ER
- Definition: serum potassium < 3.5 mEq/L
- Causes:
- decreased intake of potassium;
- Potassium loss caused by
- renal losses (diuretics, RTA);
- GI losses (vomiting, diarrhea);
- hyperaldosteronism;
- transcellular shifts (alkalosis, beta agonists, insulin); hypokalemic periodic paralysis (congenital disease).
Clinical features
- Neurologic: lethargy, paresthesia
- Musculoskeletal: rhabdomyolysis, muscle weakness, cramps
- Cardiovascular: palpitations, dysrhythmias
- GI: nausea, vomiting, abdominal distention
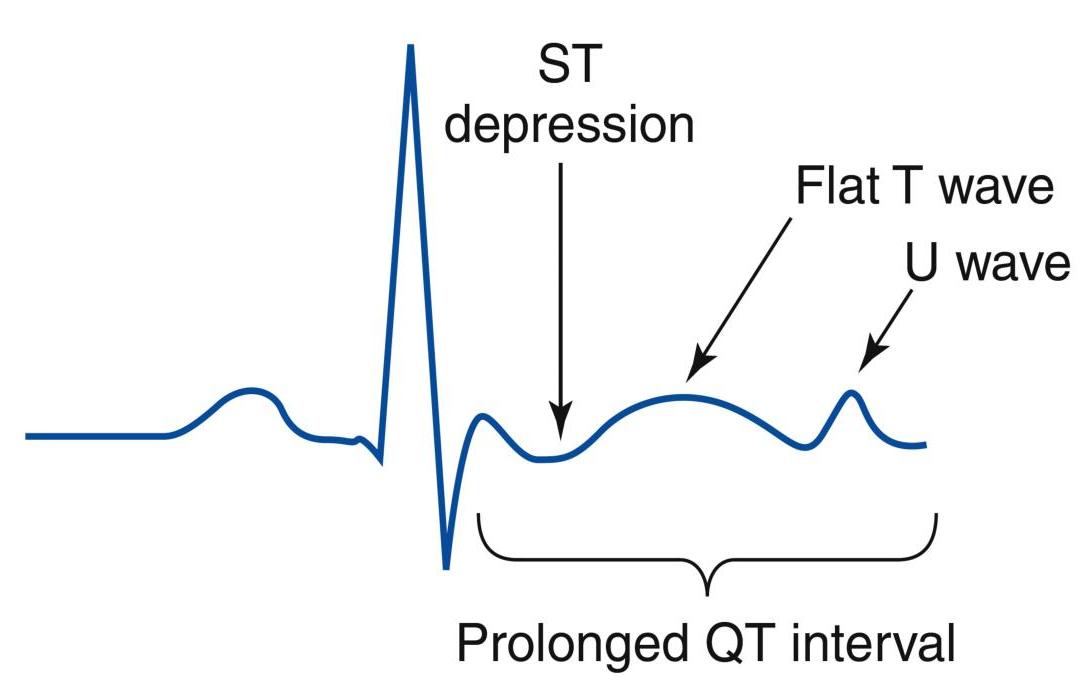
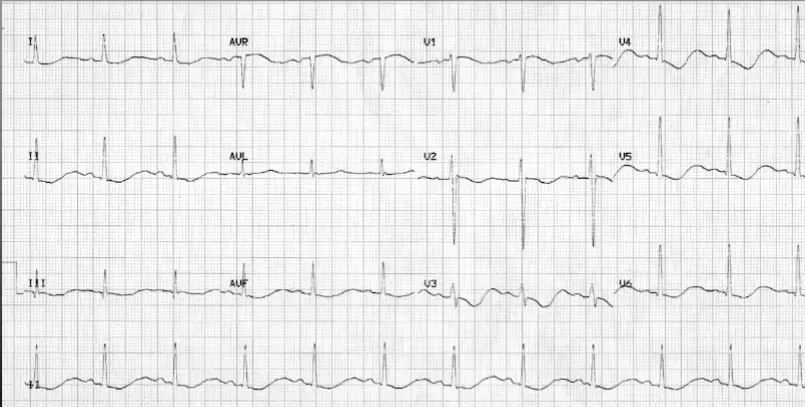
ECG changes in hypokalemia
Other ECG changes:
- first-/second-degree heart block,
- atrial fibrillation,
- ventricular fibrillation,
- Torsades de pointes,
- asystole
Treatment
| Therapy | Dose | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Oral potassium chloride | 40 to 60 mEq orally every 2 to 4 hours | For stable patients with mild hypokalemia (>3.0 mEq/L) who are able to tolerate oral intake |
| IV potassium chloride in 500 mL of a saline solution | 40 mEq Infusion rate: 10 to 20 mEq/hr | Indications of IV potassium replacement: - Severe hypokalemia (<2.5 mEq/L) - Symptomatic moderate hypokalemia (2.5 to 3 mEq/L) - Cardiac arrhythmias or prolonged QTc - When oral replacement is not tolerated or not feasible - Monitor the patient’s rhythm when treating with IV K+ - Magnesium replacement should usually accompany potassium repletion. |
Pediatrics
Definition
- Level below 3.4 mmol/L
Causes
- Malnutrition (severe)
- Increased gastrointestinal losses (e.g., vomiting, diarrhea)
- Increased skin losses (e.g., excessive sweating, burns)
- Increased renal losses (e.g., Fanconi syndrome, RTA, diuretic therapy)
- Alkalosis (metabolic and respiratory)
- Excess insulin (increases cellular uptake of potassium)
- Medications
- Diuretics (except for potassium-sparing ones)
- Insulin
- Albuterol
Presentation
Neuromuscular Signs
- Weakness, paralysis, tetany, ileus, ureteral aperistalsis, lethargy, confusion, autonomically mediated hypotension, and rhabdomyolysis.
Cardiovascular Signs
- Elevated blood pressure, bradyarrhythmia, and tachyarrhythmia.
Renal and Metabolic Abnormalities
- Hypokalemic nephropathy, and impaired insulin secretion (glucose intolerance).
Lab Tests
- Chemistry for other electrolytes
- Glucose level
- Urinalysis, urine potassium, and creatinine
- ECG
Treatment of Hypokalemia
Orally
- Bananas, tomatoes, and most other fruits, prune juice, and orange juice.
- Oral supplements: 2 mmol/kg/day in divided doses.
Severe or Symptomatic Hypokalemia
- IV potassium, dose not to exceed 0.3 to 0.5 mEq/kg/hour.
Very Important: Ensure intact urine output prior to administration of intravenous potassium. Close cardiac monitoring is critical. Z
ECG Findings
- T wave inversion
- ST depression
- Prominent U wave
