IUFD
Definition
- Def.: Antenatal diagnosis of a stillborn infant after 20 weeks’ gestation or before the onset of labor
- IUFD is suspected with any maternal report of more than a few hours of absent fetal movement.
- Definitive diagnosis is by absent fetal cardiac activity on ultrasonography.
- Fetal deaths can be categorized by occurrence during the antepartum period or during labor (intrapartum stillbirth).
Causes
- The etiology of antepartum fetal death can be divided into broad categories:
- Idiopathic/unexplained (most common).
- Maternal conditions: e.g advanced age, post-term, Trauma, sepsis, diabetes & preeclampsia, thrombophilia, Antiphospholipid syndrome.
- Fetal conditions: e.g malformations, chromosomal and genetic disorders, infections, growth restriction, TTS
- Fetomaternal conditions: fetomaternal hemorrhage (rh alloimmunization)
- Placenta and cord complications: e.g Placental insufficiency, abruption, infarction, tight knot in the cord, cord prolapse.
Diagnosis
- History :Absence of fetal movements for a few hours
- Ultrasonography ( accurate 100% )
- Spalding sign (irregular overlapping of skull bones after 7days) - 1st img
- Robert’s sign (gas shadows in the chambers of the heart & great vessels after 12h) - 2nd img
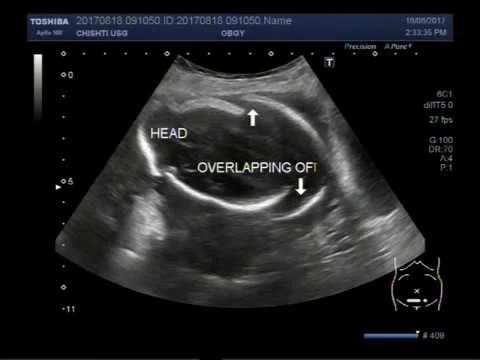
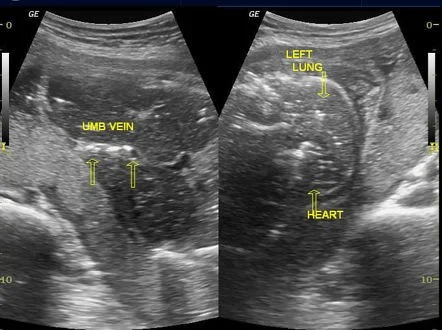
Management
- Expectant management: wait for Spontaneous labor, occurs within 2 to 3 weeks in 80% of cases.
- Active management: In cases of prolonged demise of failure of expectant, induction of labor should be offered due to emotional burden and the risk of chorioamnionitis and DIC with prolonged demise.
- Testing to determine the cause of the loss is usually negative but can include parent and fetal karyotyping, infection evaluation (TORCH), maternal thyroid screening and HbA1c, antibody screen, Thrombophilia screening, and fetal autopsy, Umbilical Cord /placenta specimen.
- Dopamine agonists to suppress lactation (cabergoline is superior to bromocriptine), should not be given to women with hypertension or pre-eclampsia.
Prevention in next pregnancy
-
Preconception counseling before next pregnancy.
-
Manage next pregnancies as high-risk
-
Women with a previous unexplained IUFD should be recommended to have obstetric antenatal care
-
And screening for gestational diabetes.
-
Antepartum fetal assessment for next pregnancy may not prevent but can significantly reduce the frequency of antenatal fetal deaths.
-
Maternal request for scheduled birth should take into account the gestational age of the previous IUFD, previous intrapartum history and the safety of induction of labour.