Treatment
Non-Operative Management
- Observation - for latent or active benign lesions
- Bisphosphonate therapy - for certain bone lesions
- Radiation therapy alone - for radiosensitive tumors
- Chemotherapy alone - for chemosensitive tumors
Operative Management
Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Radiofrequency ablation (osteoid osteoma)
- Aspiration and Injection (Simple Bone Cyst)
Tumor Removal Procedures
- Curettage and Bone Grafting (giant cell tumor)
- Marginal Resection - for benign or low-grade tumors
- Wide Resection Alone (chondrosarcoma)
- Wide Resection + Chemotherapy (osteosarcoma)
Surgical Margins Classification
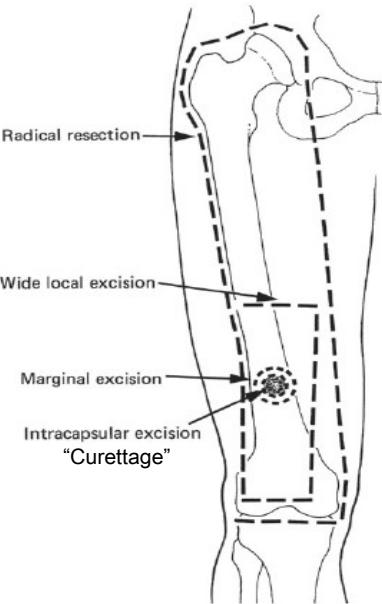
- Radical resection - removal of entire compartment
- Wide local excision - with cuff of normal tissue
- Marginal excision - at pseudocapsule
- Intracapsular excision - “Curettage”
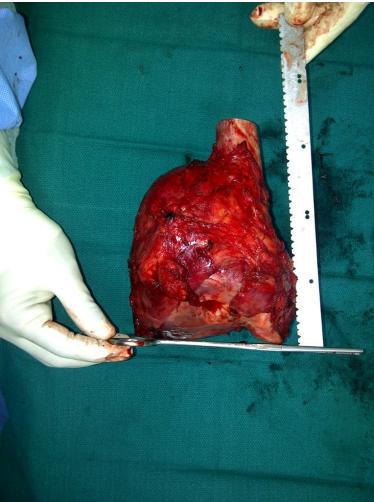
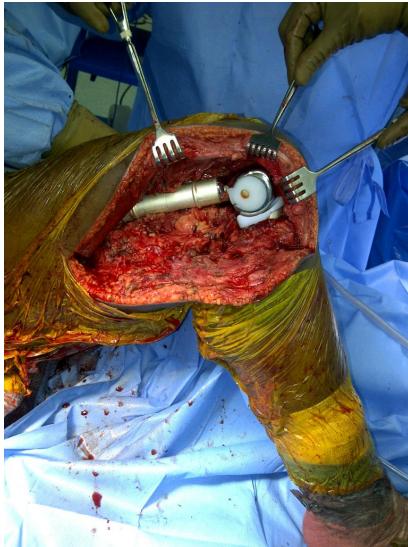
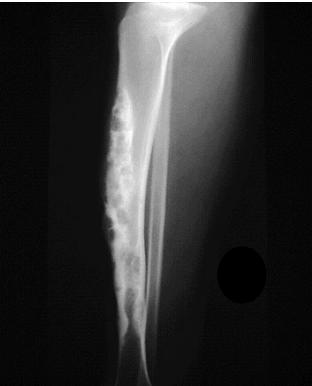
Resection & Reconstruction
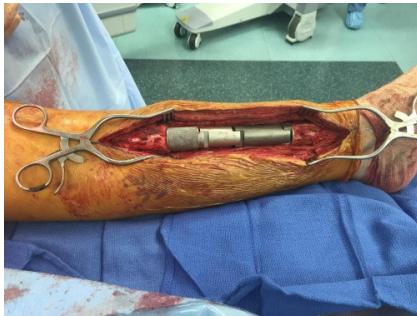
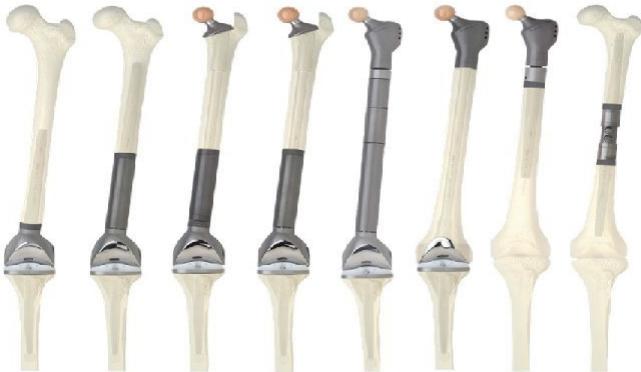
Adjuvant Therapy
Chemotherapy
Mechanisms of Action
- Induces apoptosis (programmed cell death)
- Eliminates micrometastasis in lungs
- >98% necrosis with chemotherapy is good prognostic sign
Radiation Therapy
Mechanisms of Action
- Production of free radicals causing DNA damage
- Direct genetic damage to tumor cells
Complications of Radiation Therapy
Effects on Normal Tissue
- Early effects:
- Delayed wound healing
- Increased infection risk
- Late effects:
- Fibrosis
- Joint stiffness
Serious Complications
- Post-radiation sarcoma
- Incidence ~13%
- Poor prognosis
- Post-radiation fractures