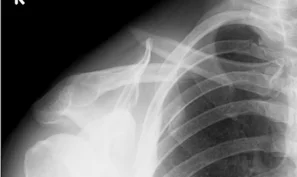
Clavicle Fracture
- One of the commonest of all fractures
- Etiology
- Direct
- Indirect trauma:
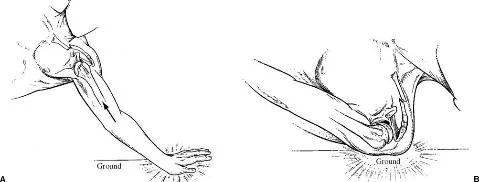
- Fall onto outstretched hand or on the shoulder
- Birth newborn injury following a difficult delivery (present as pseudo-paralysis)
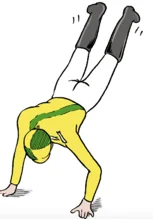

Clavicle Fracture
- Sites:
- Lateral thirds,
- Middle thirds, common (why?)
- Medial thirds
Its weakest point. The lateral fragment is depressed by the weight of the arm against trapezius, thus the shoulder droops, it is pulled medially forward by adductor function of pectoralis major causing the bone fragments to override.

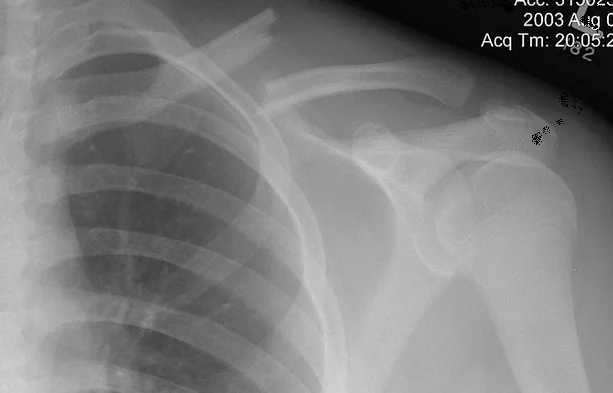
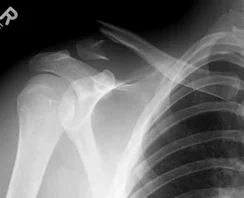
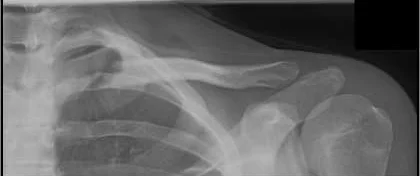
Clavicle Fracture
- Clinically;
- Pain
- Swelling
- Deformity
- Loss of motion
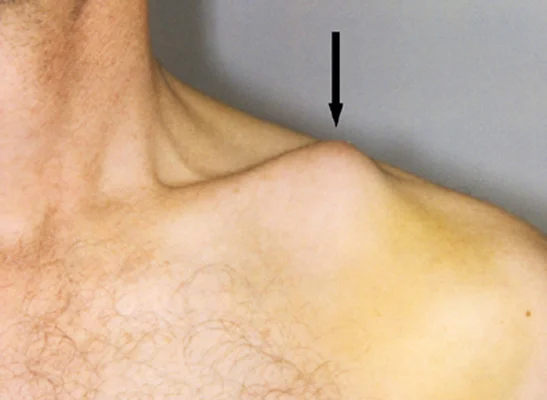
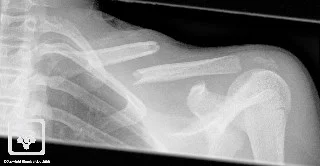
Clavicle Fracture: Management
- Non or minimal displaced: Typically conservative: heals well
- Figure-of-eight brace (bandage)
- Or Shoulder sling holding the elbow to overcome gravity

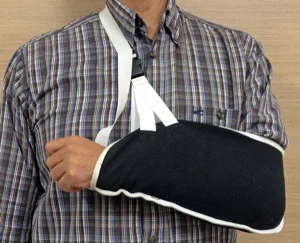
Clavicle Fracture: Management
- Surgical indications:
- Vascular compromise
- Open fractures
- Comminuted fractures with (Z-shaped) fragment
- Floating shoulder
- Severe displacement
- Tenting of the skin
- Patient’s preference
- (Athlete, active)
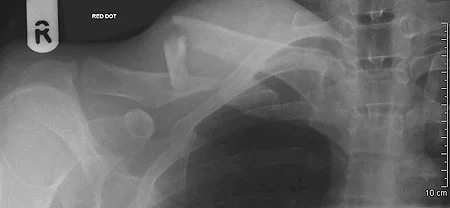

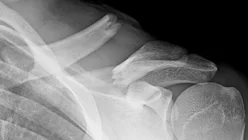
Clavicle Fracture: Management
- Surgical Treatment
- ORIF by Plate and Screws (standard)
- Elastic nail ?
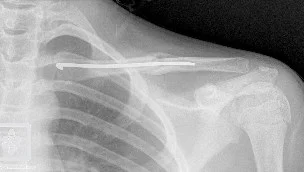
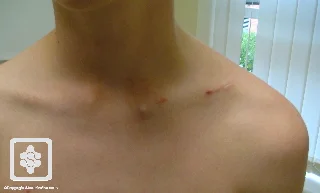
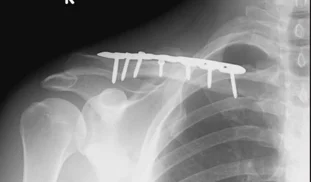
Clavicle Fracture – Complications of surgery
- Infection
- Neurovascular injury
- Pneumothorax
- Non union
- Hardware prominence
- Poorer cosmoses