Cruciate Ligament Tears
General Characteristics:
- Require a strong force to cause a tear
- ACL tears are much more common than PCL tears
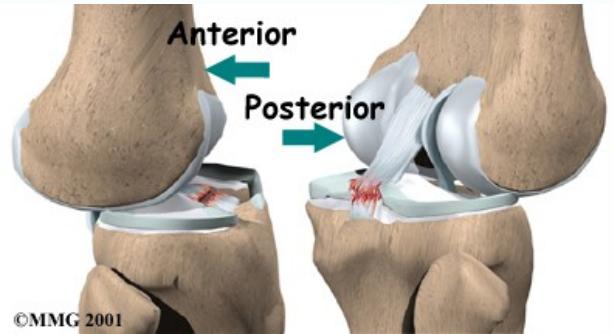
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tears
Clinical Presentation
Acute Phase:
- History of acute injury during sports
- Acute pain
- Mechanism of injury:
- Violent rotation with flexion
- Non-contact pivoting injury
- Hearing a “pop”
- Swelling – almost immediate due to haemarthrosis
Chronic Phase:
- History of giving way (sudden instability of knee)
- Repeated attacks of swelling and pain
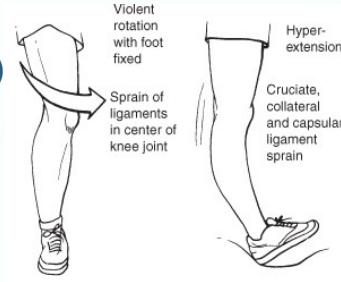
Mechanism of Injury
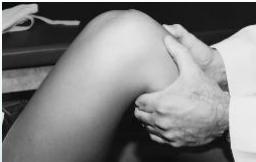
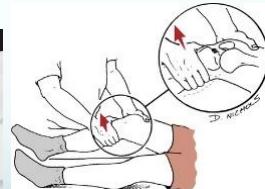
Clinical Signs and Tests
- Swelling: Initially haemarthrosis, later effusion
- Wasting of quadriceps muscle
- Special tests:
- Anterior drawer test
- Lachmann’s test
- Pivot shift test
Diagnostic Investigations
Plain X-ray
- Excludes other bony injuries
- Identifies tibial eminence fracture (signifies ACL bony avulsion)
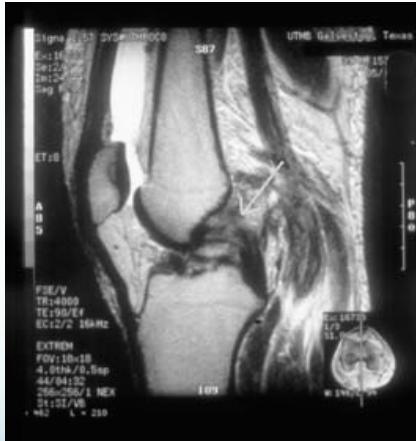
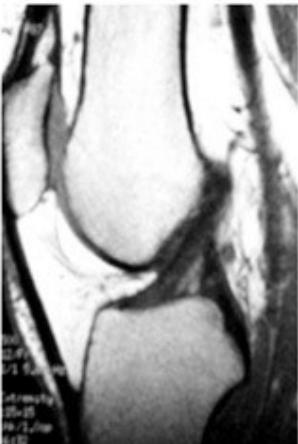
MRI (Gold Standard)
- Best imaging modality for ACL injuries
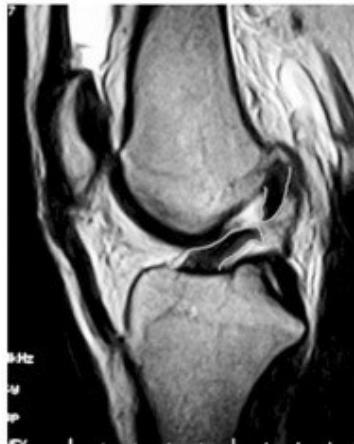
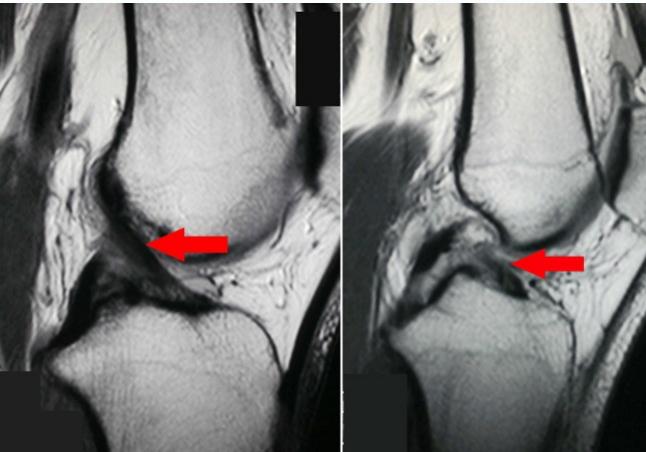
MRI Findings:
- Normal ACL
- Torn ACL
Treatment Options
Factors influencing treatment:
- Age
- Level of activity
- Instability
- Associated injuries
Common associated injuries:
- Meniscal tears (medial more common than lateral)
Conservative Treatment
Indications:
- Isolated tears with no instability
- Partial tears
- Less active patients (light sports only or sedentary)
Management:
- Quadriceps and Hamstring strengthening exercises Z
Surgical Reconstruction
Indications:
- Associated injuries
- Full thickness tears with instability
- Patients active in competitive sports
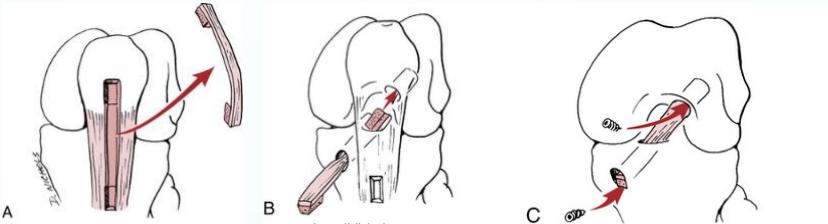
Surgical options:
- Bone-Patellar tendon-Bone (BPTB) graft
- Hamstring tendon graft
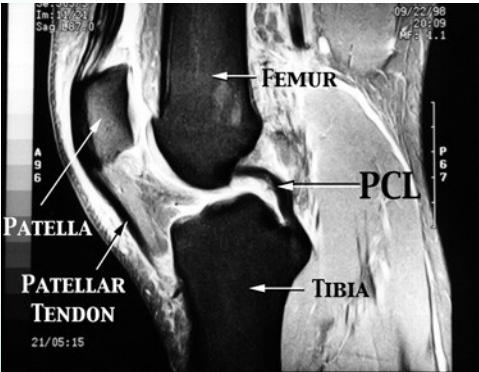
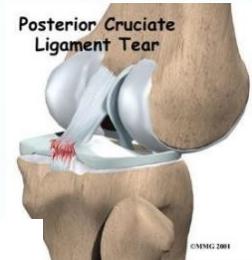
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Tears
Clinical Characteristics
- Less common than ACL tears
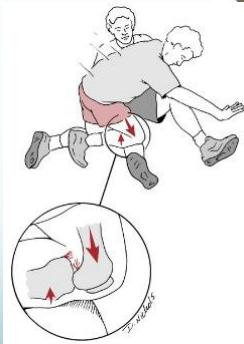
- Mechanism of injury:
- Direct blow to anterior tibia with knee flexed (Dashboard injury)
- Hyperextension or Hyperflexion
Diagnostic Investigations
MRI
- Best imaging modality for PCL injuries