Case
Pt had a wound after some days the wound became reddish, contain pus , and the pt had hypotension ….
Diagnosis: septic shock because of wound infection.
Case
Result of arterial blood gas from a patient with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus is shown
PH: 7.29 ↓ acidosis (7.35-7.45)
PCO2: 34 ↓ matched (35-45 mm Hg)
HCO3: 20 ↓ (22-30 meq/L)
Q1: Mention the acid-base abnormalities? Metabolic acidosis
Q2: Mention two relevant additional laboratory tests? Blood glucose, Ketone in blood and urine
Case
CBC result of diabetic patient his PH WAS LOW AND HCO WAS LOW AND PaCO WAS LOW I couldn’t REMEMBER the number but it was all low :
What is your diagnosis? • Metabolic acidosis
more tests will order Ketone level in urine, Blood glucose
Case
Gave you a CBC result of a patient his hemoglobin is 7
Q1- How many units of packed RBC you would give to this patient so his hemoglobin reach 10? 3 unit (1 packed RBC = 1gm of hemoglobin)
Q2- mention 4 of the possible complications of this blood transfusion?
- Hypothermia,
- Hemolytic reaction,
- Anaphylactic shock,
- Hypocalcemia,
- Infection,
- Iron overload
Case
Result from a patient who presented with episodes of melena. WBC: 8 X 10³/ mm³ (4-11 X 10³/ mm³) Haemoglobin: 8.1 g/dl (13-18 g/dl) Platelets: 170 X 10⁹/L (150-350 X 10⁹/L)
Q1: How many units of blood is needed to raise hemoglobin to ≥10 g/dl? 2 packs
Q2: Mention FOUR symptoms of transfusion reaction. Fever, chills, hypotension, chest pain
Instrument
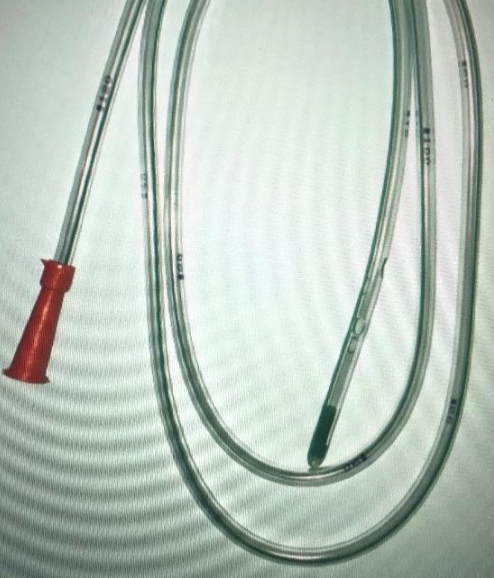
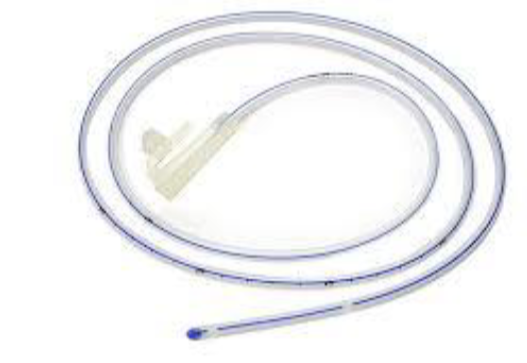 Instrument
Nasogastric tube
Instrument
Nasogastric tube
therapeutic indications feeding, gastric decompression, medications
Diagnostic indications
- Evaluation of upper gastrointestinal
- Administration of radiographic contrast to the GI tract
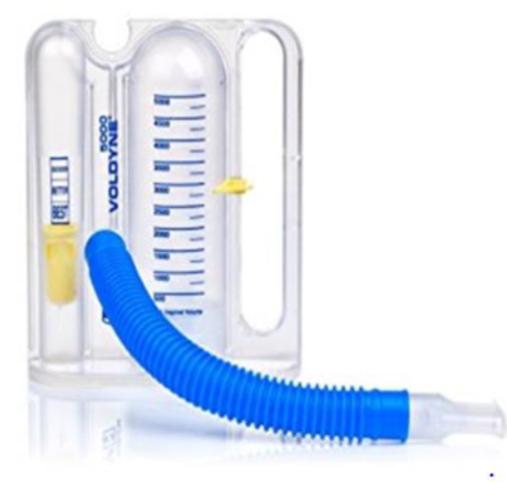 Name tool
Spirometer
Name tool
Spirometer
Mention two clinical use Postoperative to help get rid of all secretions and expand the lungs, and for asthmatic patients to monitor their condition (can be used at home)
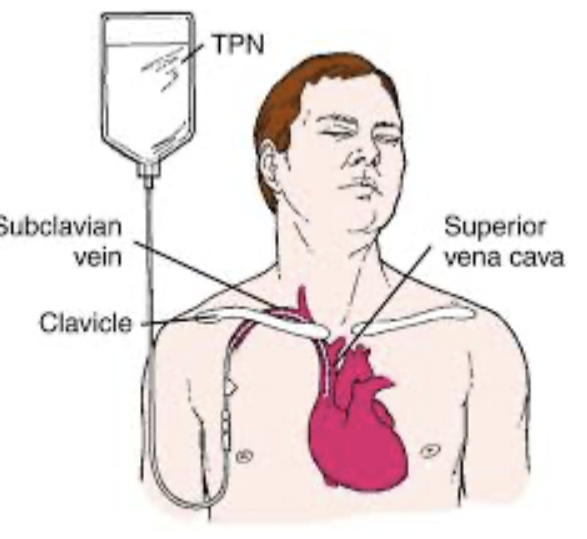
TPN
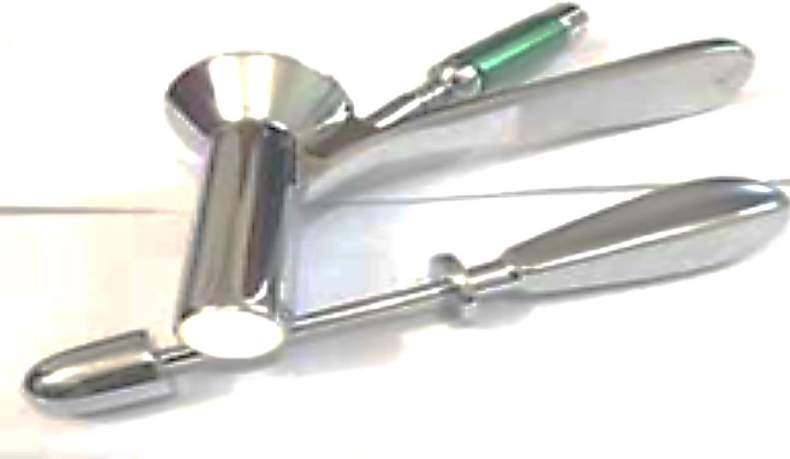 Q1: What is this tool?
Q1: What is this tool?
- Proctoscope
Q2: (A) Mention TWO of its diagnostic uses.
- Examine anorectal area to diagnose polyp,
- to take biopsy.
(B) Mention TWO of its Therapeutic uses.
- Ligation of polyp,
- and banding of hemorrhoids.
 Instrument
Folley’s (urinary) catheter
Instrument
Folley’s (urinary) catheter
three common indications
- Monitoring in put and urine output
- urine culture
Therapeutic
- Intraoperative to maintain patients urination, and to relieve urinary obstruction
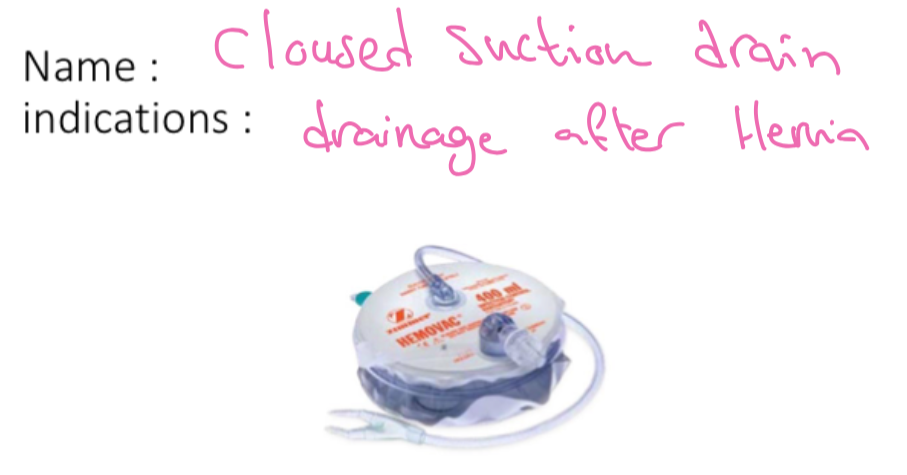
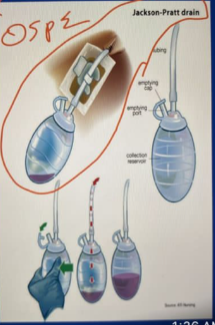 jackson pratt drain - active drain
jackson pratt drain - active drain
Surgical drains
Passive drain
- gauze drain
- penrose drain
- cigarette drain
active drain
- sump drain
- jackson pratt drain
- radivac drain
others…
Neck swelling Surgical site infection Dilation in small bowel
1. Air under diaphragm:
- Observation laprotomy
- exploratory laprotomy
2. Non midline fissure: sexual transmission disease (infection, HIV etc..)
3. Primary survey what to do? No need for details history
4.the cause of pseudocyst is? Pancreatitis Collection of pancreatic secretion + lining (Pancreatitis) Epithelial layer
5. Majority of spleen treatment? Non surgical
6. Percussion hyperresonant? Tension pneumothorax
7. Rt abdominal swelling + cystic mass in ultrasound + high eosinophilic: Hydated disease
8. What is the first thing to do when Pt has sever chest injury? Decommission of pneumothorax or incubation