Dr. M. Almadani
How to solve it?
- HISTORY
- CLINICAL EXAMINATION
- CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS
- INVESTIGATIONS
- FINAL DIAGNOSIS
- TREATMENT
Perianal Hx & Exam
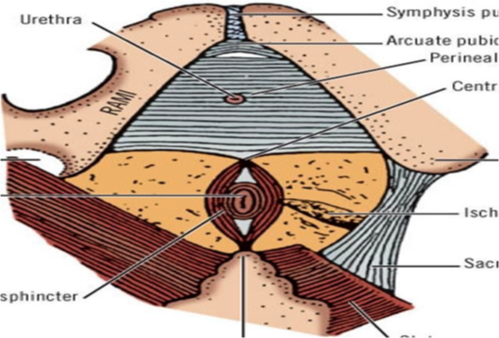
Hx - Presenting History
Pain:
- Perianal abscess, fissure in ano, anal fistula, thrombosed piles
Bloody discharge:
- Piles, fissure, fistulae, tumours (polyp, carcinoma anus/rectum)
Purulent discharge:
- Perianal abscess, fissure in ano, anal fistula
Mass or swelling:
- Abscess, piles, neoplasms
Exam
Before starting clinical examination:
- Analyze patient’s history.
- Probable diagnostic possibilities
- Think of the common diseases
- Determine physical findings consistent with these entities.
- Permission
- Privacy
- Presence of a nurse
- Precautions (hand hygiene)
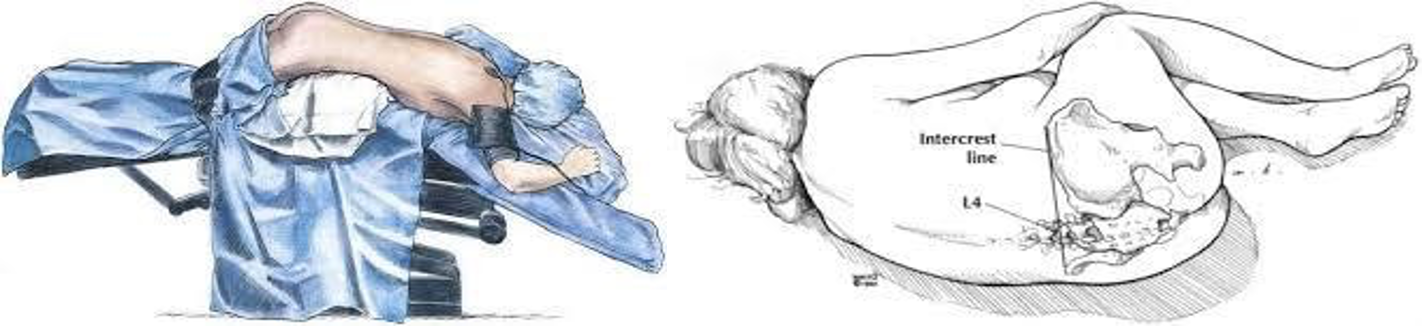
Position:
- Left lateral decubitus
- Hips flexed to 90º and knees flexed to less than 90°.
- Lift uppermost buttock to expose the area
- Jack-knife
- Lithotomy
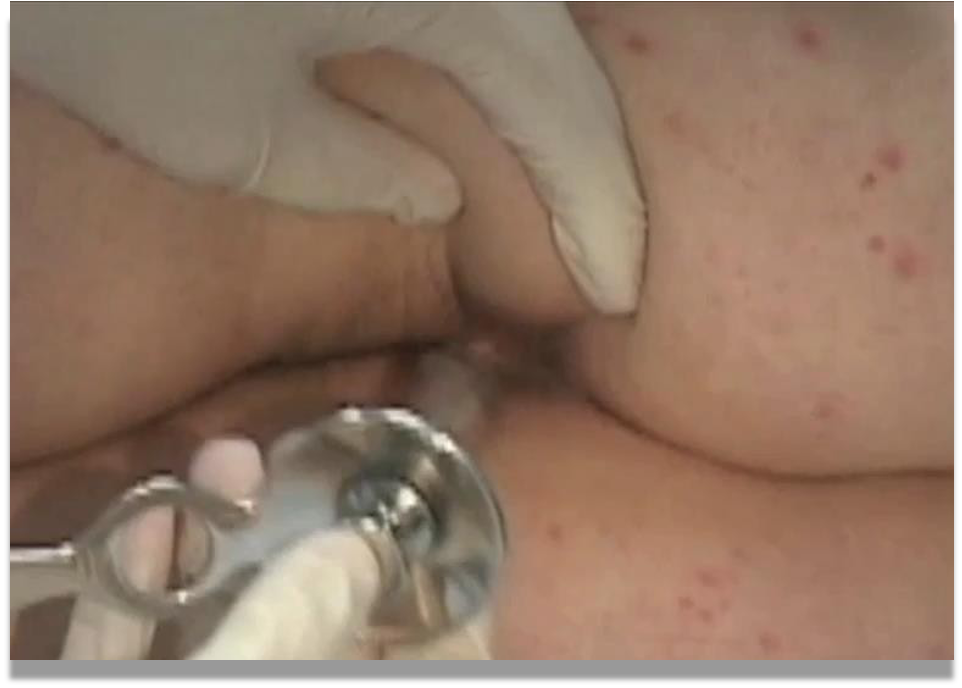
Inspection:
wear gloves lubricate, expose ano to check any abnormality
- Scar of previous surgery
- Sinus - one opening blind track
- Fistula - track connecting two epithelial surfaces
- Fecal soiling, blood/mucous discharge
- Mass protruding from anus
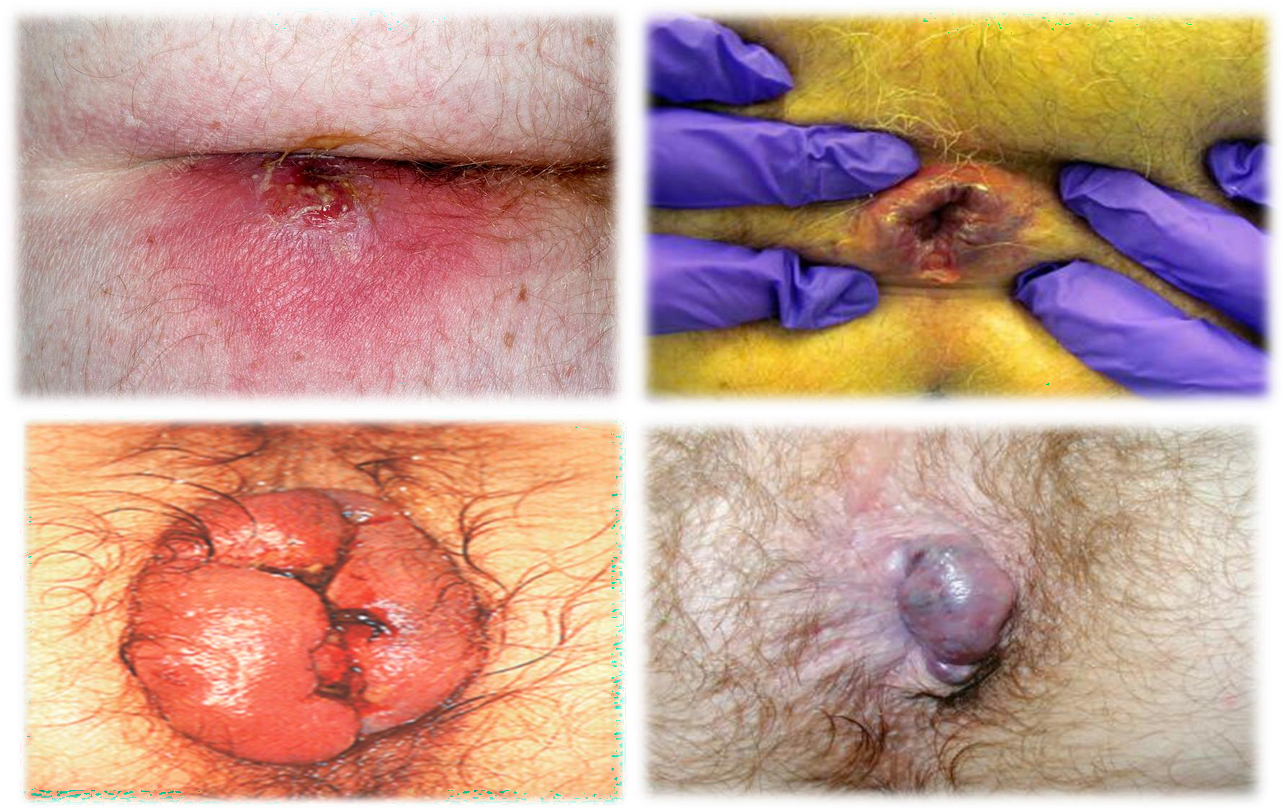 1- abscess 2- fissure - 3- thromb? 4- external hemmorhoids
1- abscess 2- fissure - 3- thromb? 4- external hemmorhoids
Palpation:
tenderness, discharge, mass
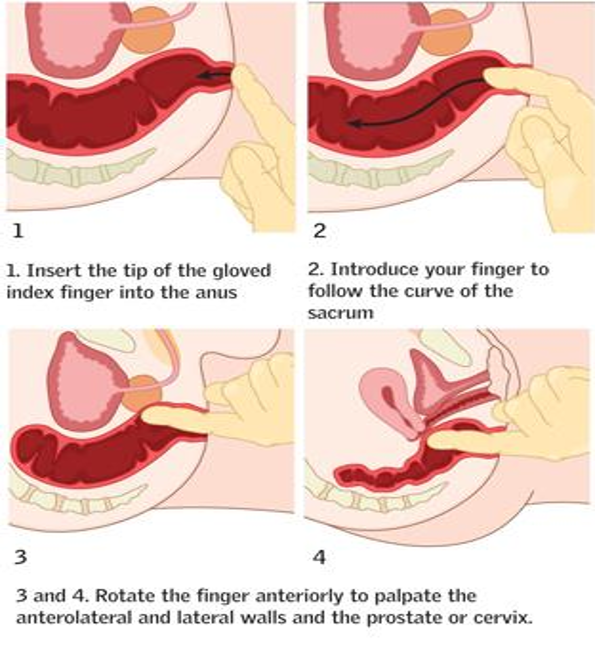
Rectal examination:
Tone, tenderness, mass, prostate, blood, stool
- Indications
- Technique:
- Inspection
- Tone (Rest/Squeeze)
- Tenderness, mass
- Prostate (Males)
- Cervix (females)
- Content (blood, stool)
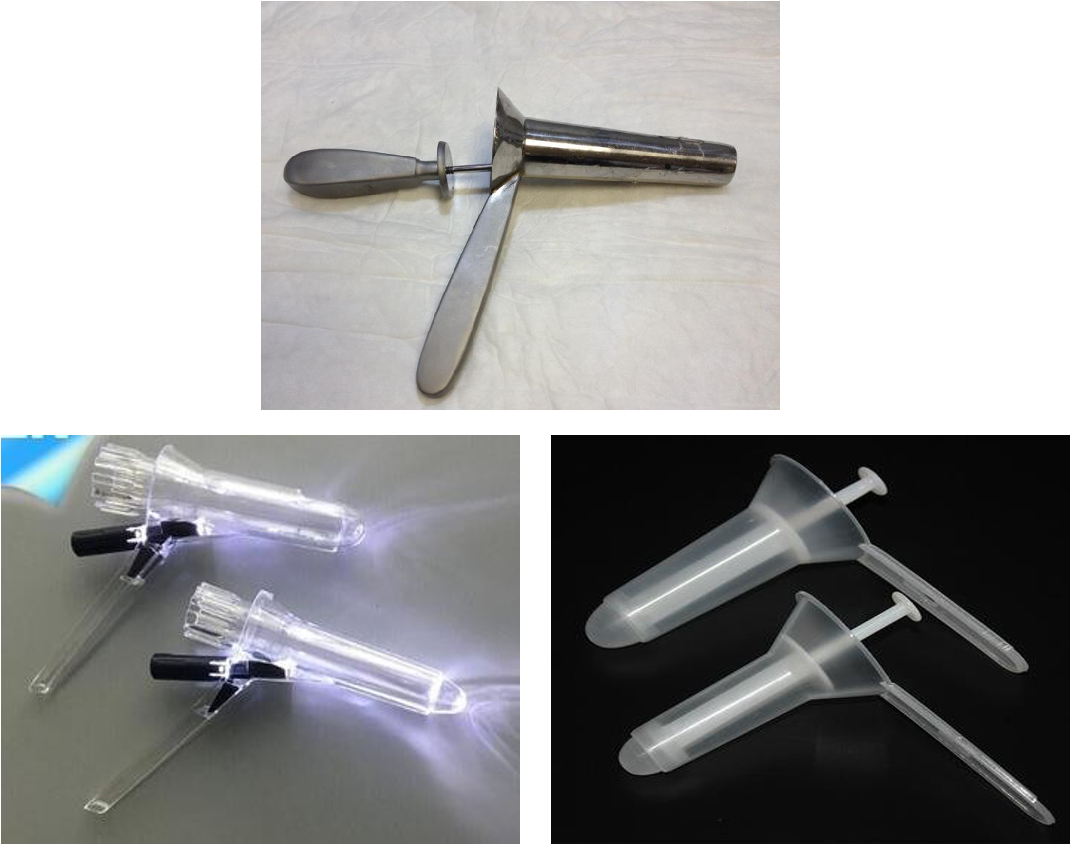
- Anoscopy (hold like gun push while holding tool in one hand)
- tell patient that he will not feel pain but discomfort
- lubricate anoscopy
- take it out slowly while checking (hemorrhoids, polyps (biopsy), ulcers)
- never push it forward after removal
- inspect anoscopy afterwards
CC Video