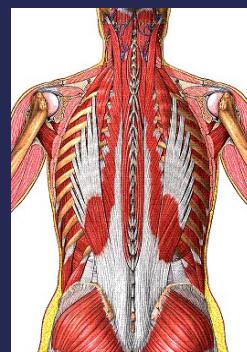
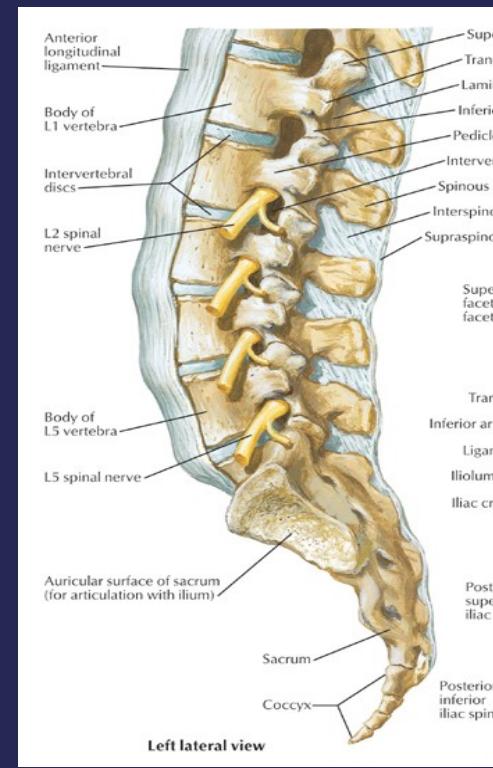
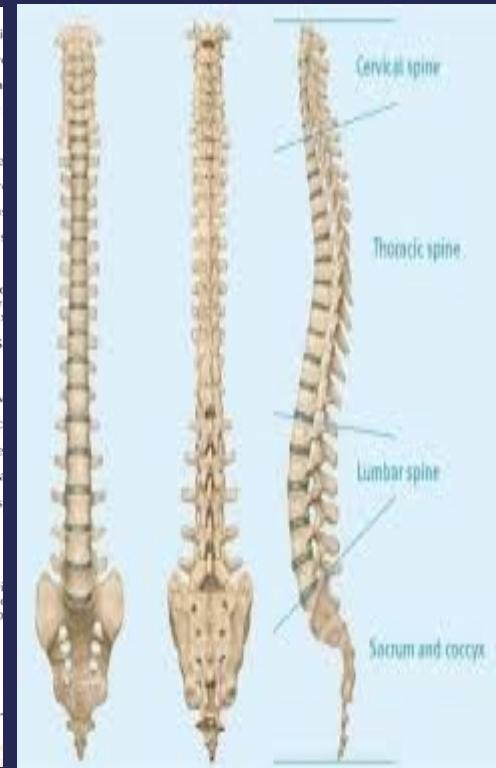
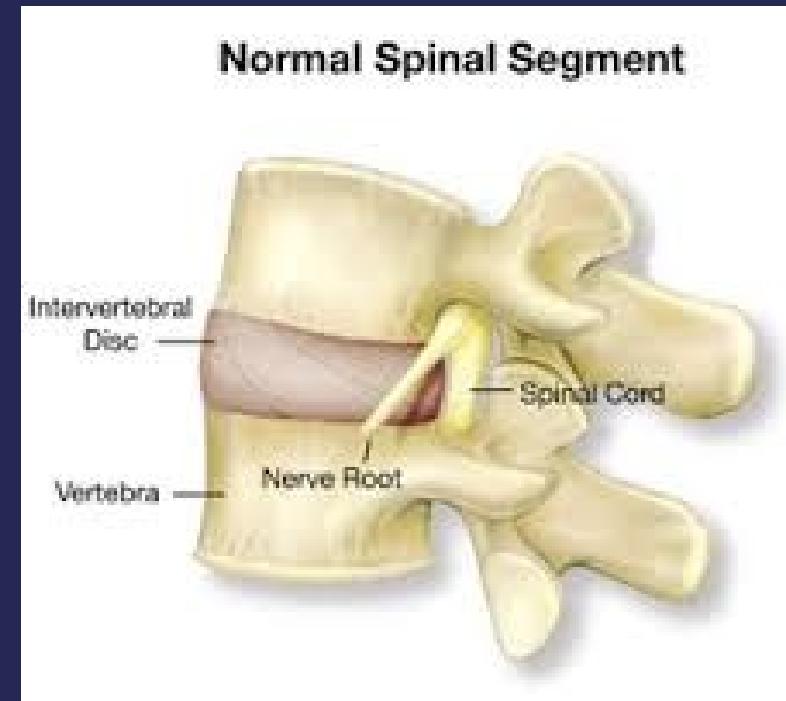
Anatomy of the Spine
Vertebral Column Structure
- Normally composed of 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar vertebrae and sacrum
- The spine has three major components:
- Spinal column (bone & disc)
- Neural elements (spinal cord & nerve roots)
- Supporting structures (muscles & ligaments)
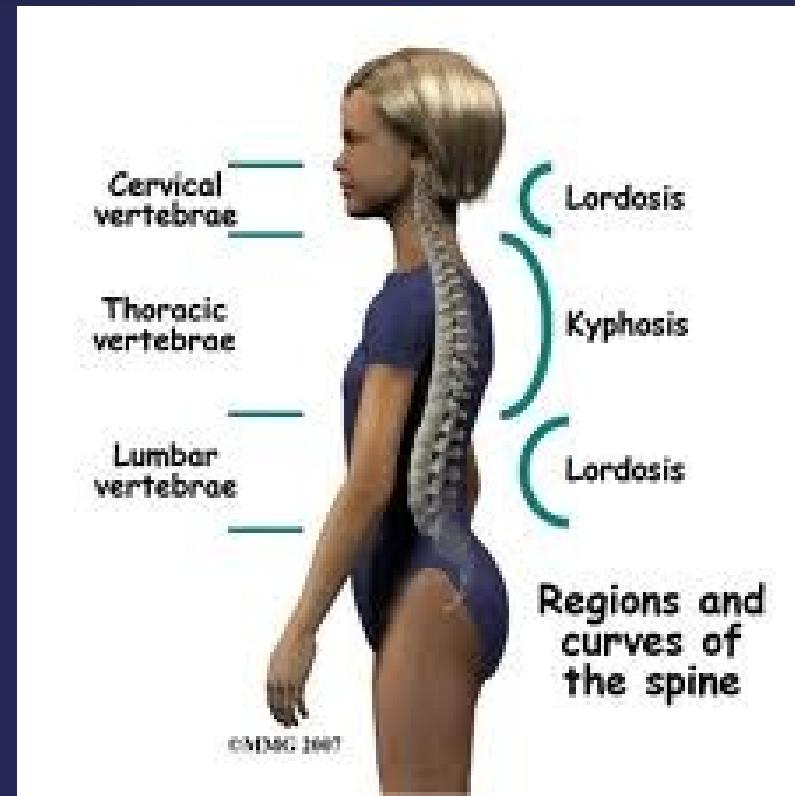
Natural Curves
The spine has four natural curves that help distribute mechanical stress during movement:
- Cervical & Lumbar (Lordotic)
- Thoracic & Sacral (Kyphotic)
Structural Unit
- A number of disorders can change the structural relationship of the spine
- Damage can affect vertebrae as well as surrounding tissues
Common Spinal Disorders
Categories of Disorders
Deformity
- Scoliosis
- Kyphosis
Infection
- Tuberculosis
- Pyogenic
Other Common Conditions
- Intervertebral disc lesion
- Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis
- Spine degeneration and spinal canal stenosis
Clinical Assessment
Symptoms
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Deformity
- Neurological symptoms (numbness, paresthesia & muscle weakness)
- Other symptoms (urethral discharge, sore eye, diarrhea)
Examination Protocol
Clinical examination is performed in three positions:
- Standing position
- Prone position
- Supine position
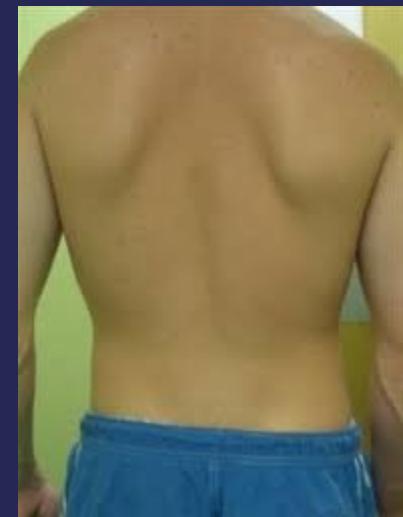
Standing Examination
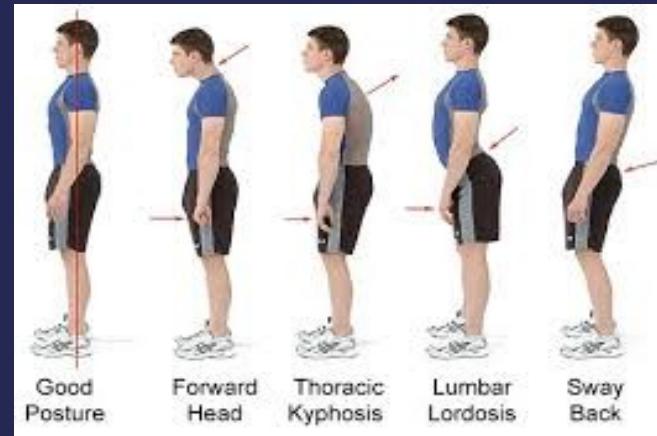
Look
- Posture
- Deformity:
- Scoliosis
- Kyphosis
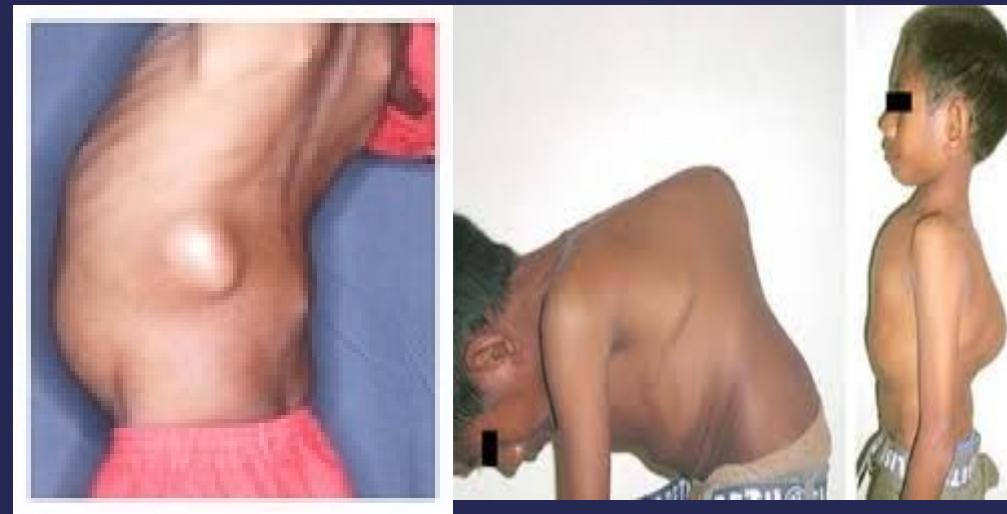
- Skin changes:
- Scar, sinus, redness
- Swelling:
- Abscess
Feel
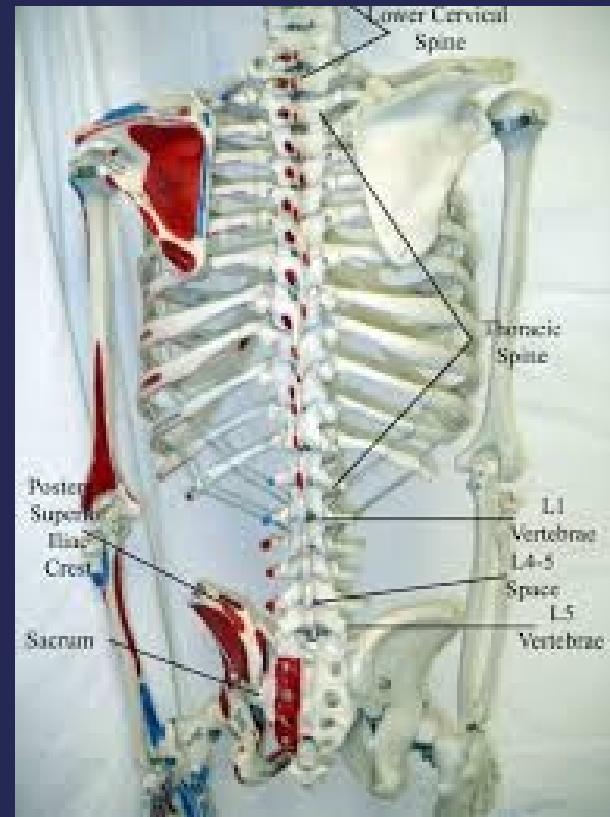
- Tenderness
- Temperature
- Bony prominences
- Step sign
Movement Assessment
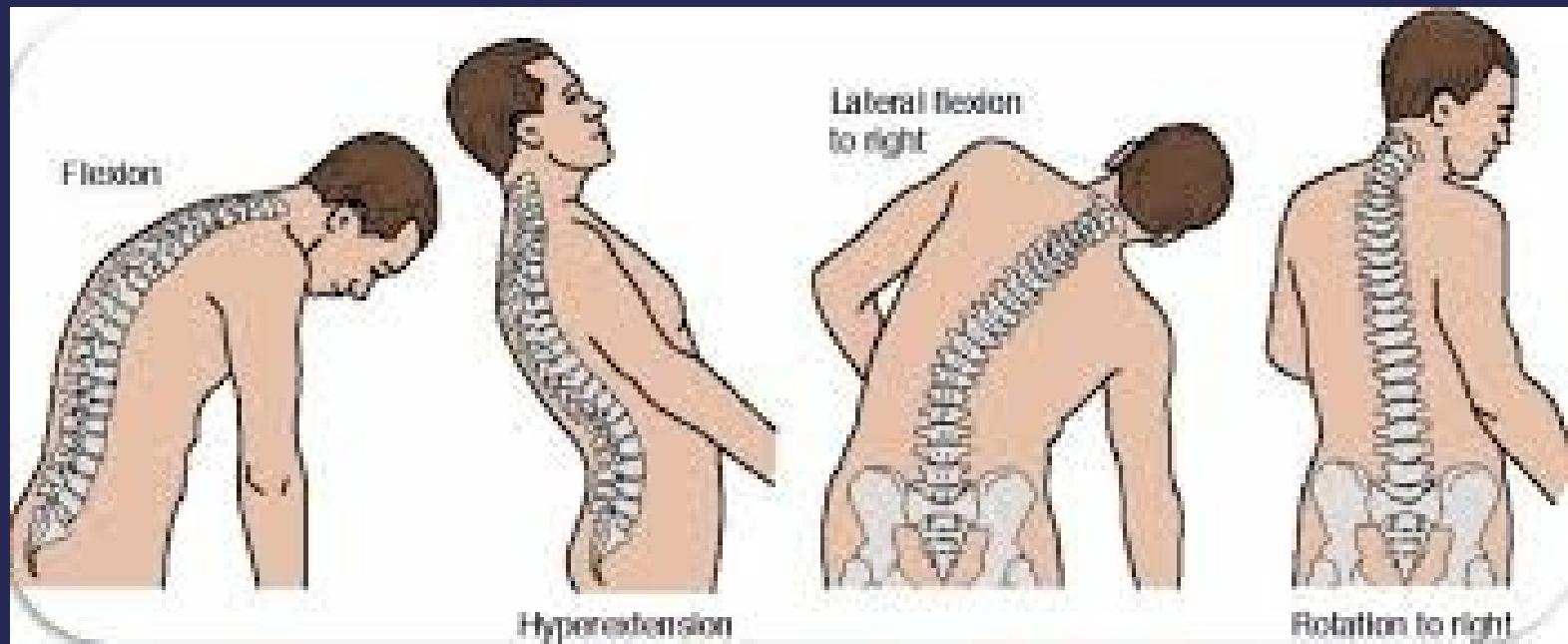
- Flexion
- Extension
- Lateral flexion
- Rotation
- Chest expansion
- Muscle power testing:
- Plantar flexor (tip toe walking)
- Dorsiflexor (heel walking)
Supine Examination
Look
- Wasting of quadriceps muscle
- Skin changes:
- Scar, sinus, redness
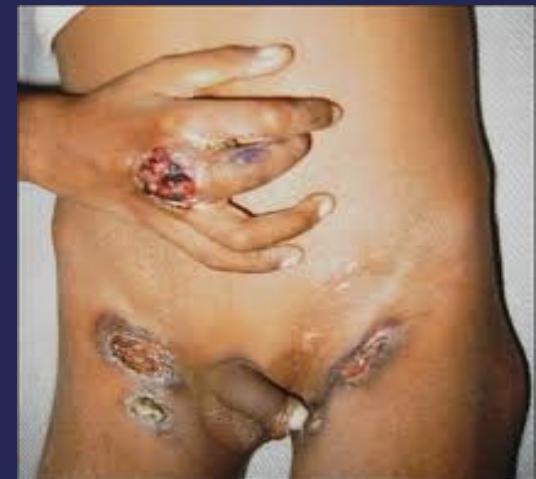
- Swelling:
- Abscess
Feel
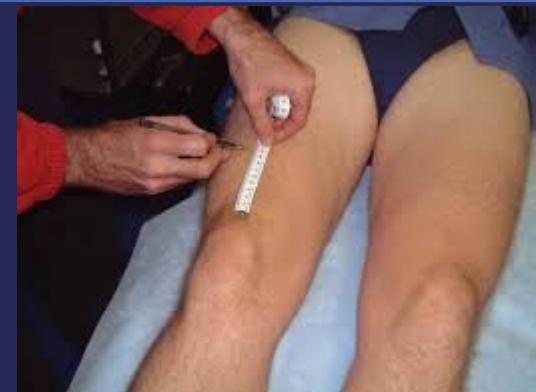
- Abdominal or groin abscess
- Pulses
Movement
- Flexion rotation of the hip to rule out hip problems
Special Tests
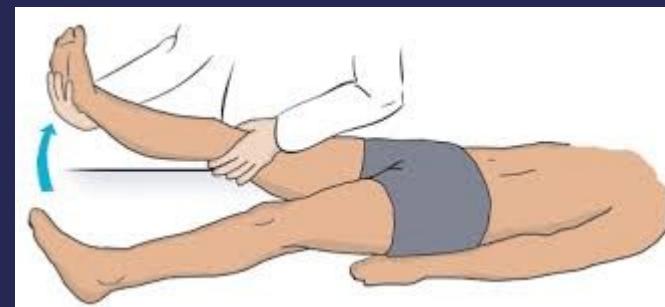
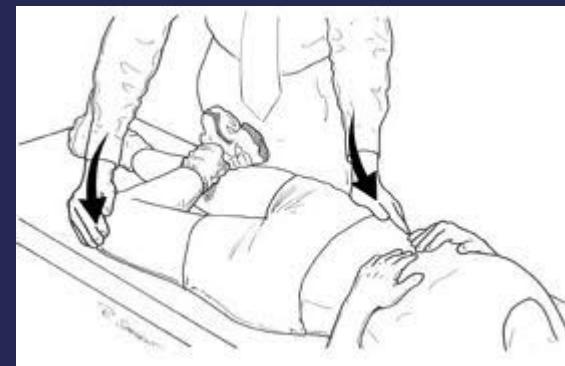
- Sciatic nerve stretch, straight leg raising (SLR) test
- Sacroiliac stress test
- Full neurological examination of lower limbs
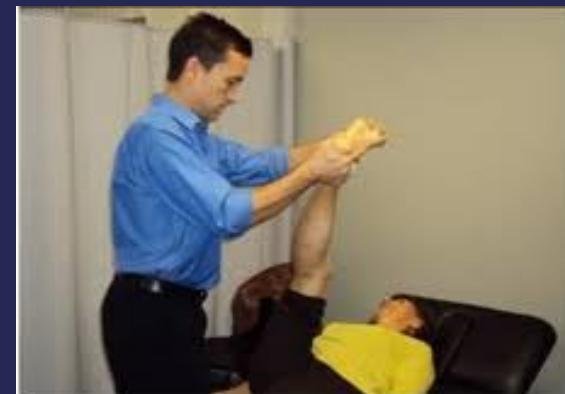
Note: Straight leg raise test with hip
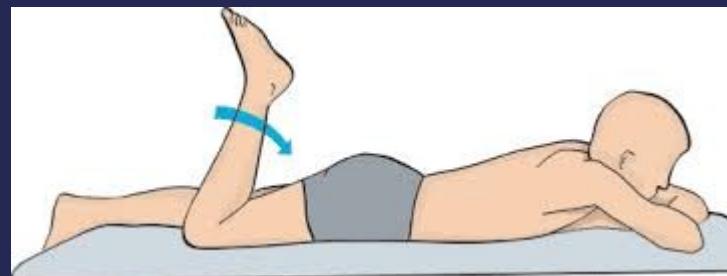
Prone Examination
Look
- Deformity
- Skin changes:
- Scar, sinus, redness
- Swelling:
- Abscess
Feel
- Tenderness
- Bony prominences
- Muscles
- Loin
- Popliteal pulse
Special Tests
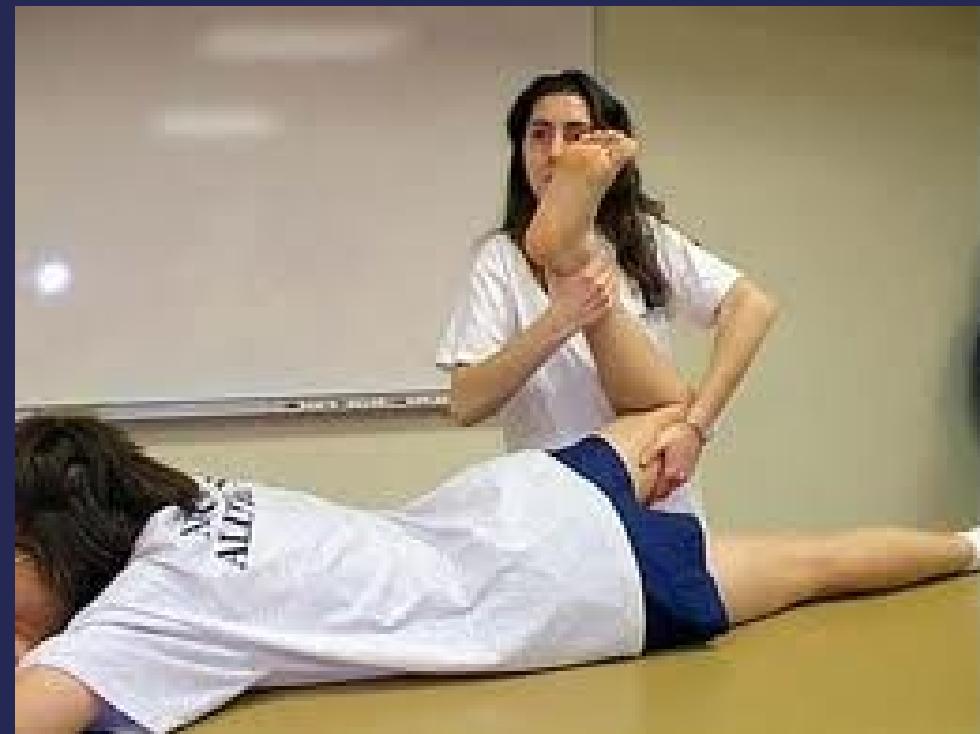
- Femoral nerve stretch test
- Sacroiliac stress test
- Hamstring & gluteus maximus muscle examination

Imaging for Spinal Disorders
X-Ray
- AP, LAT, OBLIQUE views
- Flexion-Extension LAT
- Deformity series (e.g., scoliosis series)
CT Scan
MRI
Note: Other investigations are requested according to clinical indication
