Common Foot Disorders
- Hall Hallux valgus
- Plantar fasciitis
- Achilles tendinitis
(http://www.londonorthopaedicsurgery.co.uk/ “http://www.londonorthopaedicsurgery.co.uk/“)
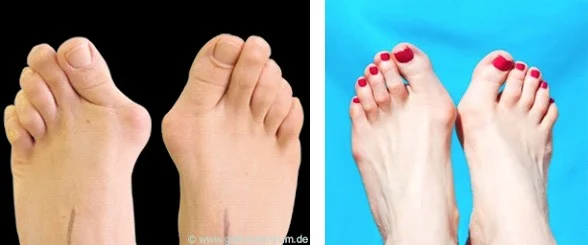
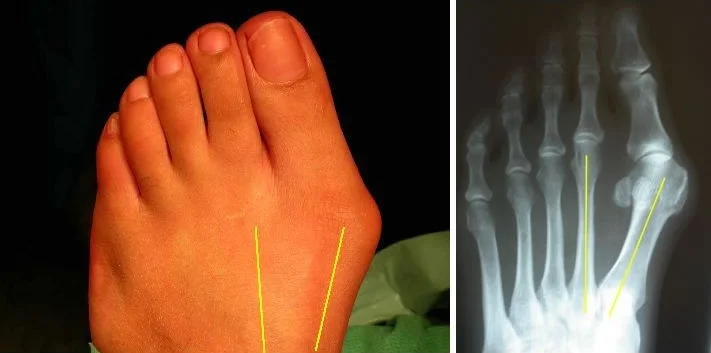
Hallux Valgus
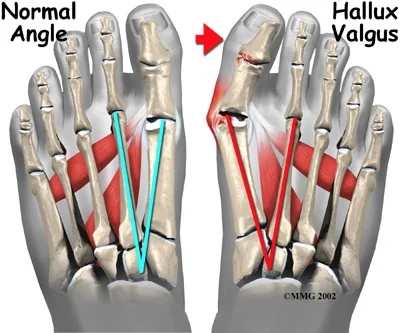
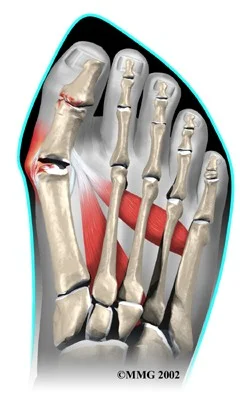
- Definition: lateral deviation of the great toe (hallux) and medial deviation of the first metatarsal
- A common deformity
- F > M
- Types:
- Adolescent
- Adult → commonest
- Geriatric
Etiology - Hallux Valgus
-
Familial: > 60%
-
2-4 % of the population
-
Wearing shoes
-
Shoes:
- High heels, or
- Pointed front
- Increase deformity & Cause?
-
Metatarsus primus varus:
- Congenital, or
- Geriatric
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
-
Deformity / Bunion / medial deviation MT-1
-
Issues in wearing shoes
-
Pain → over the bunion, forefoot
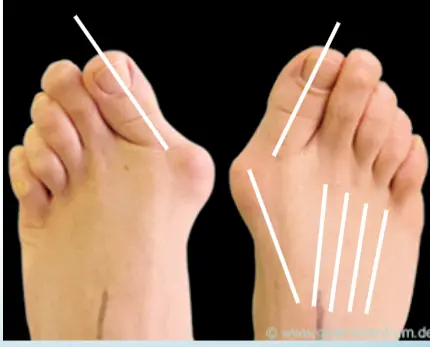
Radiology - Hallux Valgus
- XR views:
- AP standing:
- Lateral deviation of big toe
- Increased varus of 1st MT
- Subluxation of MT-Phal. joint
- AP standing:
Treatment - Hallux Valgus
-
General: reducing symptoms – does not correct deformity
- Rest
- Elevation
- Cold / ice compressions
- NSAID:
- Oral & gel
- Changes in shoe wear
- Wide front
- Activity modifications
-
Adolescent:
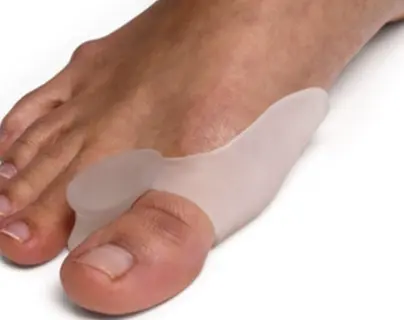
- Main complaint: cosmetic
- Wise to try conservative 1st (to delay surgery):
- Shoes: wide front, no high heals
- Silicon spacer / splints
- Surgery
-
Adult:
- Surgery usually
- Many operations
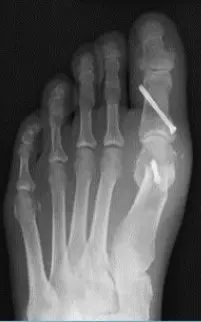
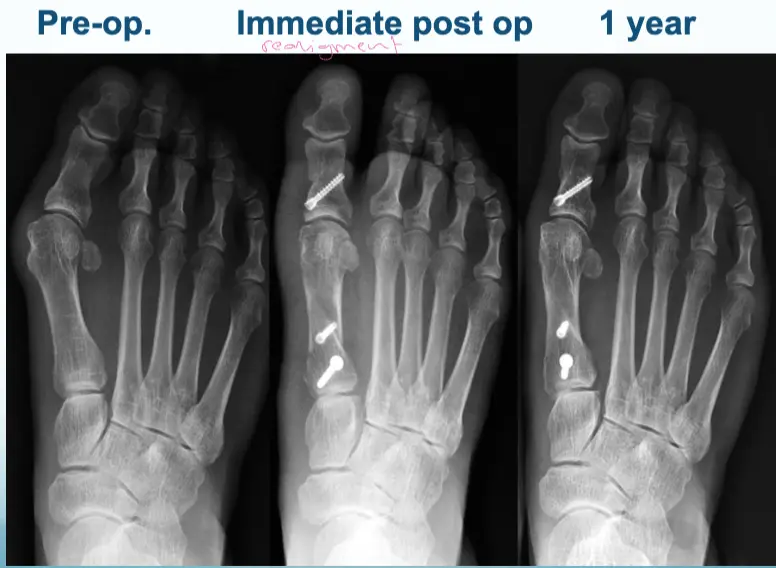
-
Aim:
- Re-align the 1st metatarsal
- Correct valgus deformity of big toe
- Soft tissue balancing
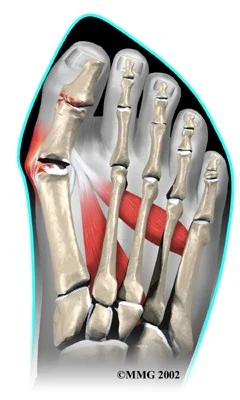

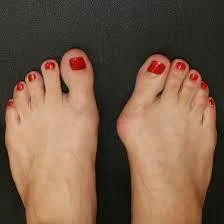
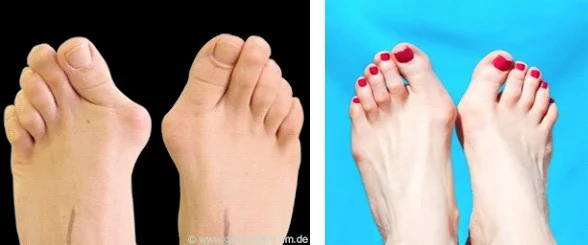 bunion
bunion
- Bunion may be (usually) inflamed / painful
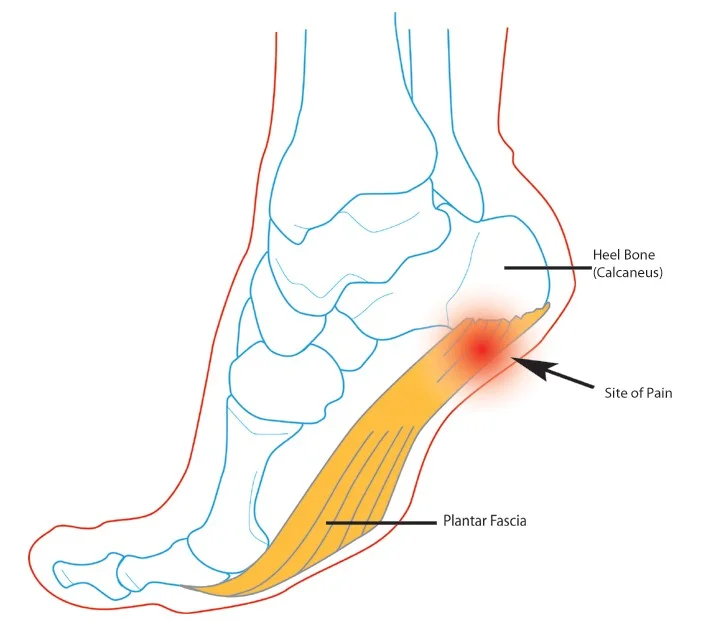
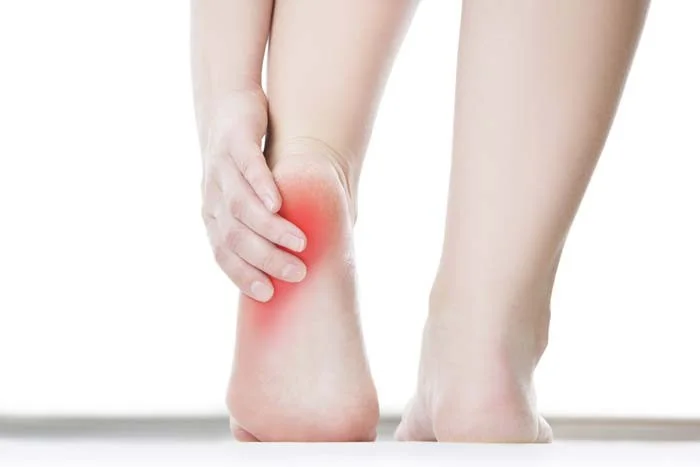
Plantar Fasciitis
- Definition → inflammation of the plantar fascia
- In the posterior 2/3 of the foot
- Painful & sometimes disabling
Causes - Plantar Fasciitis
- Insidious (not clear H/O an incident)
- Some times:
- Increased sport / repetitive stress
- Change of footwear
- Change of walking surface
- Gain of weight (pregnancy, obese)
- Prolonged standing Z
- Connective tissue disorders (as D.M, Gout, …)
Symptoms - Plantar Fasciitis
- Gradual onset
- “Start-up Pain”:
- When wake up in the morning
- After sitting for some time
- Pain:
- Pins and needles, or sharp, or persistent aches
- At hind & mid foot area
- Improves with:
- Walking for sometime
- Elevation
- NSAID
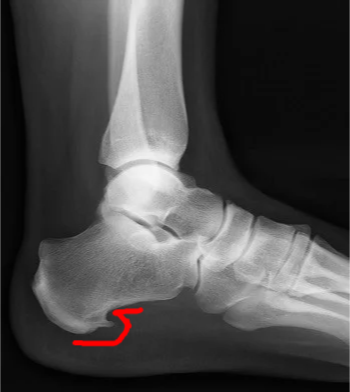
Radiology - Plantar Fasciitis
- “Calcaneal Spur” on XR:
- It’s a result NOT the cause
- Implies chronicity
- Not diagnostic
- Present in 10% of normal
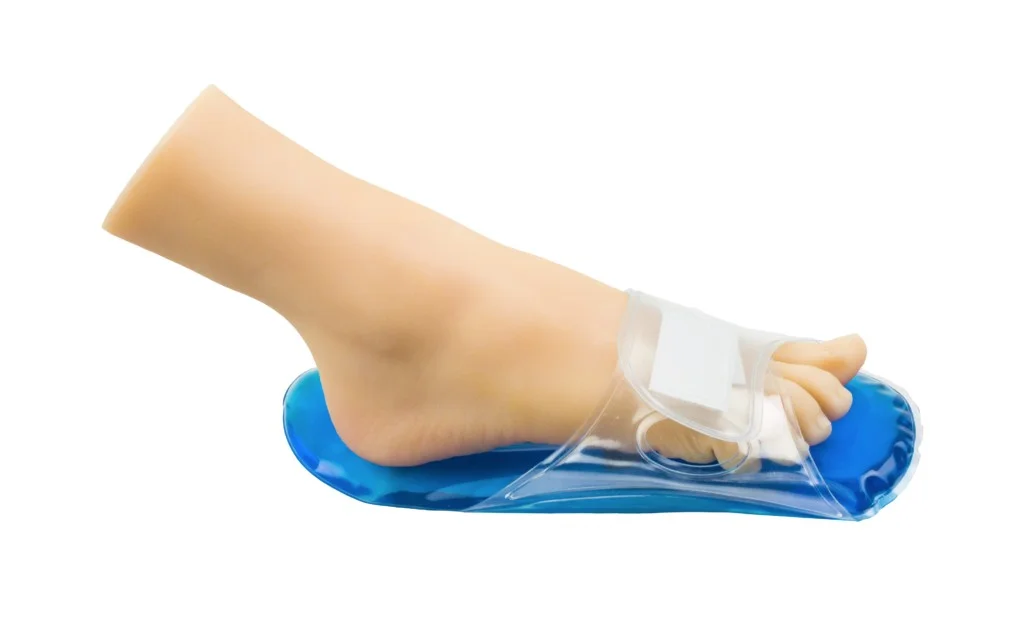
Treatment
- Conservative Management
- Rest
- Avoid repeated stress
- Elevation
- Heel cushion Z
- Reduce inflammation
- Ice compressors
- NSAID
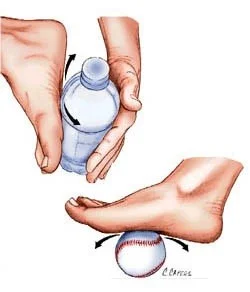
- Physical Therapy
- Stretching (calf & plantar fascia)
- Massage

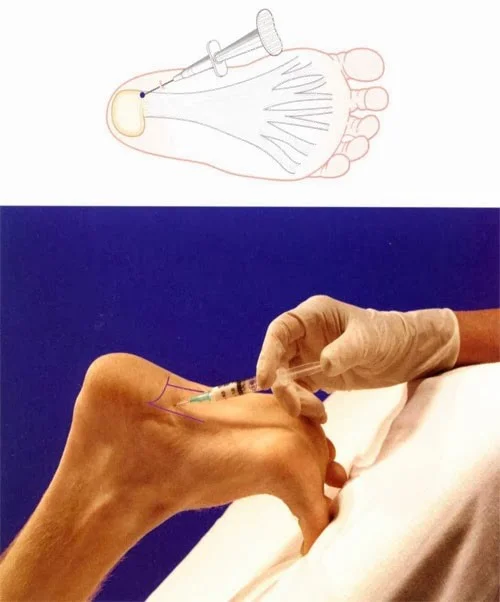
 Advanced Treatment Options
If conservative treatments fail:
Advanced Treatment Options
If conservative treatments fail:
- Rest
- Injection therapy
- Local anesthesia & steroid at the most tender point

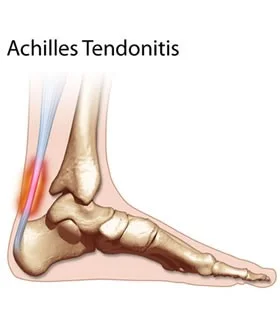
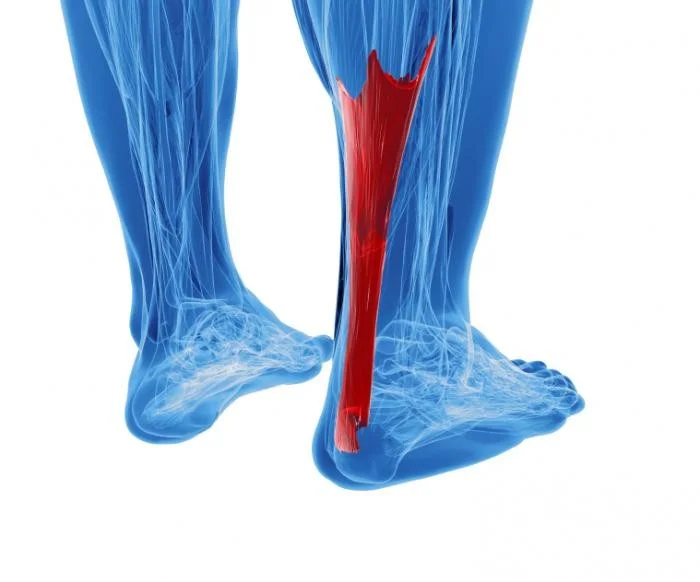
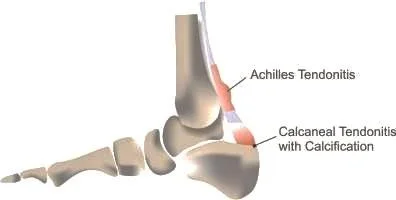
Achilles Tendinitis
Overview
Achilles tendinitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the Achilles tendon.
Types of Achilles Tendinitis
- Insertional
- at insertion into Calcaneum
- not related to activity
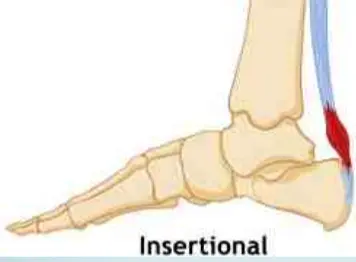
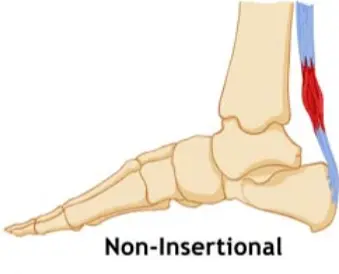
- Non-insertional
- within the tendon
- in younger active patients
Clinical Picture
- Pain: posterior foot / lower leg
- Pain is worse
- Getting up from sleep in the morning
- Gradually improves throughout the day
- After a prolonged period of inactivity/activity
- Getting up from sleep in the morning
- Difficulty in plantar flexion of the foot
- Tenderness:
- Over the lower calf muscle
- Achilles tendon
- Some swelling over the tendon (+/-)
Causes of Achilles Tendinitis Extrinsic Factors
- Prolonged walking/standing
- Repeated stress
- Sports
- Sudden increase in activity
- No proper warm-up before exercise Z
- Shoes:
- Rubbing against tendon
- Improper shoes
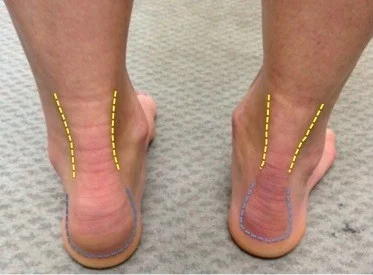
Intrinsic Factors
- Tight gastrocnemius
- Tight Achilles tendon
- Flat feet
- Genu valgus
Workup for Achilles Tendonitis
- A clinical diagnosis
- X-ray:
- may show calcification around the tendon
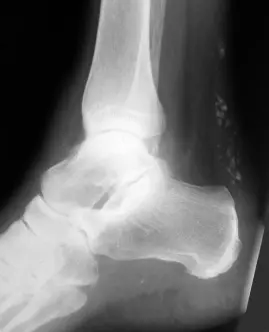

- U/S:
- Edema in tendon
- some effusion around the tendon
Treatment of Achilles Tendonitis
- Rest
- Elevation
- Cold/Ice compressions
- NSAID: oral & gel
- Physiotherapy: stretch the tendon
- Heel pads in proper home shoe to rest the tendon
Advanced Treatment for Achilles Tendonitis
- If no improvement → below knee cast with the foot in equinus, for 3-6 weeks may work
- Surgery may be needed in persistent cases
Complications of Untreated Achilles Tendonitis
- Achilles tendon pain should be treated
- If left untreated, the tendon can become weak, frayed, and eventually may rupture




Take Home Message
Key Points
- Hallux Valgus
- Conservative is still 1st line of management
- Surgery for adult moderate/severe hallux valgus
- Prevention → by proper shoes education
- Plantar fasciitis
- Conservative treatment
- Patient education is a must
- Achilles Tendinitis
- Conservative treatment