Drugs
linezolid, tedizolid
Mechanism of action:
Oxazolidinones are protein synthesis inhibitors that bind to the 50S ribosomal subunit, blocking the formation of a stable 70S initiation complex and preventing translation. This binding site is distinct from other protein synthesis inhibitors.
ANTIBACTERIAL SPECTRUM
The antibacterial action of linezolid is directed primarily against gram positive organisms, such as staphylococci, streptococci, and enterococci, as well as Corynebacterium species It is also moderately active against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and may be used against drug- resistant strains. However, its main clinical use is against drug-resistant gram positive organisms. Like other agents that interfere with bacterial protein synthesis, linezolid is bacteriostatic. However, it is bactericidal against streptococci.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Linezolid is completely absorbed after oral administration. An IV preparation is also available. The drug is widely distributed throughout the body. Linezolid is metabolized via oxidation to two inactive metabolites. The drug is excreted both by renal and non renal routes. No dose adjustments are required for renal or hepatic dysfunction.
Tedizolid is eliminated primarily by the liver and may not be sufficiently concentrated in the urine to treat UTIs
ADVERSE EFFECTS
-
The most common adverse effects are gastrointestinal upset, nausea, diarrhea, headache, and rash.
-
Thrombocytopenia has been reported, mainly in patients taking the drug for longer than 10 days.
-
Linezolid possesses non-selective monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity and may lead to serotonin syndrome if given concomitantly with: large quantities of tyramine- containing foods, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). The condition is reversible when the drug is discontinued.
-
Irreversible peripheral neuropathies and optic neuritis (causing blindness) have been associated with greater than 28 days of use, limiting utility for extended-duration treatments. This may occur after even more prolonged therapy (months) because of toxicity to mitochondria.
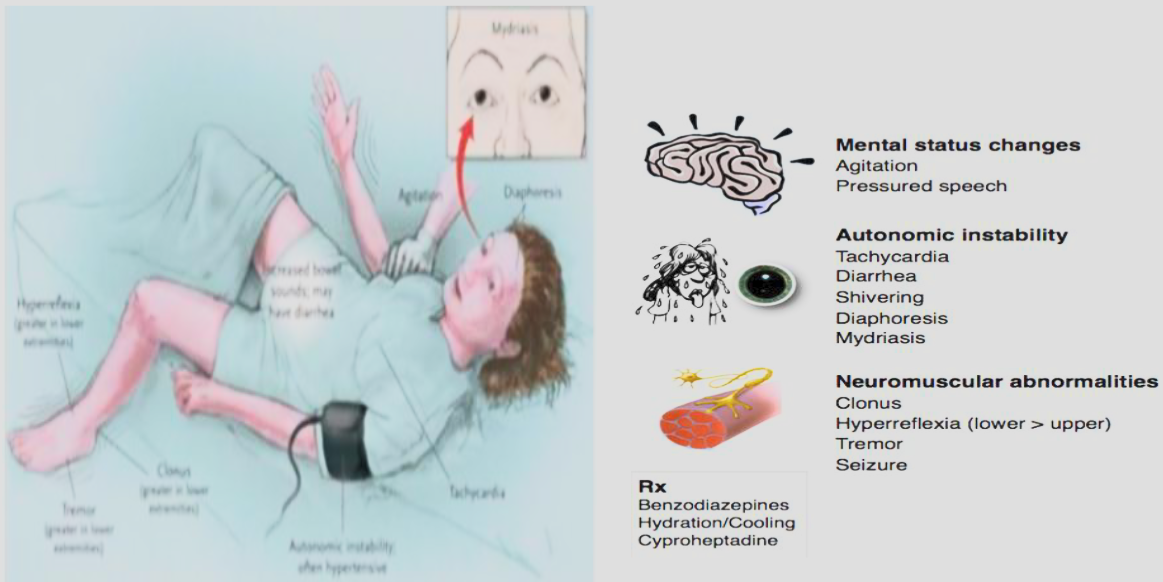
SEROTONIN SYNDROME It is a cluster of autonomic, motor & mental status changes resulting from excess serotonin [5(HT)]