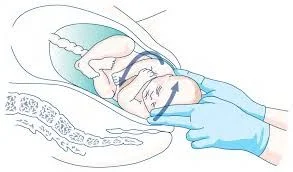
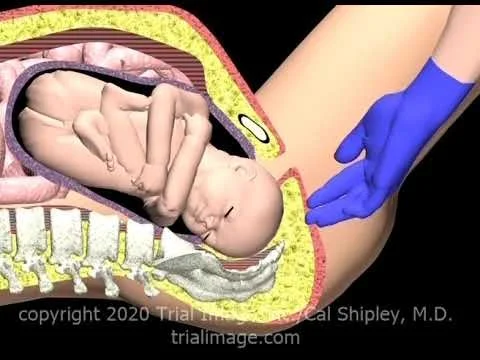
Shoulder Dystocia
Definition
Vaginal cephalic delivery that requires additional obstetric manoeuvres to deliver the fetus after the head has delivered and gentle traction has been unsuccessful in delivering the shoulders.
Associated with significant morbidity both for the mother and fetus.
Maternal complications include:
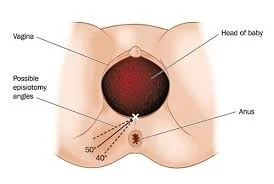
- increased perineal trauma (third- and fourth degree tear).
- postpartum haemorrhage,
- psychological trauma.
Fetal complications include:
- brachial plexus injury.
- fractured clavicle or humerus.
- hypoxic brain injury.
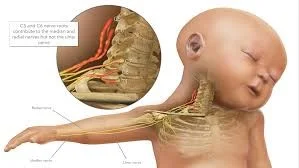
Prevention
- Diagnosis.
- optimal control of gestational and insulin-dependent diabetics
- reduction of maternal obesity.
- Careful plan for mode of delivery in women with previous shoulder dystocia delivery.
Risk Factors
- macrosomia.
- poorly controlled gestational and insulin-dependent diabetes.
- maternal obesity.
- previous shoulder dystocia.
- instrumental.
Warning Signs
- failure of restitution of head following delivery of the head.
- retraction of the fetal head against the perineum (turtle sign).

Abnormal Labour Management
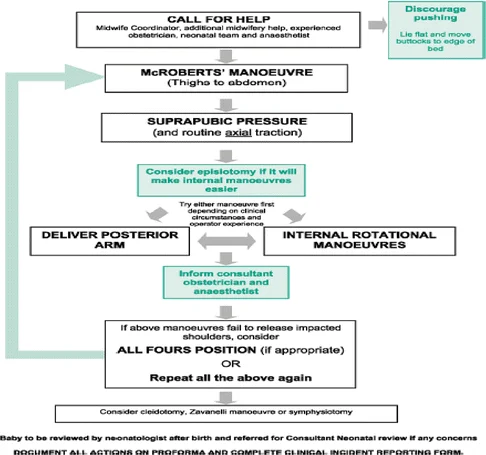
CALL FOR HELP
Key Personnel to Call
- Midwife Coordinator
- Additional midwifery help
- Experienced obstetrician
- Neonatal team
- Anaesthetist
Management of Shoulder Dystocia
Initial Steps
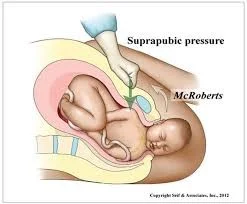
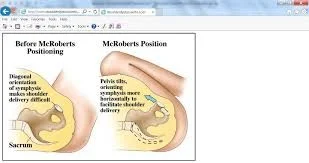
- McROBERTS’ MANOEUVRE
- Thighs to abdomen
- SUPRAPUBIC PRESSURE
- And routine axial traction
- Consider episiotomy if it will make internal manoeuvres easier
- Try either manoeuvre first depending on clinical circumstances and operator experience
Further Actions
- DELIVER POSTERIOR ARM
- INTERNAL ROTATIONAL MANOEUVRES
- Inform consultant obstetrician and anaesthetist
- If above manoeuvres fail to release impacted shoulders, consider
- ALL FOURS POSITION (if appropriate)
- OR
- Repeat all the above again
- Consider cleidotomy, Zavanelli manoeuvre or symphysiotomy
Post-Delivery Care
- Baby to be reviewed by neonatologist after birth and referred for Consultant Neonatal review if any concerns
- DOCUMENT ALL ACTIONS ON PROFORMA AND COMPLETE CLINICAL INCIDENT REPORTING FORM
Additional Measures
- Discourage pushing
- Lie flat and move buttocks to edge of bed
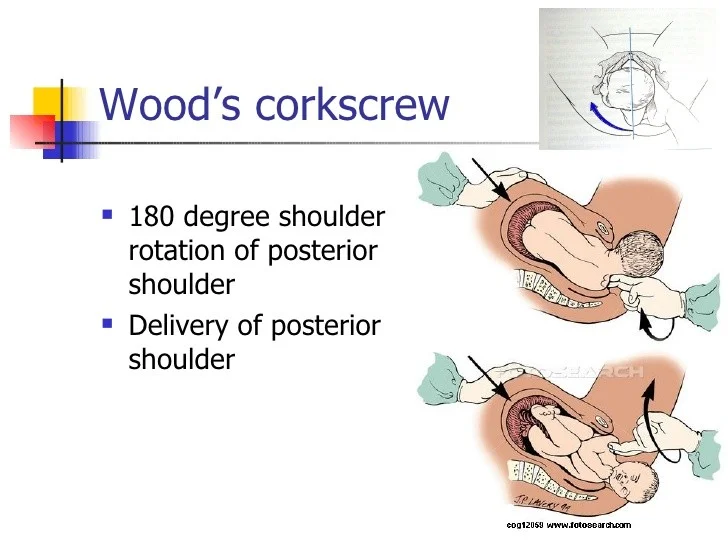
Wood’s Corkscrew Manoeuvre
- 180-degree shoulder rotation of posterior shoulder
- Delivery of posterior shoulder
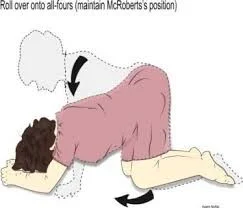
- Roll over onto all-fours (maintain McRoberts’s position)
Procedures Used in Shoulder Dystocia Management
Key Manoeuvres
- McRoberts maneuver
- thighs are abducted and flexed onto her abdomen.
- (suprapubic pressure)
- Rubin II maneuver (posterior pressure on anterior shoulder)
- Wood’s corkscrew maneuver
- posterior shoulder is rotated to anterior position.
- Delivery of the posterior shoulder first
- All fours position with the back arched.
- This widens the pelvic outlet
- Zavanelli’s maneuver
- Cleidotomy
- Maternal symphysiotomy
Management Protocol
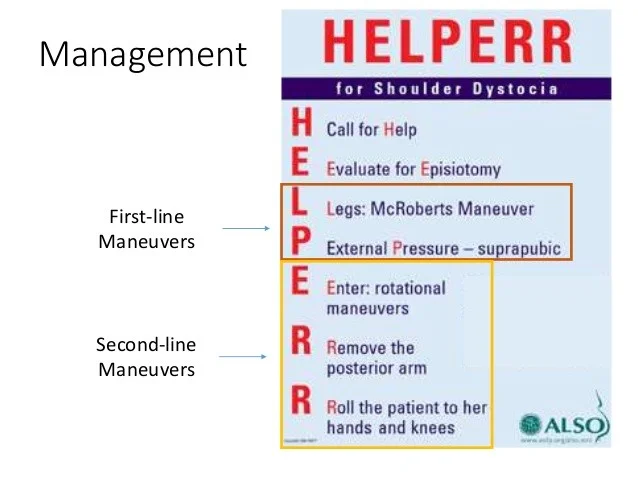
First-line Maneuvers
- H - Call for Help
- E - Evaluate for Episiotomy
- L - Legs: McRoberts Maneuver
- P - External Pressure - suprapubic
Second-line Maneuvers
- E - Enter: rotational maneuvers
- R - Remove the posterior arm
- R - Roll the patient to her hands and knees