Diabetes & Pregnancy
DR RAYAN ALBARAKATI

GDM Definition:
Glucose intolerance with onset first recognition during pregnancy
Varieties:
- Preexisting DM
- GDM (A1 & A2)
Introduction
Most common medical complication of Pregnancy
3-8 % of pregnancies
- GDM 90% - (half develop DM after pregnancy)
- Preexisting DM 10%
Physiological changes during pregnancy
- Pregnancy is a state of insulin resistance & relative glucose intolerance
- This is due to placental production of anti-insulin hormones : hPL, cortisol, and glucagon
- FBS might be low (increased insulin sensitivity in 1st trimester) and increased glucose uptake
- Postprandial glucose increased
- Insulin increases by 2 folds in N women
- Insulin requirements increased (fetal growth)
- ↓ Renal threshold for glucose glycosuria (Increased GFR, tubular reabsorption is less efficient)
EFFECT OF PREGNANCY ON pt with DM
Insulin requirement increased reaching a max at term & being about 2 X the pre-pregnancy requirement
Pt with diabetic nephropathy:
- Deterioration in renal function
- Proteinuria.
- Usually reversed after delivery
EFFECT OF PREGNANCY ON DM
-
2 X increase in retinopathy
-
Hypoglycemia (with tight control of BG level)
-
Ketoacidosis: rare unless associated with hyperemesis, infections, tocolytics & corticosteroid Rx
-
Increased risk of PIH especially in pt. with pre-existing hypertension & nephropathy
-
Postpartum hemorrhage … why ? *
(placentomegaly - polyhydramnios- macrosomic baby)
EFFECTS OF DM ON PREGNANCY
Increased risk of abortions
- increased incidence of congenital abnormalities
- 5% with Hb A1c > 8
- 25% with Hb A1c > 10
- Sacral agenesis, congenital heart defects, skeletal abnormalities & neural tube defects - (most common congenital heart diseases;)
- Perinatal & neonatal mortality increased 2-4 X
- Unexplained IUFD at term (more in macrosomic babies)
NTD: Spina Bifida
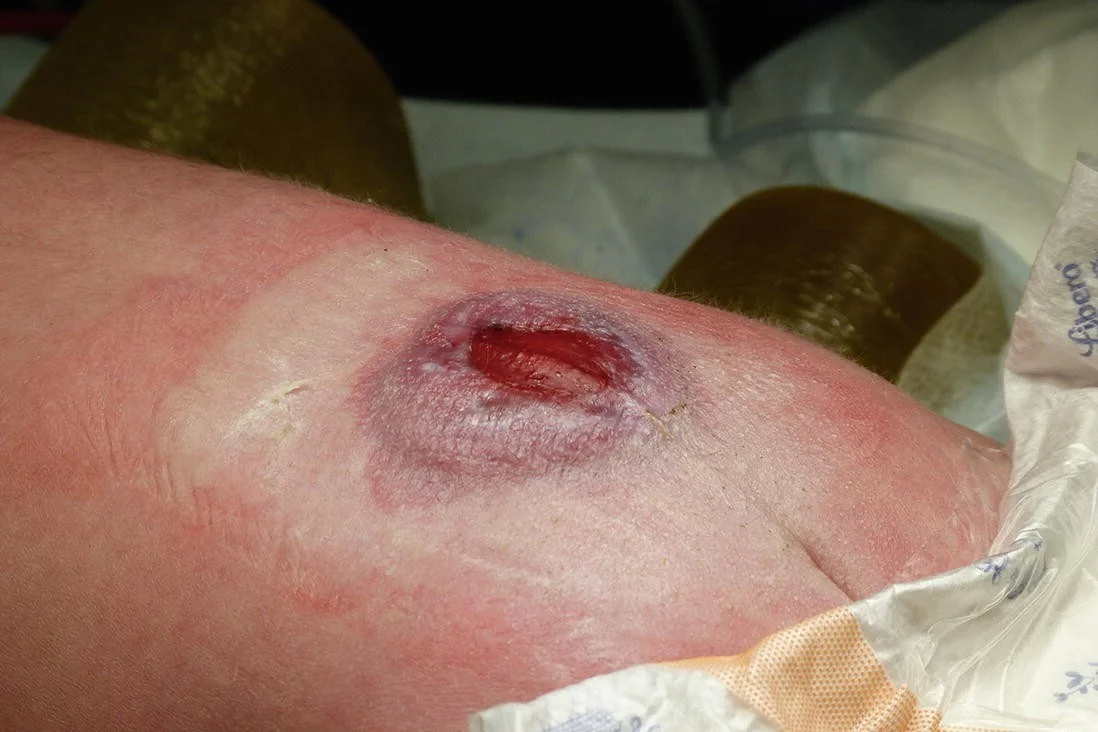
Caudal regression
AKA sacral agenesis
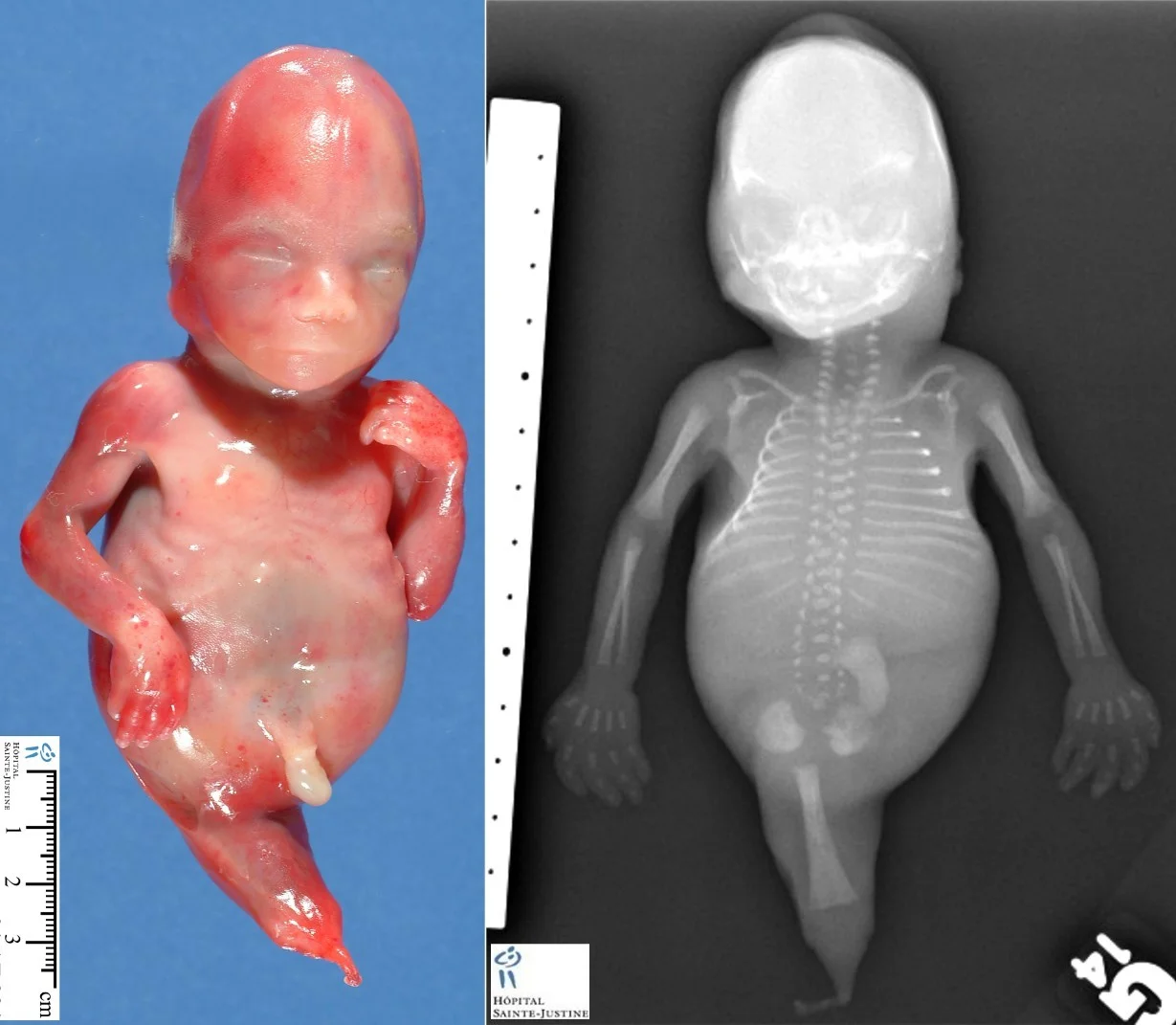
EFFECTS OF DM ON PREGNANCY
Macrosomia >4000g
- Risk increased with poor diabetic control
- Not eliminated by tight control
- Increased risk of operative delivery, birth trauma, & shoulder dystocia
Hyperglycemia: fetal polyuria - polyhydramnios -PROM - PTD
Delayed lung maturity
Prematurity
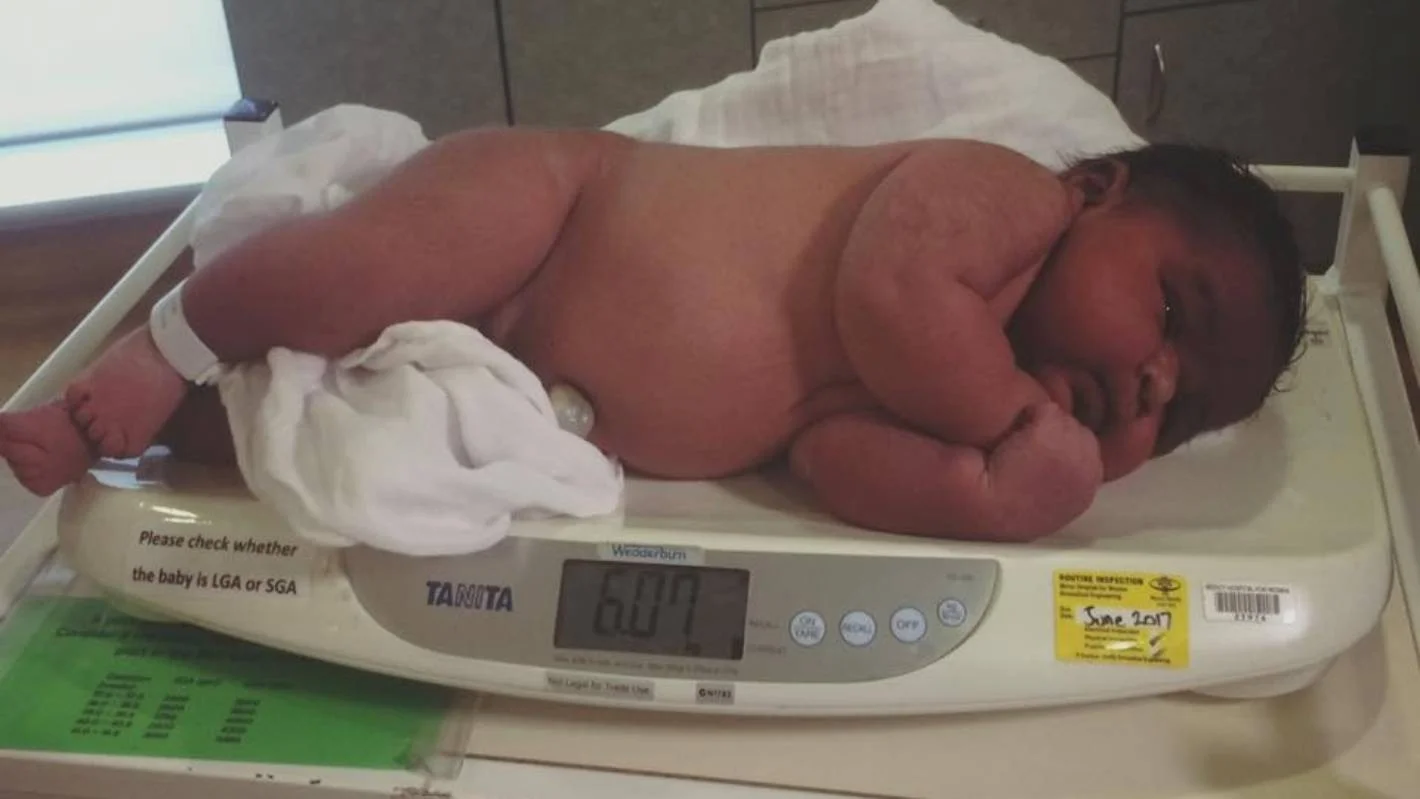
EFFECTS OF DM ON PREGNANCY- Postnatally y
infant is at risk of:
- Hypoglycemia
- hypotension (low glucose and low Ca & Mg)
- Electrolytes imbalance (↓ Ca++, ↓ Mg++)
- Polycythemia causing hyperviscosity & jaundice — why ? hypoxia
Preexisting Diabetes:
- Preconception Counselling
- risk of NTD ~1-2% (
- Folic Acid 1-4 mg /day
- BG 3.5-5.3 prior to meals
- switch /adjust insulin +/- OHA
GDM High Risk Factors
- Maternal age >25
- Family history
- Glucosuria
- Prior macrosomia
- Previous unexplained stillbirth
- PCOS
- ethnic group: Hispanic, Asians, Black
Screening
- 24-28 weeks routine
- screen at 1st prenatal visit if high risk
- 50 g GCT at 1 hour (don’t need to fast prior to test)
- ≥ 130 mg/dl → OGTT
- ≥ 200mg/dl → No further tests & start treatment.
- Diagnostic test → 3-hour 100g OGTT
Values on 100g OGTT
| # | Timing | Max Normal Blood Glucose level (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Fasting | 95 |
| 1 | 1 hr | 180 |
| 2 | 2 hr | 155 |
| 3 | 3 hr | 140 |
- 2 or more abnormal readings is diagnostic for GDM
Maternal Risks
- Increased birth trauma
- Operative delivery **
- 50% lifetime risk in developing Type II DM
- recurrence risk of GDM is 30-50%
- Cesarean section if baby wt. ≥ 4250-4500 g
Fetal Risks
- Increase in congenital anomalies
- increased risk of stillbirth
- Macrosomia
- Birth trauma (shoulder dystocia)
Management
- Goal is to optimize BG levels
- Minimize risk of adverse perinatal outcomes
- diet +/- OHA
- exercise
- insulin therapy
Diet : general principles
Composition:
- 50% CHO
- 20% Protein
- 20% fat
Total calories to be divided :
- 25% breakfast
- 30% Lunch
- 30% Dinner
- 15% at bedtime snack
Calories intake
- BMI>27 → 25 kcal/kg/ideal body weight/d
- BMI 20-26 → 30 kcal/kg/ideal body weight/d
- BMI<20 → 38 kcal/kg/ideal body weight/d
Normal weight gain 10-12 kg Exercise : Walking 30 min after meals
Insulin
Types:
- Rapid (Lispro) 30-90 min
- short acting (regular) 2-3 hours
- Long acting (NPH) 6-10 hours
Dosage calculation & timings:
- depends on: (Body weight, Trimester)
- Divided doses (AM - PM)
- How & what insulin to mix ?
OHA
-
Types :
- Glyburide
- Metformin
- Both safe in pregnancy
- Both to be used prior to meals (30-60 min)
- Both cross the placenta
- Both can be used with diet alone or combined with insulin
-
Effects:
- Lower mean birth Wt.
- Less macrosomia
- Less Gestational Wt. gain
- Treatment failure between 15 -30%
Glyburide
- Starting dose of 2.5 to 5 mg once daily
- Increased as needed up to 20 mg/Day in divided doses
- Higher risk of hypoglycemia than insulin
Metformin
-
Starting dose 500mg with dinner
-
can be increased to 1000 mg with dinner or 500 mg with dinner and breakfast
-
Usual effective dose 1500-2000 mg daily divided into two doses
-
Maximum daily dose is 2500 mg.
-
Extended Release (XR) form is preferred over the regular type
-
Not recommended to be used in patients with Htn., PET, or at risk of IUGR or pt. with Renal disease
Insulin Dosage calculation
- Insulin units = body weight (kg)
- ×0.6 (First trimester)
- ×0.7 (Second trimester)
- ×0.8 (Third trimester)
- Dosage schedule: give 2/3 in AM and 1/3 in PM
- Before breakfast: 2/3 NPH, 1/3 regular or lispro
- Before dinner: 1/2 NPH, 1/2 regular or lispro (if on lispro, administer additional dose before bedtime snack)
 #RR Controller gastric secretory release insulin
#RR Controller gastric secretory release insulin
Insulin Total dose Calculation
Total Insulin units = Body Wt. (Kg) × Trimester
- Body Wt. (Kg)
- Trimester
- 1st → 0.6
- 2nd → 0.7
- 3rd → 0.8
Total Insulin units is divided into:
- AM: 2/3rd
- PM: 1/3rd
What & how to mix INSULIN?
-
AM dose: 2/3rd NPH and 1/3rd Lispro or Regular
-
PM dose: ½ NPH and ½ Lispro or regular
Insulin Type & Total dose distribution
- Total Insulin units
- AM
- 2/3rd
- (2/3rd NPH and 1/3rd Lispro or Regular Ins)
- PM
- 1/3rd
- (½ NPH and ½ Lispro or regular)
- AM


Timing of Delivery
GDM Diet controlled
- Same as nondiabetic
- IOL at 40 - 41 weeks if undelivered
GDM on Insulin/Type II/Type I
- Well controlled → Deliver by 38+ to 39 weeks
- Suboptimal control → deliver following confirmation of lung maturity
Mode of Delivery :
- Vaginal delivery is recommended
- c/s for maternal or fetal indications
- Ultrasound estimates of fetal weight become significantly inaccurate after 4kg
- High risk for shoulder dystocia
- C/S delivery if EFW is >4250g
Peripartum/Intrapartum Management
- Withhold subcutaneous insulin from onset of labor or induction
- IV D10 @50cc/h
- insulin in NS usually starting at 0.5-1u/h insulin rate usually based on BG and pre-delivery insulin requirement
- BG hourly
- target: 4-6mmol/L
Postpartum
GDM:
- D/C insulin
- 6 - 12 weeks postpartum 75g OGTT
- Yearly fasting BG
- Advise for weight control & exercise
- With breastfeeding mothers add 500 kcal/day for the pregnancy diet
- Life risk of developing DM-II is 50%
Pre-pregnancy DM:
- stop insulin infusion
- Begin subcutaneous insulin
- Resume previous schedule at 1/2 -2/3 the pre-pregnancy dose
- Maintain IV D5W @50cc/h until oral feeds tolerated
- Refer to MD outpatient for follow-up.