Ovarian Cancer
Overview
Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in the tissue of the ovary and is called the overlooked disease or the silent killer.
Epidemiology
- Ovarian cancer is the second most common gynaecological cancer after uterine cancer.
- It causes more deaths than any other gynaecological cancer.
- Older women are at highest risk (frequently in women between 55 and 75 years of age).
- 75% will survive one year and about 25% will survive 5 years after treatment.
Pathophysiology
- Ovarian cancer, the cause of which is unknown, can originate from different cell types.
- Most ovarian cancers originate in the ovarian epithelium.
- They usually present as solid masses that have spread beyond the ovary.
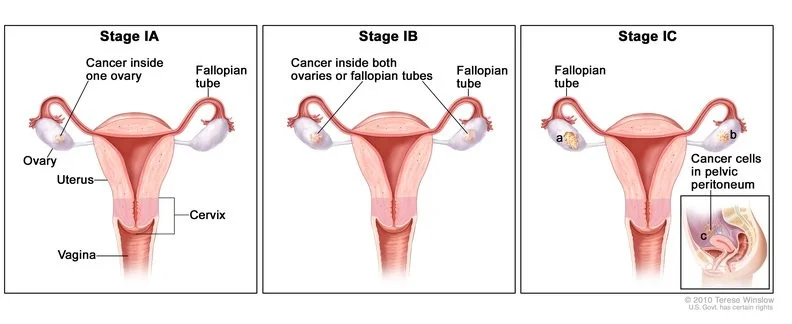
Stages of Ovarian Cancer
- In stage 1, the cancer is limited to the ovaries.
- In stage 2, the growth involves one or both ovaries, with pelvic extension.
- Stage 3 cancer has spread to the lymph nodes and other organs or structures inside the abdominal cavity.
- In stage 4, the cancer has metastasized to distant sites

Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer
-
Nulliparity
-
Early menarche (before 12 years old)
-
Late menopause (after 55 years old)
-
Increasing age (over 50 years of age)
-
High-fat diet
-
Obesity
-
Persistent ovulation over time
-
First-degree relative with ovarian cancer
-
Inherited.
-
Older than 30 years at first pregnancy.
-
Positive BRCA-1 and BRCA-2 mutations. Z
-
Personal history of breast, bladder, or colon cancer.
-
Hormone replacement therapy for more than 10 years.
-
Infertility.
Clinical Manifestation
- Pelvic discomfort or pain
- Persistent indigestion, gas, or nausea
- Abdominal pressure, swelling, or bloating
- Urinary urgency or burning with no infection
- Changes in menstruation.
- fatigue
- Vague abdominal pain
- diarrhoea or constipation
- unexplained weight loss or gain
- ascites
- a palpable abdominal mass
- back pain

Assessment
- History
- Physical examination
- Investigation:
- Ultrasound: Low positive predictive value for cancer
- Tumour markers - CA 125 Z
Treatment
There are many different kinds of treatments available, depending on certain factors, like: * The stage and size of the tumours * Age * General health * Desire to have kids
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation Therapy: The main goal is to reduce pain symptoms
- Biotherapy/Immunotherapy