Miscarriage
By dr Mona Ahmed

LEARNING OBJECTIVES
- Understand the social and emotional context of early pregnancy loss.
- Understand why a high suspicion of pregnancy is needed in all women of reproductive age with symptoms.
- Obtain a detailed knowledge of the clinical presentation and management of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy.
- Obtain an awareness of less common early pregnancy conditions, including recurrent miscarriage, gestational trophoblastic disease and hyperemesis gravidarum.





Miscarriage
is a pregnancy that ends spontaneously before 24 weeks’ gestation or (or before viability).
- What is viability? More than 24 weeks of gestation or more than 500 gms.
Incidence:
15 - 20% of pregnancies.
Classification:
- Spontaneous miscarriage: occurs without medical or mechanical.
- induced abortion
![]()
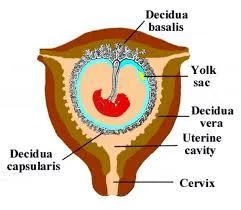
Pathophysiology
Haemorrhage into the decidua basalis lead to:
A. Necrotic changes in the tissue adjacent to the bleeding. B. Detachment of the conceptus. C. The above will stimulate uterine contractions resulting In expulsion.
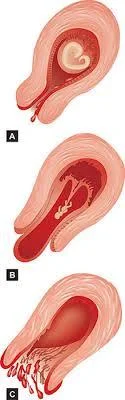
RISK FACTOR
- Maternal age - more than 35years.
- Increased gravidity.
- Previous history of miscarriage.
- Multiple pregnancy
Causes of miscarriage
Fetal causes & maternal causes
Fetal causes:
- Chromosomal e.g. Trisomy.
- Structural e.g. Neural tube defect.
- Genetic e.g. X- Linked diseases
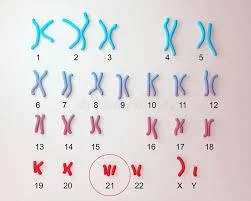
Maternal causes:
Immunological:
- Autoimmune diseases :APL.
uterine abnormality:
- septate uterus & cervical incompetence. Z
Endocrine :
Infections (maternal/fetal):
- as TORCH infections.
- listeria
Environmental toxins:
- alcohol.
- Smoking.
- drug abuse.
- ionizing radiation.

Clinical presentation
- The most common sign of miscarriage is vaginal bleeding.
- Abdominal pain.
- Hypovolemic shock.
- Expulsion of products of conception.
- A symptomatic.
- Each type has its own symptoms
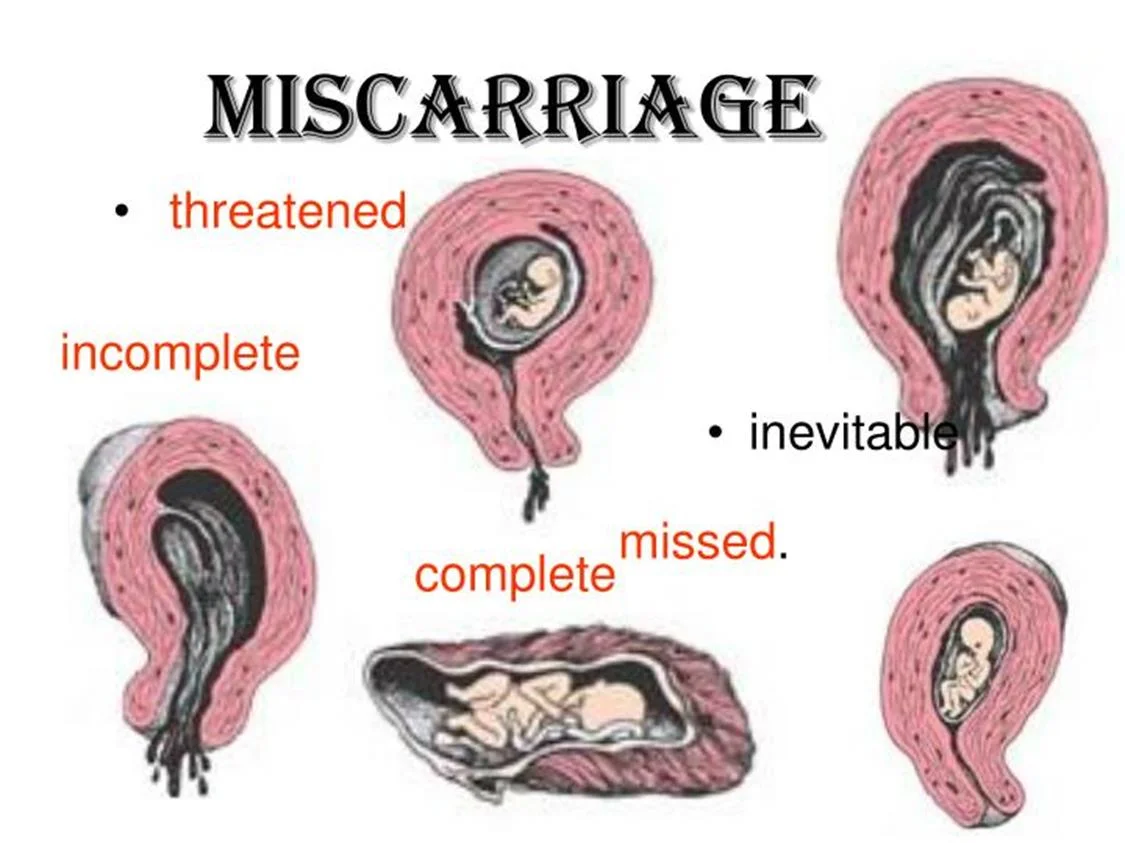
TYPES
MISCARRIAGE
- Threatened Miscarriage
- Incomplete Miscarriage
- Inevitable Miscarriage
- Missed Miscarriage
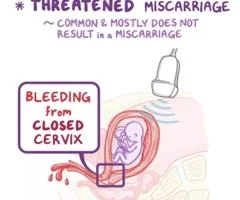
Threatened miscarriage
-
Clinical feature:
- Amenorrhea.
- Mild bleeding (spotting).
- Mild pain.
-
On examination:
- Uterus corresponding to the date.
- PV: closed cervical os.
-
Investigations:
- Pregnancy test (hCG): +ve.
- US: viable intra uterine fetus.
-
Management:
- reassurance.
- Rest.
- Repeated U/S
- Progesterone support.
THREATENED MISCARRIAGE
~ COMMON & MOSTLY DOES NOT RESULT in a MISCARRIAGE
BLEEDING from CLOSED CERVIX
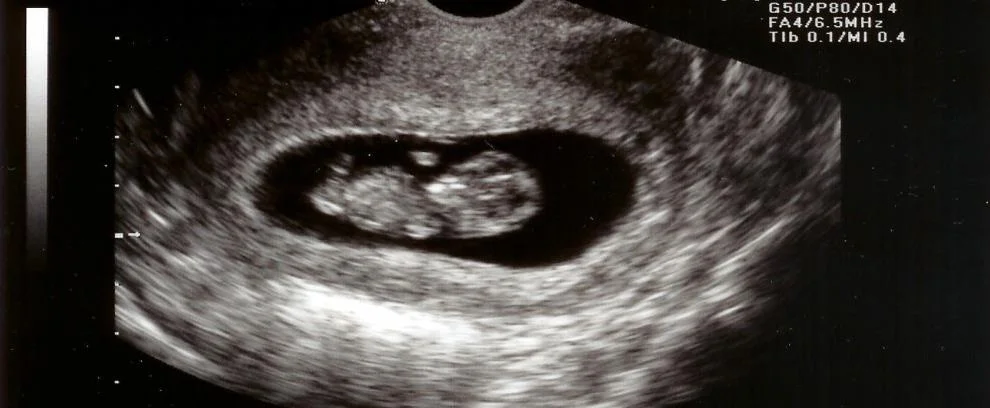
Inevitable miscarriage
-
Clinical feature:
- Amenorrhea.
- heavy bleeding accompanied with clots (may lead to shock).
- Severe lower abdominal pain.
- On examination:
- P.V.: opened cervical os + product inside the cervical canal.
-
Management:
- I.V fluids.
- Blood if need.
- Digital evacuation if possible.
- Ergometrine & syntocenon.
- evacuation of the uterus (medical/surgical).
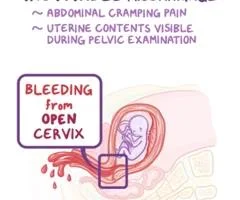
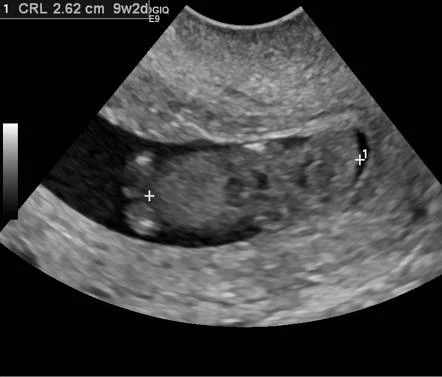
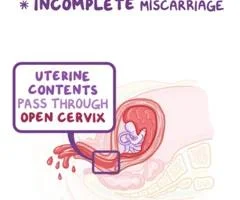
Incomplete Miscarriage
Clinical feature:
- Partial expulsion of products
- Bleeding
- colicky pain continue.
On examination:
- P.V.: opened cervix.
- retained products may be felt through it.
Investigations:
- US: retained products of conception.
Treatment :
- Medical or surgical.
- Surgical evacuation.
- Medical evacuation(prostaglandins , syntocenon).
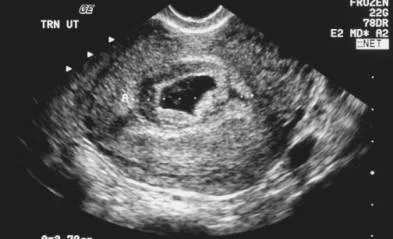
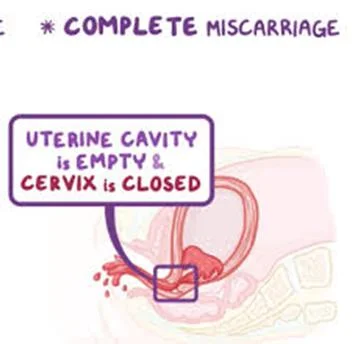
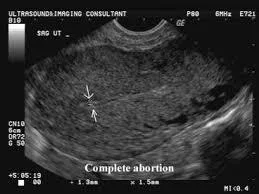
Complete miscarriage
- Clinical feature:
- Expulsion of all products of conception.
- Cessation of bleeding and abdominal pain.
- on examination:
- P.V.: closed cervix.
- Investigations:
- US: empty uterus.
- Treatment:
- Supportive.
Missed miscarriage
-
Clinical feature:
- gradual disappearance of pregnancy Symptoms Signs.
- Brownish vaginal discharge.
- Milk secretion.
-
Investigations:
- Pregnancy test: negative( but it may be + ve).
- US: absent fetal heart pulsations.
-
Complications :
- Hypofibrinogenemia .
- Infection.
- DIC
-
Treatment :
- conservative: Wait 4 weeks for spontaneous expulsion -
- Surgical:( D&C) if Spontaneous expulsion does not occur after 4 weeks. Or if it’s the choice of the pt .
- Medical: PGs.
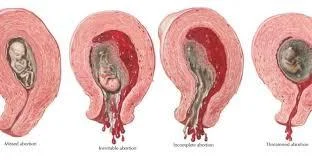
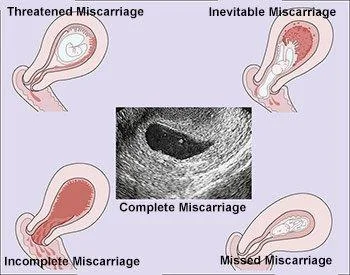
Types of miscarriages with ultrasound findings and clinical presentation
| Type of miscarriage | Ultrasound scan (USS) findings | Clinical presentation | Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Threatened miscarriage | Intrauterine pregnancy with FH | Vaginal bleeding Abdominal pain Speculum cx os closed | Supportive |
| Inevitable miscarriage | Intrauterine pregnancy (with no FH) | Vaginal bleeding Abdominal pain Speculum cx os open | Expectant medical or surgical |
| Incomplete miscarriage | RPOC | Vaginal bleeding Abdominal pain Speculum cx os opened Retained products found in the os | Remove RPOC if possible at time of examination(speculum) Expectant medical or surgical |
| Complete miscarriage | Empty uterus Serum h CG to exclude EP (If no previous one with intrauterine pregnancy ) | Vaginal bleeding & Abdominal pain resolved Speculum cx os closed | Supportive |
| Missed miscarriage | IUP No FH | A symptomatic often diagnosed at booking UUS | Expectant medical or surgical |
Investigations
- Transabdominal/TVUSS:
- a single ultrasound scan can diagnose a miscarriage if there is a pregnancy within the uterine cavity.
- Haemoglobin and ‘Group and Save’ (or cross-match if patient is severely compromised):
- Assess degree of vaginal loss and rhesus status.
Management
- expectant
- medical
- surgical
- approach depending on clinical presentation and patient choice
- Expectant management
- To avoid surgery
- urinary pregnancy test after 3 weeks and it is positive
- let pt come again She may need surgical treatment if she start to bleed heavily.
- Expectant management
Medical management
- Used in outpatient setting
- allow women to miscarry at home. It involves
- prostaglandin E analogue (misoprostol).
- progesterone antagonist (mifepristone)(if >9wks’).
The side-effects include:
- Pain.
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea.
- women are routinely provided with pain relief and antiemetics). post-treatment pregnancy test is recommended
Women may need surgical treatment if medical treatment fail.
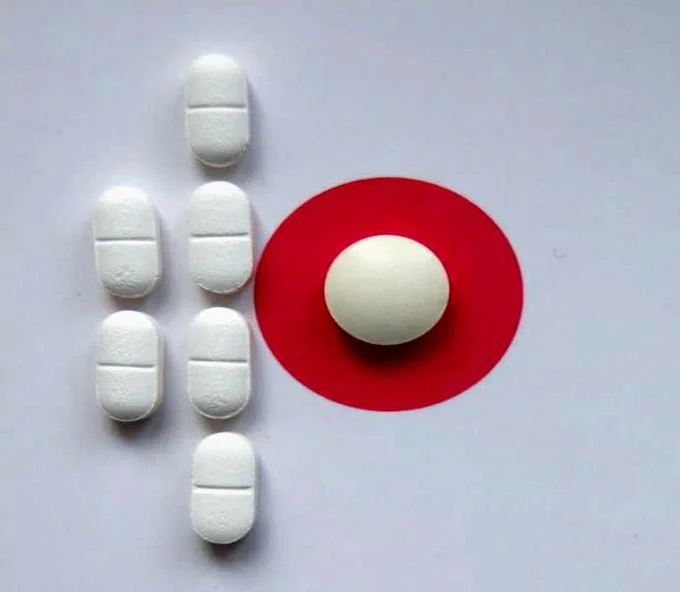
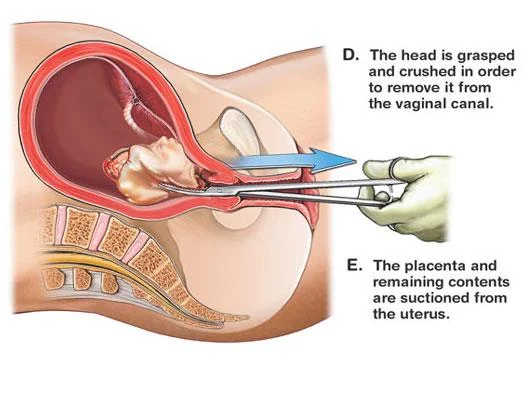
Surgical management
-
if there is:
- persistent excessive bleeding.
- haemodynamic instability.
- if women favour it.
-
It can be done by Surgical evacuation.
-
Evacuation risks:
- uterine perforation.
- postoperative pelvic infection.
- cervical trauma and subsequent cervical incompetence. Z
D. The head is grasped and crushed in order to remove it from the vaginal canal.
E. The placenta and remaining contents are suctioned from the uterus.
Recurrent miscarriage
Definition:
Loss of three or more consecutive pregnancies.
Incidence:
- 1% of pregnancies.
Risk factors:
- Advancing maternal and paternal age.
- Obesity.
- Balanced chromosomal translocations.
- Congenital abnormalities.
- Uterine structural anomalies and cervical incompetence. Z
- Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). Z
LMW

Investigations
- testing for antiphospholipid antibodies
- imaging of the uterus.
- Products of conception should be sent for cytogenetic analysis to detect chromosomal abnormality.
- peripheral blood karyotyping of both partners should be performed.
Most couples have normal investigations
Diagnosis of cervical incompetence: Z
-
From history
- Three or more miscarriage es.
- Painless vaginal bleeding.
- decreased gestational age in subsequent pregnancy.
-
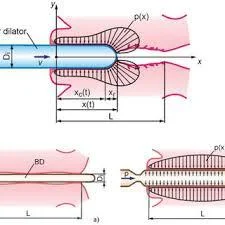
From investigations:
- Hagar dilator(No.8).
- HSG.
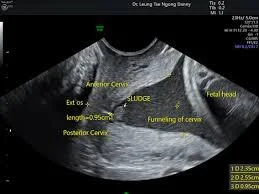
- During pregnancy: US Funnel shape, short cervix.
Management:
- Cervical cerclage.
SEPTIC MISCARRIAGE
- Following an incomplete miscarriage due to ascending infection.
- Or following criminal abortion.
- Clinical picture: -
- Symptoms:
- Offensive bloody vaginal discharge.
- Increased body temperature.
- Lower abdominal pain (pelvic peritonitis)
- generalized peritonitis.
- Signs:
- Increased pulse rate.
- Dehydration.
- toxicity.
- Symptoms:
- Clinical picture: -
Investigations:
- Blood.
- FBC.
- BHCG.
- Renal profile.(2ry to septic shock).
- Blood grouping & cross matching.
- ESR.
- High vaginal swab for C/S.
- Blood culture & sensitivity(if needed).
Treatment:
- Antibiotic.
- iv fluids.
- blood transfusion.
- Evacuation of retained product.

SEPTIC SHOCK
- Tachypnea Tachycardia
- Hypotension Hypothermia
- Oliguria
- Sepsis
- Multi organ failure
Anti-D administration
- All rhesus-negative women who have a surgical procedure to manage an EP or miscarriage should be offered anti-D immunoglobulin.
- Anti-D is not required for
- Threatened miscarriage.
- complete miscarriage.
- medical management of miscarriage or EP.
- but guidelines differ, and prophylaxis is often given
Notes
In all form of miscarriages: general clinical assessment should be made:
- vital signs.
- abdominal examination.
- vaginal examination.
- All needed investigations +/- ws:
- Send product for histopathology.
- Management should be according to clinical Type & gestational age.
Don’t Forget!!
- Pt emotionally distressed by her physical symptoms & loss of her baby. So
- Support her.
- Explain the causes & reassure her she is not guilty
may also be due hypothyroidism or diabetes for reccurent miscarriage