Malignant Bone Tumors
Overview
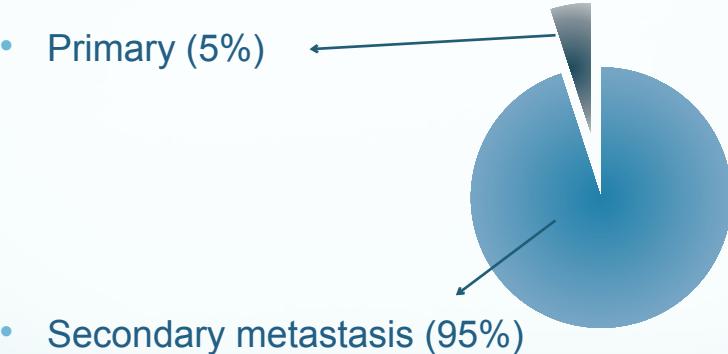
- Primary (5%)
- Secondary metastasis (95%)
Distribution of Primary Malignant Bone Tumors
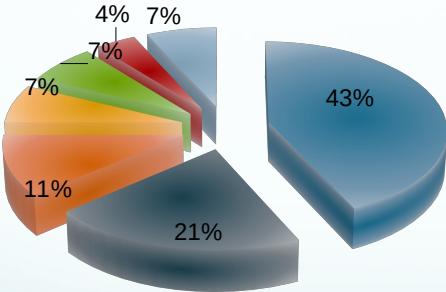
- Plasma Cell Myeloma 43%
- Osteosarcoma 21%
- Chondrosarcoma 11%
- Lymphoma 7%
- Ewing’s Sarcoma 7%
- Chordoma 4%
- Other 7%
Types of Primary Malignant Bone Tumors
- Multiple myeloma
- Osteosarcoma
- Chondrosarcoma
- Ewing’s sarcoma
Multiple Myeloma
- B-Cells of bone marrow
- Plasma cells mainly
- Age: 45-65 yrs.
- Bone pains
- Increased serum Calcium
- Bence Jones protein in urine
Source: Apley’s System of Orthop. And Fractures
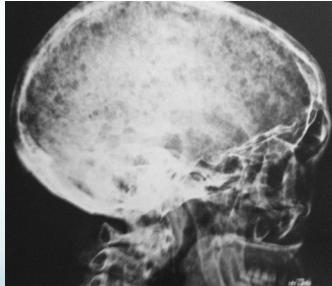
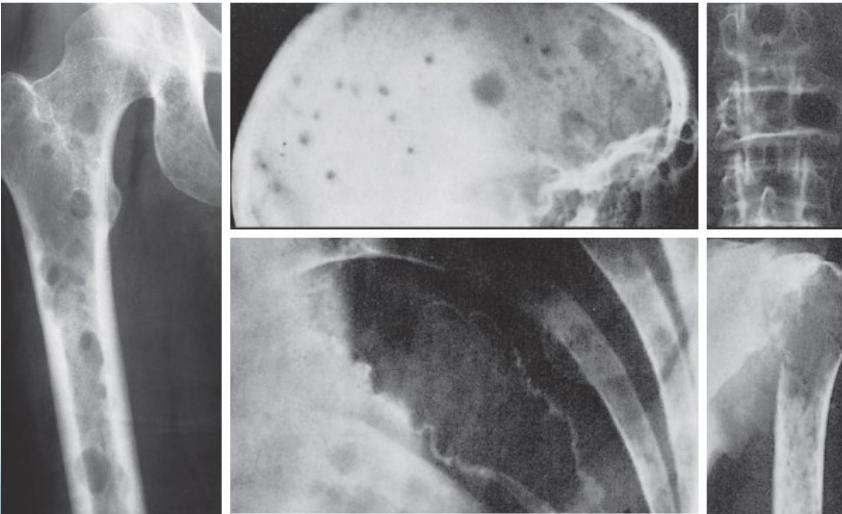
Radiological Features
- X-ray:
- Multiple punched-out lesions
- Osteoporosis & Vertebral compression fracture:
- If both present in a male >45: ? Myeloma
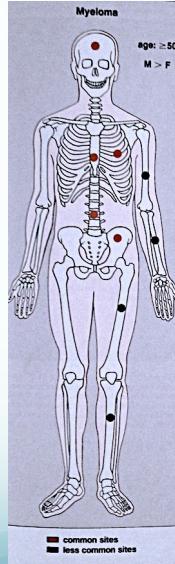
- Common sites:
- Skull, Prox. Femur, vertebrae
- Bone marrow biopsy
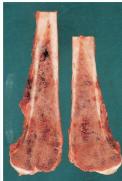
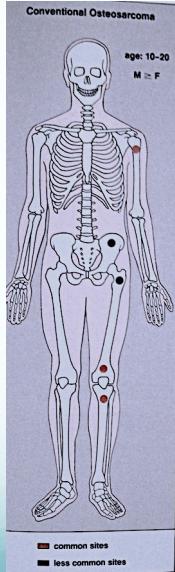
Osteosarcoma
- Usually highly malignant:
- (10% already lung metastasis)
- Children – adolescents (10-20 yrs.)
- Presentation:
- Pain
- Mass
- Site:
- Metaphysis of long bones
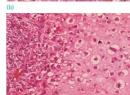
- Pathology:
- Bone forming: osteoblastic
- With chondroblastic areas
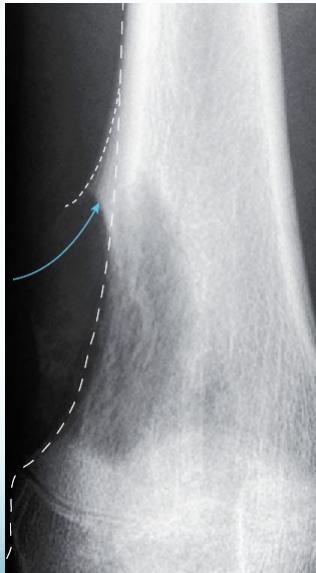
Radiological Features
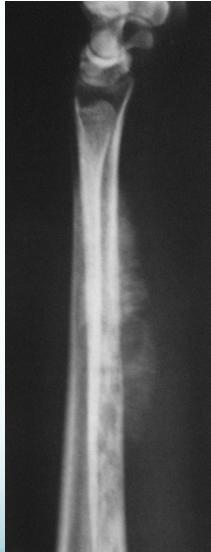
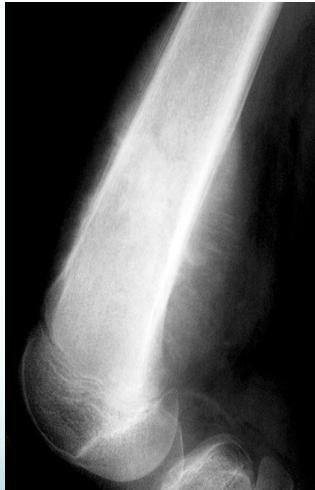
- X-ray:
- Radiolucency and sclerosis
- Poorly defined margins
- Extends into soft tissue
- Periosteal reaction:
- Sunburst (sun-ray) appearance
- Codman’s triangle
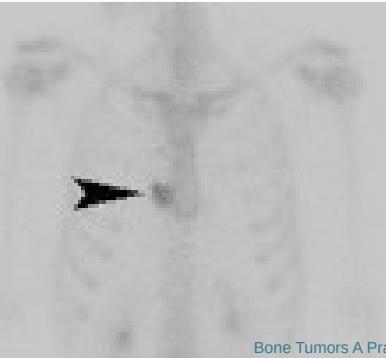
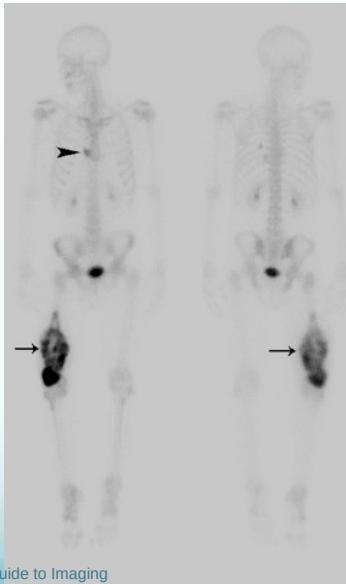
Additional Imaging
- Bone scan:
- Primary lesion
- Metastasis
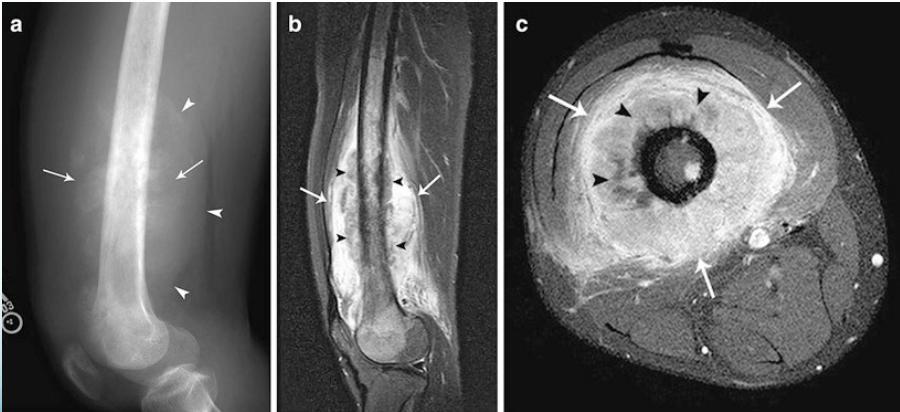
- MRI very informative
Treatment
- Look for metastasis
- Biopsy a must:
- Well planned incision
- Chemotherapy
- Surgery:
- Wide resection
- Amputation
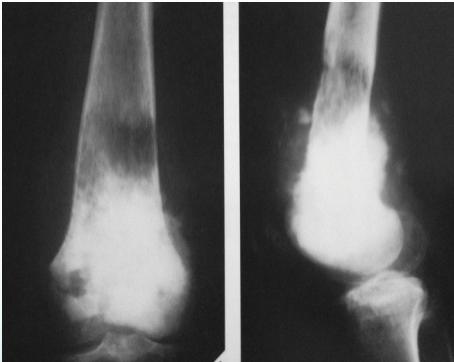
Source: Orthopedic Radiology. A Greenspan. Lippincott-Raven
Ewing’s Sarcoma
- From bone marrow cells
- A round-cell tumor
- Age: 10-20 yrs.
- Tubular bone
- Tibia, fibula, clavicle
- Presentation:
- Throbbing pain
- Swelling
- Tenderness
- Hotness
- ESR raised
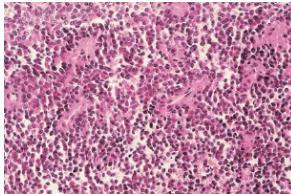
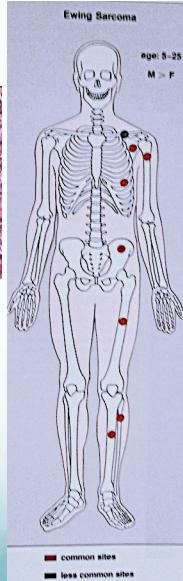
Source: Apley’s System of Orthop. And Fractures
Differential: Osteomyelitis ?
Radiological Features
- X-ray:
- Diaphyseal
- Bone destruction
- New bone formation:
- Along the bone
- “Onion-peel” layers
- ? “Sun-ray”
- ? Codman’s triangle
- Secondaries – in skeleton
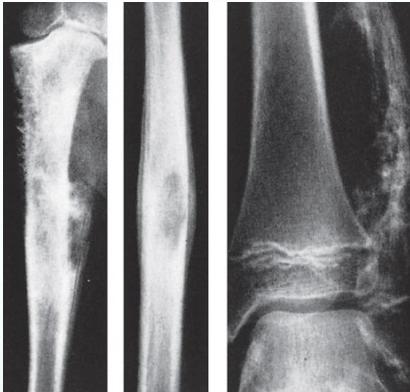
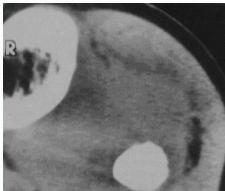
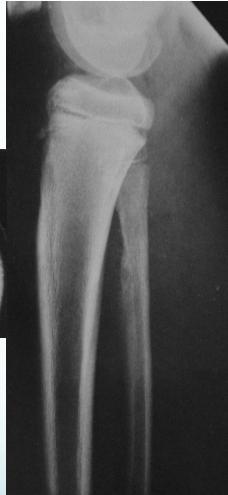
Source: Apley’s System of Orthop. And Fractures
Treatment
- Poor prognosis – a killing tumor
- Radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy – multiple drugs