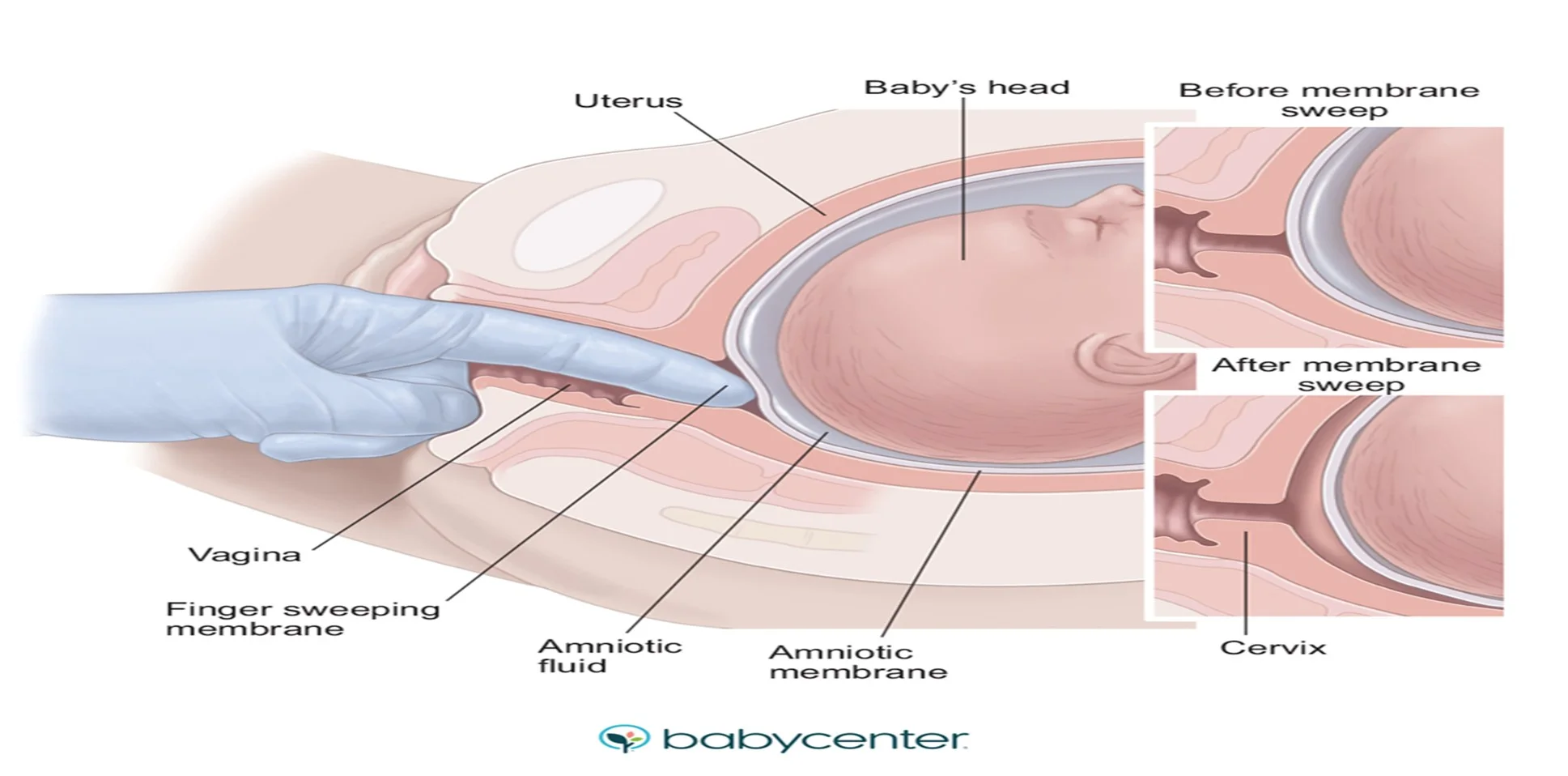
- Membrane sweep (offer weekly from 40 weeks).
- Ballooning.
- Surgical : ARM (cervix must be favourable).
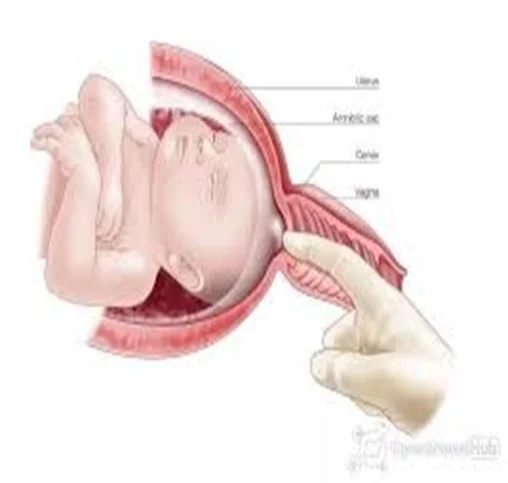
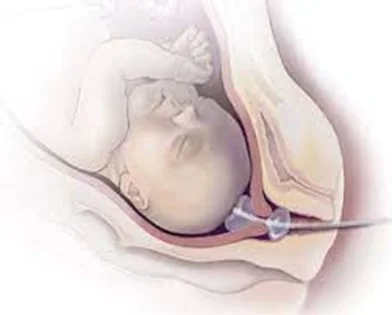
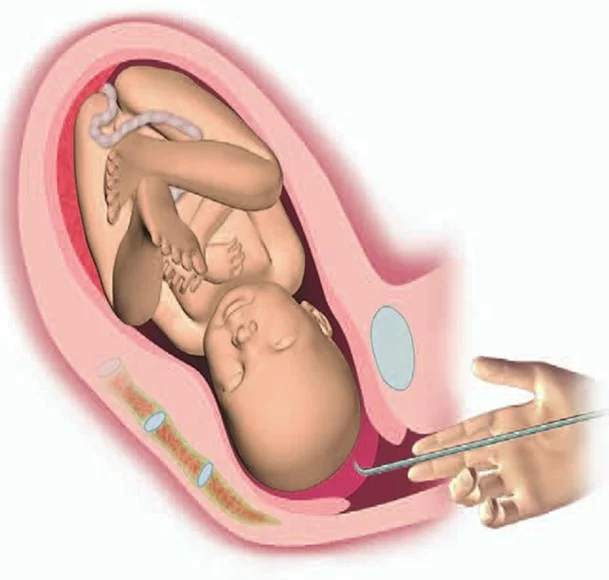
Membrane Sweep
Procedure
Medical Induction Methods
Medications Used
- Prostaglandin gel, tablet to ripen.
- cervix & initiate contractions.
- Oxytocin infusion(membranes ruptured first, spontaneous or artificial).
Mifepristone and misoprostol.
- Mifepristone (antiprogesterone).
- Misoprostol (prostaglandin). used only to induce labour following intrauterine Fetal death (IUFD).

Complications of Induction of Labour
Potential Risks
- Increase need for epidural analgesia (pain).
- Increase rates of instrumental delivery.
- PPH secondary to uterine atony(long labour).
- Uterine hyperstimulation.( treated by stopping the oxytocin and if necessary administration of a tocolytic drug).
- Uterine rupture.
- Fetal compromise may( uterine hyperstimulation(brady cardia).
- Cord prolapse(high head).
No evidence of a higher rate of caesarean section
Medical RR
- prostaglandings (if closed cervix)
Mechanical
- sweeping
- balooning Surgical
- E?REM - spontanious rupture of membrane - then give Oxytocin (If open)