ORTH536
Introduction to Orthopedics
Introduction to The Course
Moaath A. Alamir, MBBS, SB-Orth
masoa86@gmail.com
What is Orthopedic Surgery ?
- Derived from the Greek word
- Orthos: straight, free from deformity
- Paidon: child
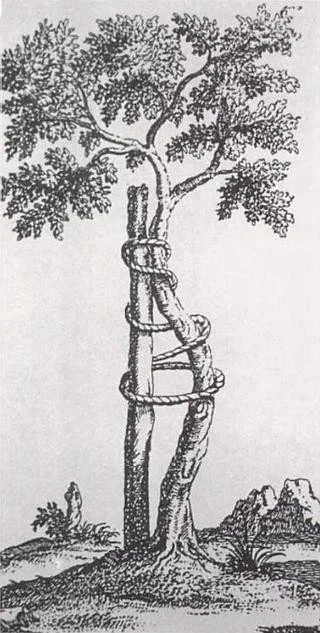
- In 1741, Dr. Nicholas Andry published Orthopedie
- the Art of Correcting and Preventing Deformities in Children.
- Straight stake tied to a crooked sapling



Saudi Orthopedic Association Logo Evolution

What is Orthopedic Surgery ?
Welcome to the Division of ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY
Branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system using both surgical and non-surgical means of management.

Who Do We Treat?
Subspecialties ??!!
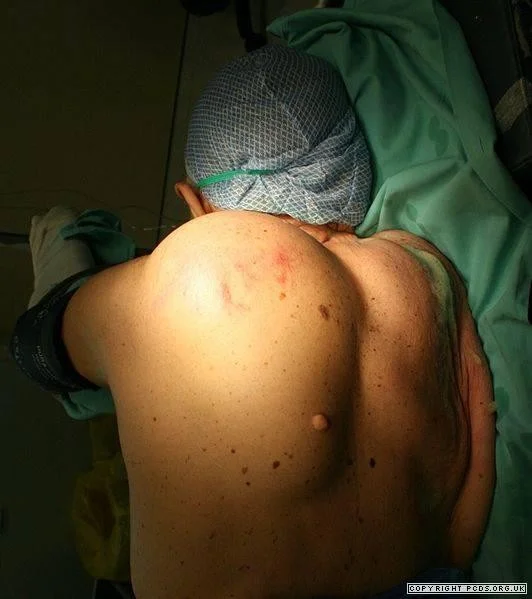
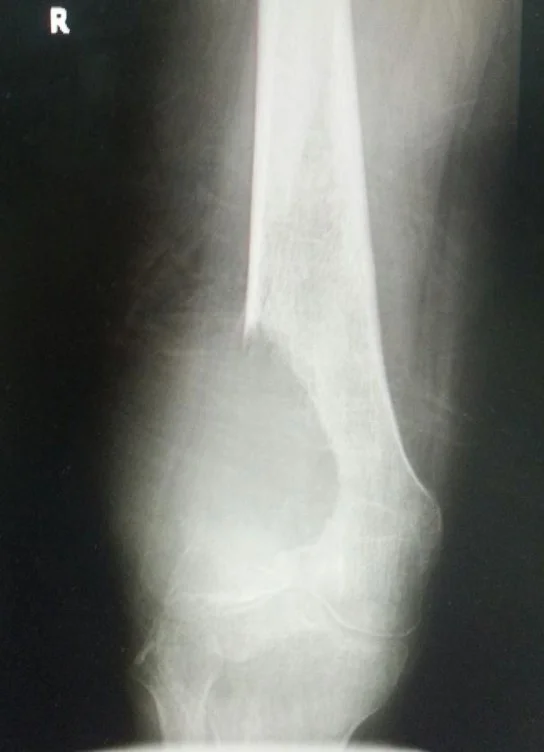
- I have a fracture
- I need to fix it
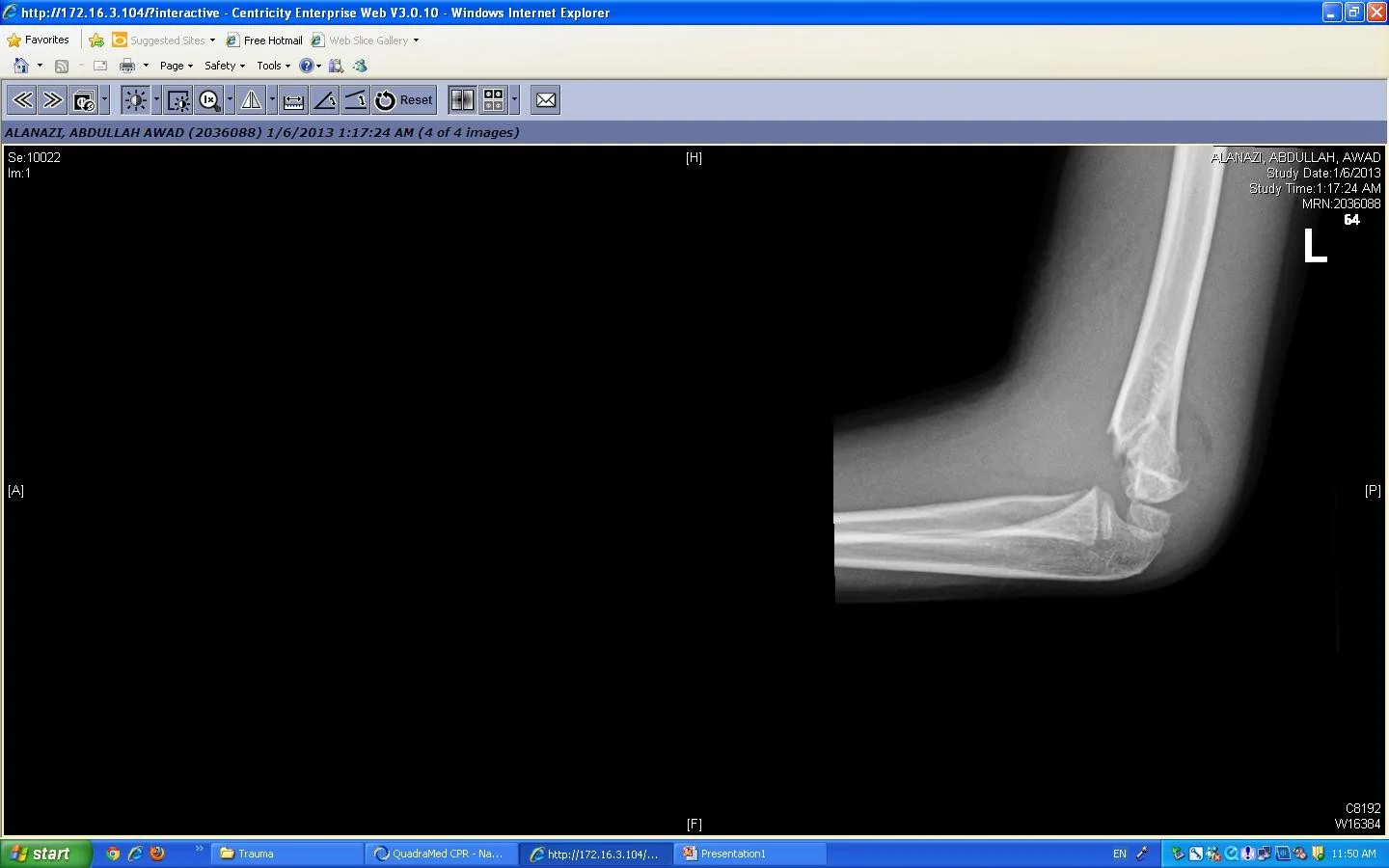
Subspecialties ??!!
 #VID
#VID
Subspecialties ??!!
- Foot & Ankle
- Arthroplasty
- Pediatric
- Sport
- Spine
- Trauma
- Upper Limb
- Oncology
Trauma
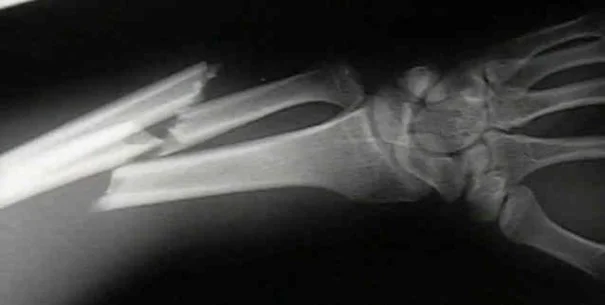
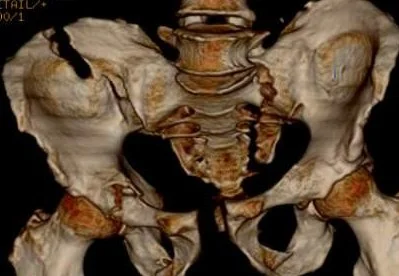
Pediatric Orthopedic
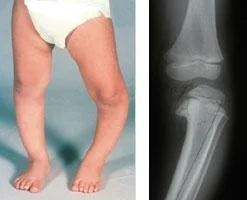
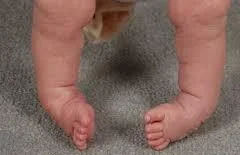


Arthroplasty
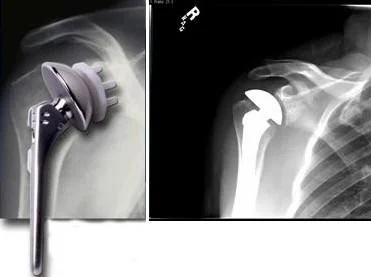

Spine Surgery

Sport Surgery

Foot & Ankle

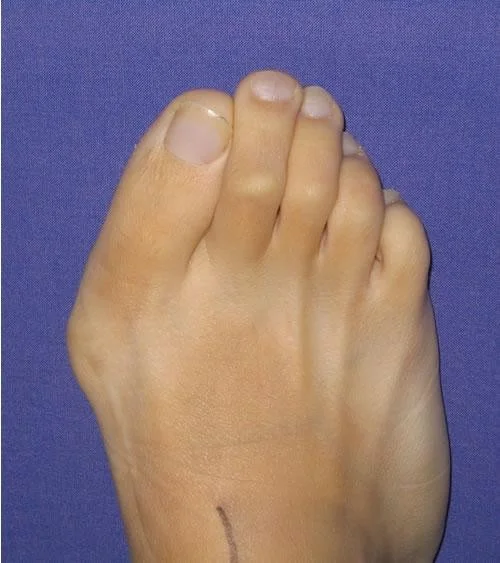
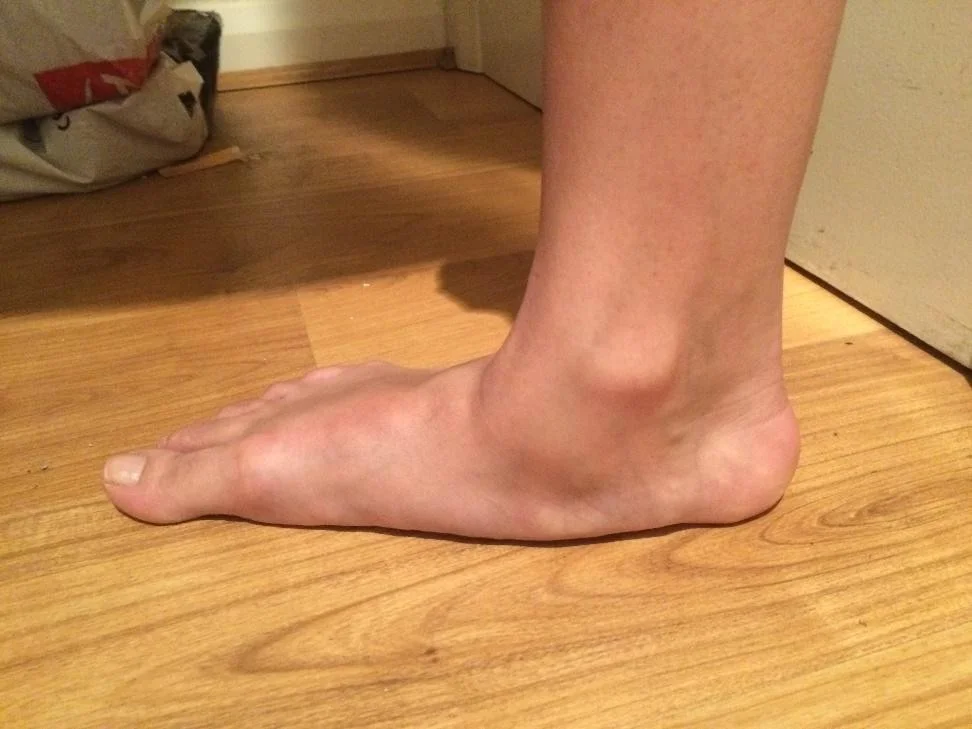
Oncology


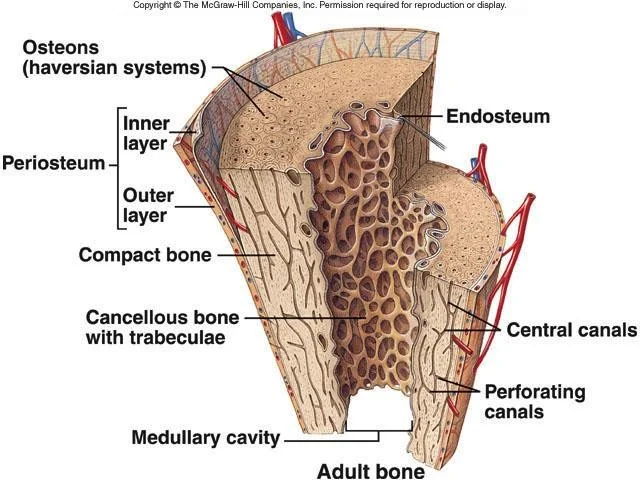
Basic Anatomy of Bone
- Periosteum
- Endosteum
- Cortex
- Cortical bone
- Medulla
- Cancellous bone
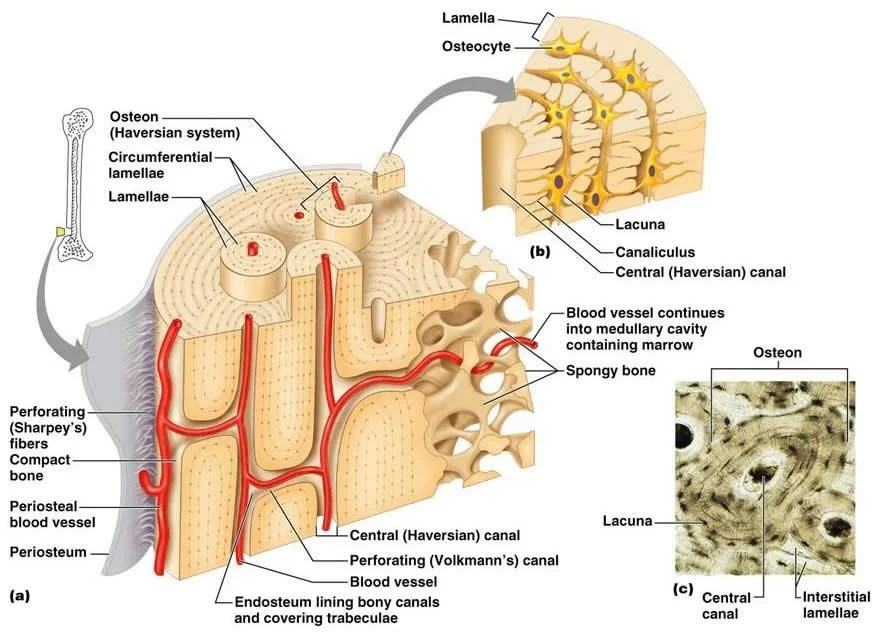
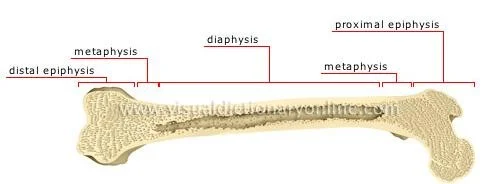
Basic Anatomy of Bone
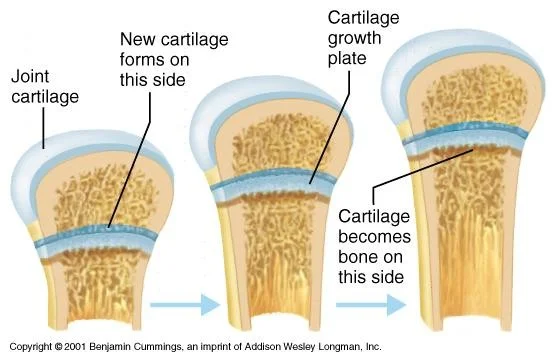
- Epiphysis
- physeal plates(child)
- Diaphysis
- Metaphysis

Bone components
A: Matrix:
- Inorganic (Minerals): (60%)
- Ca hydroxyapetite, Ca phosphate
- Organic: (40% of dry weight)
- Collagen fibers
- Cells
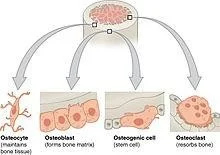
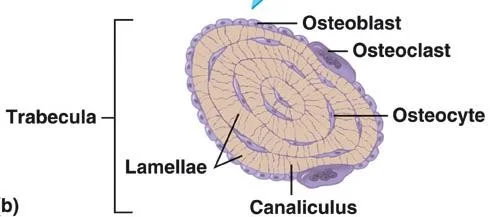
B: Cells:
- Osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes
- Osteon:
- a unit, not a cell
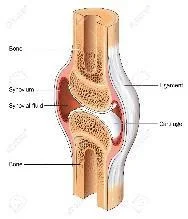
Basic Anatomy of Joints
- Types:
- Fibrous (slight movement)
- Tibio-fibular Syndesmosis
- Cartilaginous (some movement)
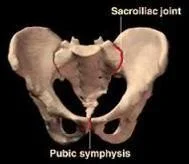
- Symphysis pubis, Intervertebral disk
- Synovial (more movement)
- Elbow, Hip, Knee
- Fibrous (slight movement)
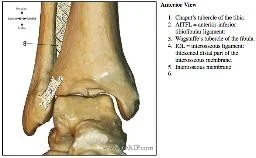
Types of Synovial Joints
-
Plane / Gliding( ACJ)
- Vertebrae
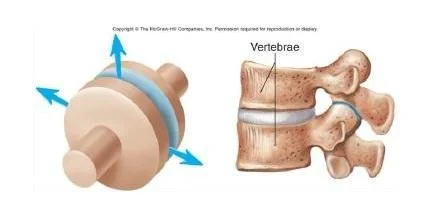
- Vertebrae
-
Saddle(CMC )
- Carpal bone (trapezium)
- Proximal metacarpal bone of thumb
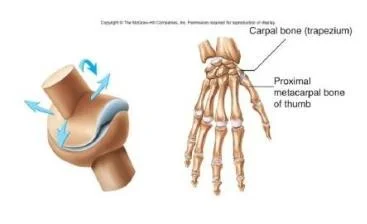
-
Hinge(knee)
- Humerus
- Ulna
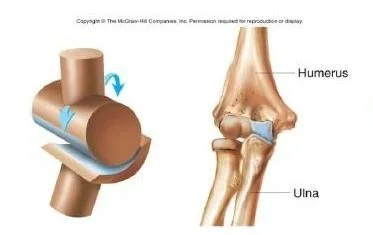
Types of Synovial Joints
-
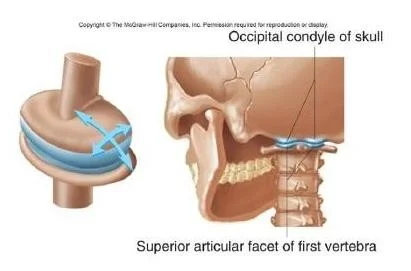
Pivot(atlas-axis)
- Radius
- Ulna
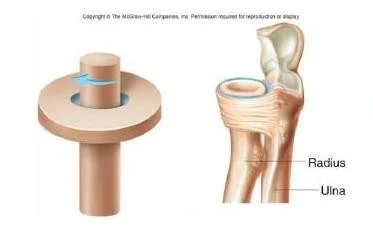
-
Ball & Socket(hip)
- Scapula
- Humerus
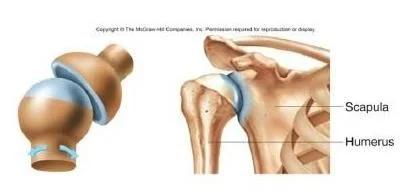
-
Ellipsoid(MTP,MCP)
- Occipital condyle of skull
- Superior articular facet of first vertebra
Divisions in Orthopedics
- Arthroplasty (joint replacement)
- Arthroscopy &sports
- Foot & ankle
- Hand (Upper limb)
- Oncology
- Pediatric orthopedics
- Spine
- Trauma
Structures affected
- Bones
- Joints
- Muscles
- Nerves
- Tendons
Diseases
- Congenital
- Developmental
- Infections / Inflammations
- Metabolic
- Tumors / tumor-like
- Neuromuscular
- Traumatic
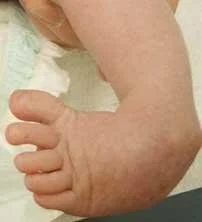


Descriptive terms
-
Proximal / Distal
-
Medial (Ulnar in forearm & hand) / Lateral (Radial in forearm & hand)
-
Anterior( hand: Palmar), ( foot: Plantar), (hand & foot: Volar)/ Posterior= Dorsal
-
Hallux: Big toe
-
Genu: Knee
-
Coxa: Hip
-
Cubitus: Elbow
-
Pes: Foot
-
Pullicis: Thumb
-
Indecis: Index
-
Capital: Head
Descriptive terms
- Valgus: away from midline
- Varus: towards midline
Describing position of distal part in relation to proximal part

Tilting vs. angulation
-
Tilting:
- Describes position of distal fragment in relation to proximal
-
Angulation:
- Describes position of apex of angulation

Courses in Your Level
| Code | Course Name | Weeks | Credit Hrs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| ORTH536 | Orthopedics | 6 | 4 |
| GYN535 | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 6 | 6 |
| EMR539 | Emergency | 6 | 4 |
| FRNS537 | Forensic Medicine | 15 | 3 |
Forensic time will change with each course
- with ORTH: Tuesday 8-10
ORTH536 - Objectives
Knowledge of common orthopedic diseases & musculoskeletal injuries (traumatology) 1.1 Describe the etiology, pathogenesis & clinical presentation 1.2 Describe the management, prognosis & complications
Cognitive Skills of common orthopedic diseases & musculoskeletal injuries (traumatology)
- 2.1 Analyze clinical data gathered from history, physical examination & diagnostic investigations to formulate differential diagnosis
- 2.2 Demonstrate the ability to make clinical judgement & construct appropriate immediate & long-term management plans by adopting strategies of Evidence-Based practice.
- 2.3 Differentiate life-threatening & organ-threatening conditions & propose an acute management plan
Interpersonal Skills & Responsibility
- 3.1 Demonstrate ability to accurately convey relevant explanations & information to colleagues & other professionals to develop a share plan of patient’s care
- 3.2 Demonstrate professional attitude & follow ethical principles including respect for physicians & health workers & patients’ confidentialities
Communication, Information Technology & Numerical
- 4.1 Communicate effectively with patients & their families
- 4.2 Demonstrate the ability to present a case using IT techniques & proper communication skills
Psychomotor
- Demonstrate the ability to perform a proper history taking & physical examination, following high ethical standards
- Demonstrate the ability to perform basic diagnostic & treatment procedures correctly
Orthopaedics Course Overview
Summary - Objectives
The Orthopaedics course aims to achieve several key objectives:
- History: Understand the historical context and development of orthopaedic practices.
- Clinical examination: Develop skills in conducting thorough clinical examinations.
- Investigations: Learn about various investigative techniques used in orthopaedics.
- Principles of management: Understand the principles guiding the management of orthopaedic conditions.
- Identify major life-threatening & limb-threatening emergencies: Recognize and manage emergencies in orthopaedics and trauma.
- Perform basic skills properly and safely: Acquire the necessary skills to perform basic orthopaedic procedures safely.
- Maintain high ethical and professional standards: Uphold ethical and professional standards in practice.
Time Frame – Six Weeks
The course is structured over six weeks as follows:
- First week: Theoretical knowledge and tutorials.
- 4 weeks clinical rotation in hospitals:
- Outpatient, inpatient, operating room, cast room, ER.
- Includes 3 days/week in the college for lectures, tutorials, practicing history taking, clinical examination, and case scenarios for management.
- Week 5: Case presentations by students.
- Week 6: Assessment through MCQ, Slide show, Clinical Scenarios, and Clinical Exam.
Assessment
The assessment is divided into two components:
Written Assessment (30%)
- 50 MCQs.
- Mid-Block Exam in Week 3:
- 20 questions (12 marks).
- Covers lectures as per the blueprint.
- Final Exam:
- 36 questions (18 marks).
- Covers all lectures.
Clinical Assessment (70%)
- Covers all topics in the course.
- Case presentation: One case (10 marks) in Week 5.
- Slide show: 15 slides (35 marks).
- Clinical Case scenario: One case (5 marks).
- History taking: One case (5 marks).
- Clinical/Skill examination: Two joints/one skill (15 marks).
Attendance
- Attendance will be taken for all sessions.
- Lectures/Tutorials in the college: Register closed after 15 minutes.
- Hospital training (AM/PM): Attendance will be recorded.
- Use only ONE signature.
- Absence >25% = Denial of participation.
Program Structure
The program consists of several components, including:
- Clinical in hospital: Represented in blue text.
- Lectures: Represented in green text.
- Skill Tutorials: Represented in blue text.
- Clinical Tutorials: Represented in blue text.
- Discussion of recorded Lecture: Represented in green text and positioned to the right of the table.
- Exams: Represented in red text.

Optional Activities
-
Mondays in hospital alternative:
- Operation Room (Prof. Mamoun, Dallah Hospital).
- 4 students each (16 students total).
-
Optional extra on Saturdays:
- Clinic (Prof. Mamoun, Dallah Hospital).
- 2 students each (8 students total).
List arranged through students’ group leader.
References
The following textbooks are recommended:
- Apley and Solomon’s Concise System of Orthopaedics and Trauma.
- Clinical Orthopedic Examination. Ronald McRae.
- Netter’s Orthopaedic Clinical Examination. An Evidence-Based Approach, 2e (Netter Clinical Science).

E-learning Management System
- All presentations & course material can be downloaded.
- All correspondence, Announcements, Changes, Interactions are managed through the system.
- All correspondence using the Al-Maarefa e-mail: 123456789@student.mcst.edu.sa.
Sincere Personal Advice
- Take notes in all sessions.
- Print material (Lectures/Tutorials) before the teaching session and add notes.
- Read from books, your notes, and slides.
- Read regularly according to teaching topics and cases seen in the hospital.
- Read before/after lecture/session; ideally, the same day.


Course Summary
- The Orthopedic course is interesting and logical.
- It is related to Anatomy and mechanics.
- Covers all types of diseases and injuries affecting bones and joints.
- Uses special descriptive terms.
Contact Information
Personal phone number: 0561993366.
