The word “fungus” is a Latin word meaning “mushroom”
Fungi, unlike the plants, are heterotrophs (cannot make their own food), and their cell walls is made of chitin unlike the plants whose cell wall is composed of cellulose.
Fungi are found throughout the Earth including on land, in the water, in the air, and even in plants and animals.
There are more than 100,000 different identified species of fungi that vary widely in size from microscopically small to the largest organisms on Earth at several square miles large.
The most common fungi that you are likely to see or use everyday are mushrooms, molds and yeasts .
- In good immunity it’s FINE•
- BUT in poor immunity it’s bad.
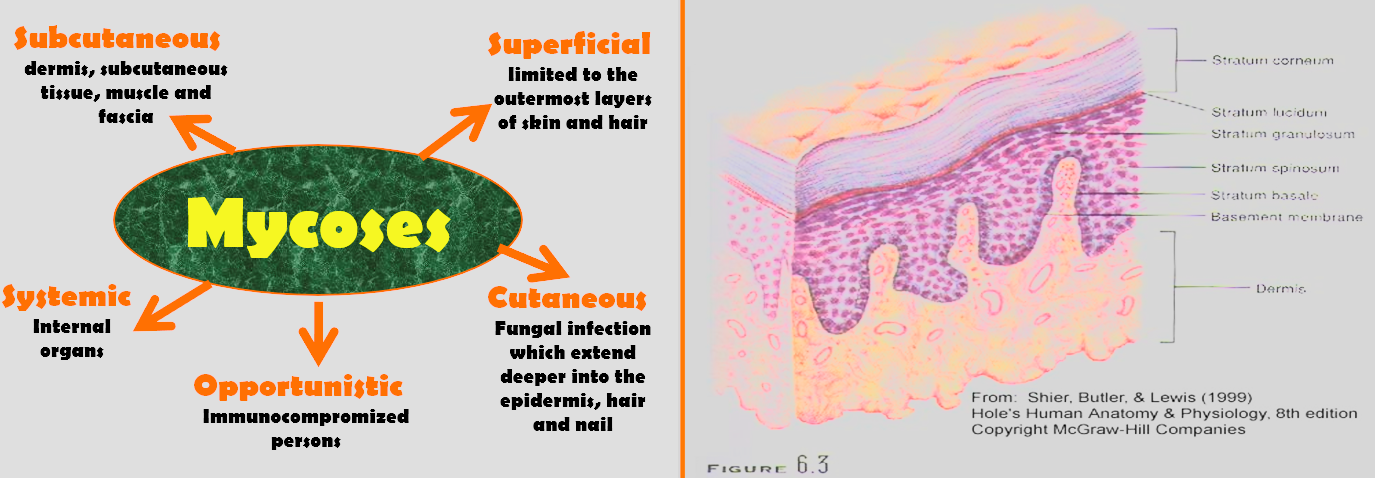
Mycoses Z
Infectious diseases caused by fungi are called mycoses, and they are often chronic in nature. Mycotic infections may be superficial and involve only the skin (cutaneous mycoses extending into the epidermis), ==while others may penetrate the skin, causing subcutaneous or systemic infections.
Below epidermis = is SEVERE and require drug taking.
#Y The incidence of fungal infections such as candidemia has been on the rise for the last few decades. This is attributed to: An increased number of patients with chronic immune suppression due to organ transplantation, Cancer chemotherapy, or Infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Most pathogenic fungi are opportunistic and require a compromised host or disrupted anatomical barrier in order to cause infection in humans. In a way, the increase of systemic fungal
infections can be seen as a marker of medicine’s advance, because improvements in transplantation, oncology, rheumatology, neonatology, geriatrics, and other fields have created more susceptible hosts for fungi.
Selective toxicity :
fungi have a rigid cell walls composed largely of chitin; unique for the fundus . In addition, the fungal cell membrane contains ergosterol rather than the cholesterol found in mammalian membranes. Also, other unique structures. These structural characteristics are useful in targeting chemotherapeutic agents against fungal infections.
Antifungal pharmacotherapy has several challenges that often make fungal infections more difficult to treat than bacterial infections. One is that pathogens can be more difficult to isolate on culture than bacterial organisms. This makes the prompt initiation of empiric therapy important when invasive fungal infections are suspected. Prophylaxis may also be used in highly susceptible populations to prevent fungal infections from developing.
Mold vs. Yeast. Y
Microscopic fungi exist in two basic forms: yeasts and molds.
- Yeasts are unicellular forms of fungi that reproduce by budding.
When they are left to grow in colonies, yeasts have a moist, shiny appearance.
-
Molds are multicellular fungi that consist of many branching hyphae and can reproduce either by translocation of existing hyphae to a new area, or through spore formation and spread (hence, one bad apple really does spoil a bunch).
-
In addition to these two basic forms, there are dimorphic fungi that can exist in either form. These fungi are often mold-like at room temperature but yeast-like at body temperature.
Fungal Categories
| Category | Fungi Types |
|---|---|
| Yeasts | Candida, Cryptococcus Z |
| Dimorphic Fungi | Histoplasma, Blastomyces, |
| Molds | Aspergillus, |
Types of Fungal Pathogens (loss of immunity) Z
| Category | Pathogen |
|---|---|
| Opportunistic Pathogens Systemic Infections | - Candida albicans (Most common) - Cryptococcus neoformans - Aspergillus - Pneumocystis carinii (Mentioned as fungus/Bacteria) From other organisms from outside - Blastomyces dermatitidis - Histoplasma capsulatum |
| Superficial Infections | - Dermatophytes affecting (skin ,hair And nails= Onychomycosis (nail fungus) - Candida albicans may be :vulvovaginal and oral (common in children & in intercourse transmission) |
Bacteria vs Fungi Comparision Z
| Characteristic | Bacteria | Fungi |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | no | yes |
| Ribosomes | 70S | 80S |
| Cell Wall | Peptidoglycan | Chitin |
| Membrane | No sterols | Ergosterol |