Lichen Planus

- Is a non infectious immunological mediated skin disorder.
- It is a disorder in which lymphocytes attack the epidermis.
- It can be associated with autoimmune disorders such alopecia areata, ulcerative colitis.
Aetiology.
- It is unknown.
- Drugs can cause it-streptomycin,chloroquine,methyldopa, phenothiazine.
- It has also been linked to ,bone marrow transplant,hepatitis B infection,exposure to colour film in colour film developers.
Clinical Features
-
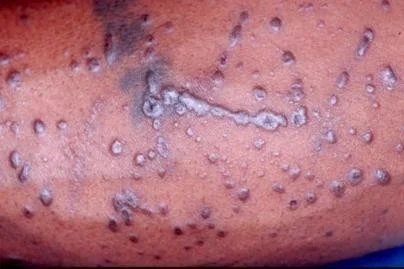
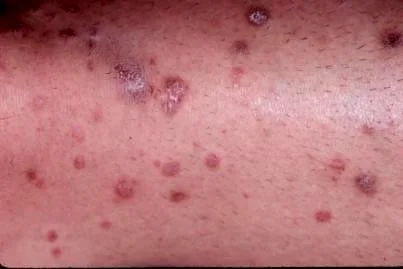
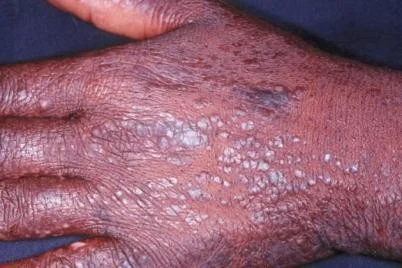
Typical itchy papules, demarcated by skin lines on the extremities especially the volar aspects.
-
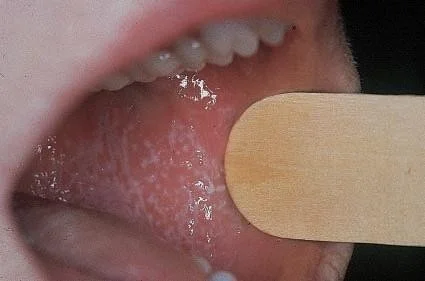
White streaky pattern on the surface of the papules (wickham’s striae) white network buccal mucosa, top surface of papule; characteristic of Lichen Planus - itchy papule.
-
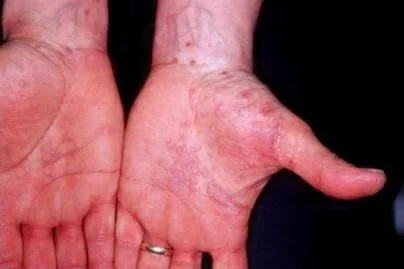
It occurs on joint flexures especially the wrists (diff scabies contactdermatitis) , genitals, inner thighs.
-
Koebner’s phenomenon is also present.
-
Neighbouring papules may join together to form plaques that resembles lichen growing on trees.
-
White lacy plaques in the mouth.
Variants
- Annular -area of central clearing.
- Atrophy-in mucous membrane.
- Bullous
- Follicular
- Hypertrophic -around the ankles.
- Ulcerative-on soles and mucous membrane.
Prognosis
-
It is a self - limiting disorder in which individual lesions lasts for months and the eruption as a whole tends to last for about a year.
-
As lesions resolve, they become flatter, darker and leave discrete brown macules.
Complications
- Nail and hair loss may be permanent.
- Ulcerative form in the mouth may lead to squamous cell carcinoma. Z
- Ulceration over bony prominences may be disabling.
Differential Diagnosis
- Lichenoid drug reactions- antimalaria, NSAIDS, b-blockers.
- Discoid lupus erythematous- wickhams’s striae or oral lesions are absent.
- Oral candidiasis.
- Gold and heavy metals reaction.
Investigations.
-
Diagnosis is usually obvious clinically, but a biopsy can confirm the diagnosis if necessary.
-
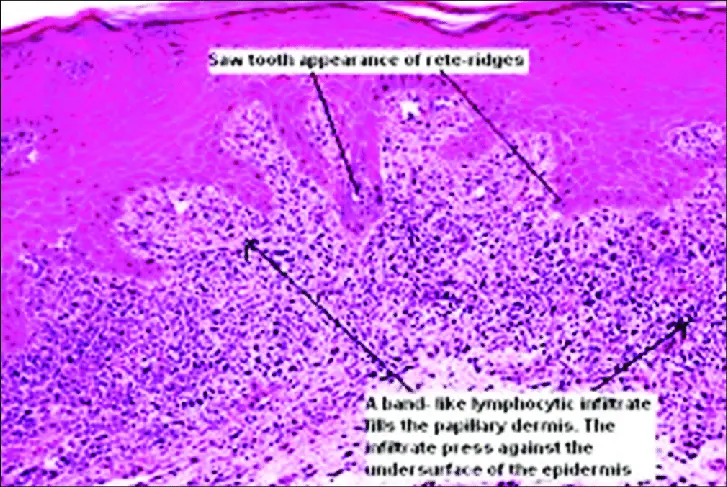
Histology→ hyperkeratosis, focal hypergranulosis, thickening of the epidermis (saw toothed appearance) Z ,separation between dermis and epidermis.
Treatment
- Stop offending agent.
- Potent topical corticosteroids-to relieve the symptoms & flatten the plaques.
- UV radiation-reduce pruritus , help clear the lesions.
- Systemic corticosteroids-prednisolone .
- Anti-histamines → for sedation