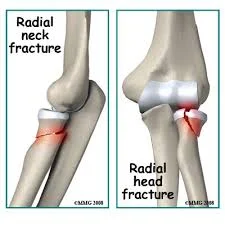
Fracture Radial Head / Neck
- Pain at elbow
- Localized swelling
- Inability to supinate/pronate. Might still be able to flex/extend elbow slightly
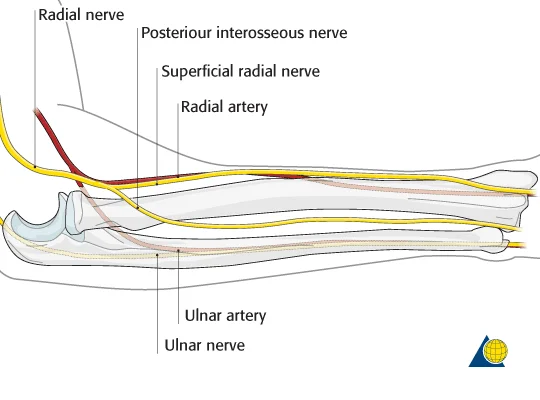
Possible Associated Injury
- Examine the wrist:
- For disruption of the distal radio-ulnar joint
- The posterior interosseous nerve
- damaged by the initial injury or by the surgery performed to treat the fracture
- Therefore, document functional status preoperatively
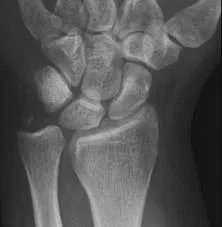
X-ray
- A visible posterior fat pad on the lateral view of the elbow is a sign of occult intra-articular trauma
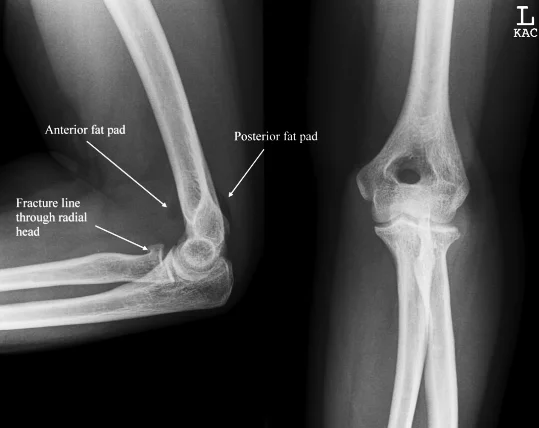
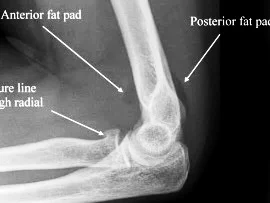
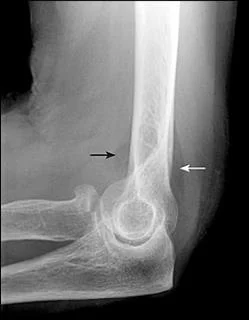
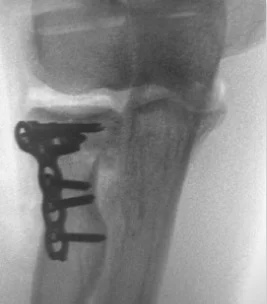
Fracture head
- Management In Minimal head displacement:
- Conservative treatment
- Cast above elbow & sling
- Early motion to minimize elbow stiffness
neck of radius
- Management if the fracture involves more than 33% of the articular surface or is sever displaced
- Surgical treatment:
- ORIF if possible
- Radial head Replacement if comminuted /inoperable
- Surgical treatment:
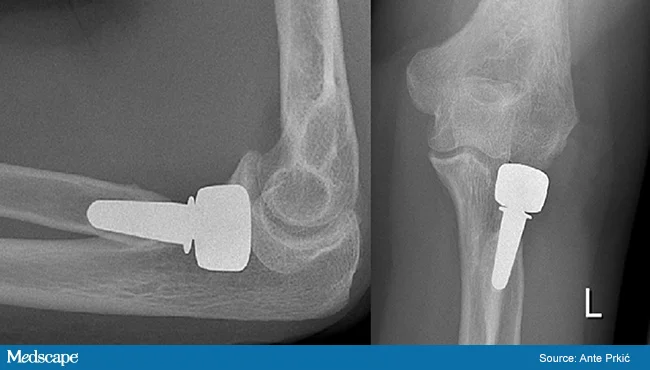
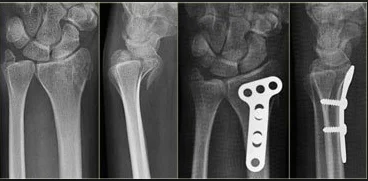
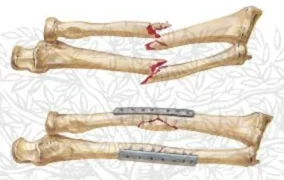
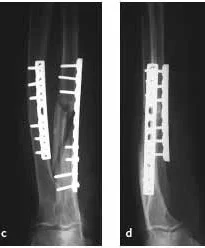
Forearm Fractures
- (Considered as a joint)
- Management:
- Undisplaced:
- Possible conservative - cast & follow up
- Displaced:
- Anatomical Open reduction and internal fixation by Plating and screws( best fixation)
- Early motion - Prevents stiffness
- Undisplaced:


Forearm fractures - Complications
- Compartment Syndrome
- Neurovascular injury
- Infection in open # or postop
- Mal-union (if treated conservatively) * loss of supination/pronation
- Nonunion
- Posttraumatic radioulnar synostosis (3- 9% )


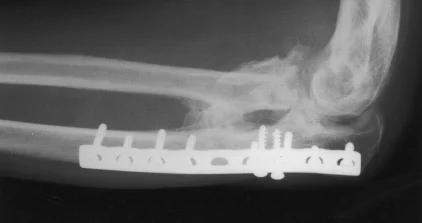
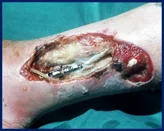
Galeazzi Fracture/ Dislocation
-
Fracture of the radius with dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint
-
“Fracture of necessity”
- Necessitates surgery
-
Fracture of the radius with dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint
-
“Fracture of necessity”:
- Necessitates surgery
- Plating of radius
- Reduction of distal radio-ulnar joint (+/- Fixation)
- Necessitates surgery
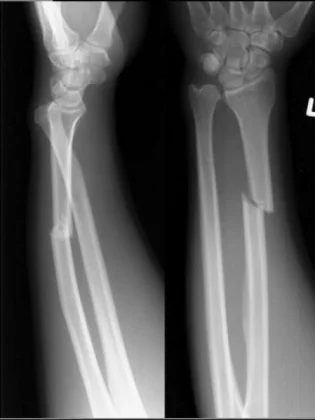
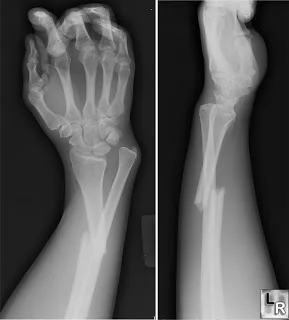
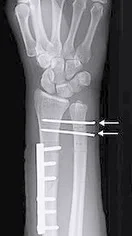
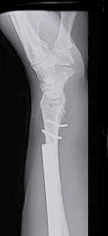
Monteggia Fracture/Dislocation
- Fracture of the proximal third of the ulna with dislocation of the head of the radius
- Dislocated head of radius missed if two joints are not included on the x-ray
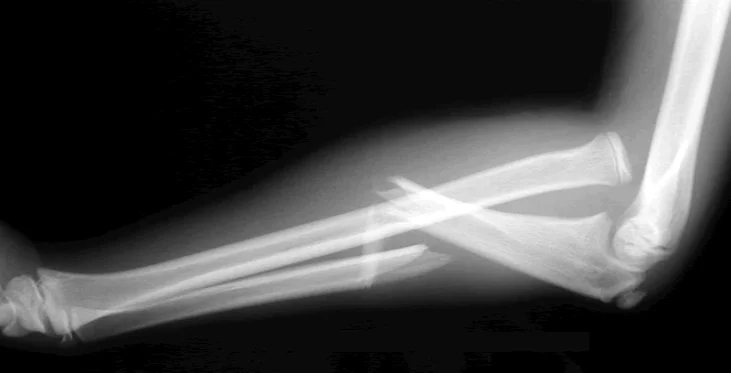
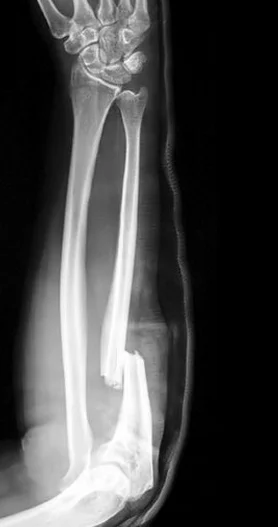
- Fracture of the proximal third of the ulna with dislocation of the head of the radius
- “Fracture of necessity”. Treated by:
- Open reduction and internal fixation of ulna
- Closed reduction of head of radius
- +/- fixation
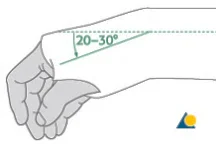
Colle’s Fracture
- Extra-articular fracture of the distal radius with dorsal and radial displacement of the wrist “Dinner fork” deformity
- Seen in elderly with osteoporosis
- Caused by falling on the outstretched hand
Treatment
- Undisplaced : Cast alone
- Displaced: (Sedation/ UGA / ULA), closed reduction, casting Wrist immobilized in flexion & ulnar deviation
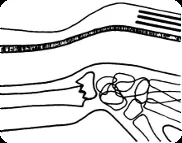
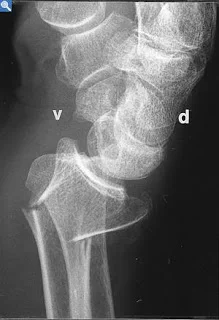
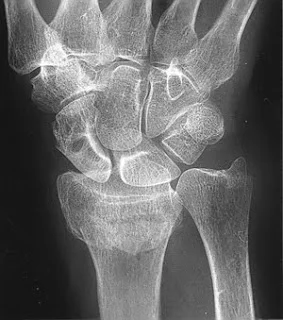
Intra-articular Distal Radius Fracture
- treated by anatomical open reduction, internal fixation and early mobilization