Physeal Histology
- Physis: 4 zones
- Germinal zone
- Proliferative zone
- Hypertrophic zone
- Enchondral ossification

Epidemiology
- Incidence:
- 20% of all skeletal injuries in children
- 50% occur in the distal radius
- Problems:
- Some are intra-articular
- Possibility of growth affection
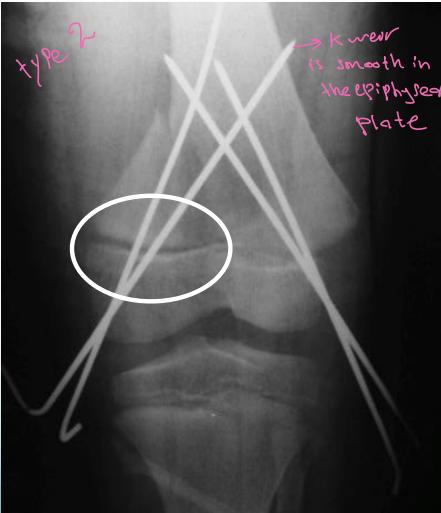
Classification – Salter-Harris
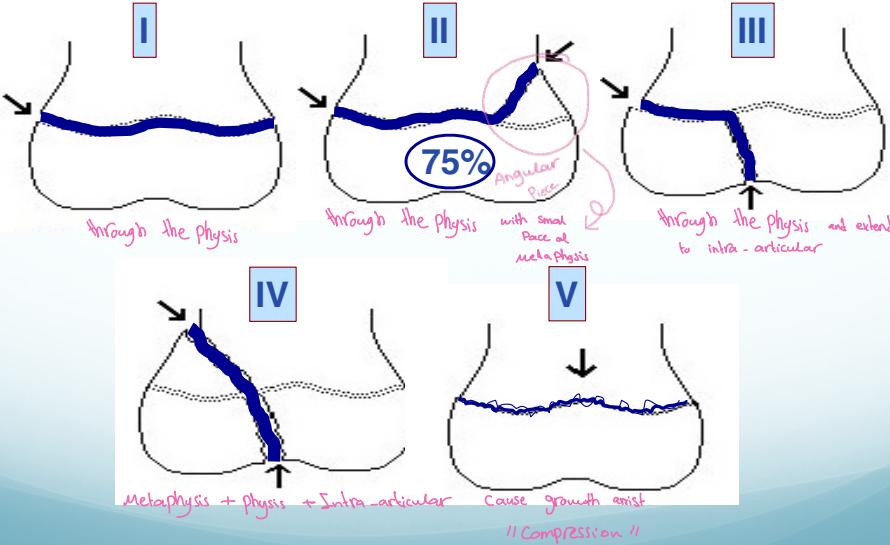
- Type I - Through the physis
- Type II - Through the physis with small piece of metaphysis (75%)
- Type III - Through the physis and extend to intra-articular
- Type IV - Metaphysis + physis + Intra-articular
- Type V - Cause growth arrest “Compression”
Treatment of Physeal Injuries
Extra-articular (Type I / II)
- Stable: conservative
- Unstable: K-wire / screws with cast
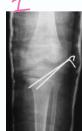
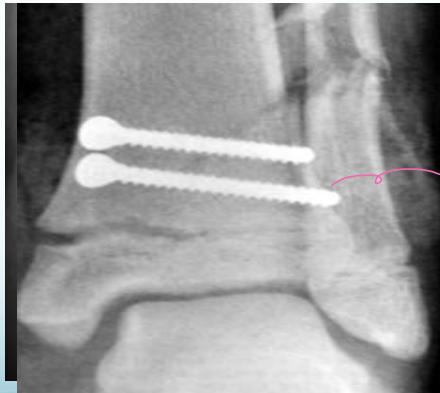
Intra-articular (Type III / IV)
- Anatomical reduction and internal fixation
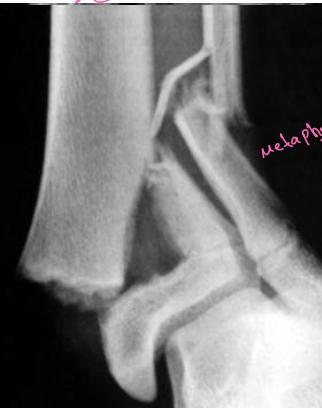
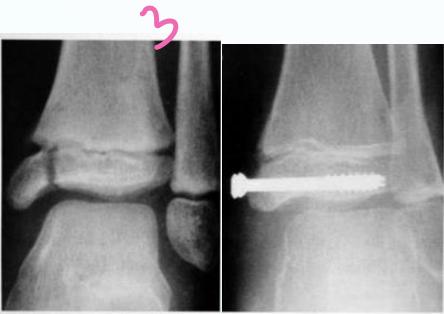 growth plate through epiphysis, not complete
growth plate through epiphysis, not complete
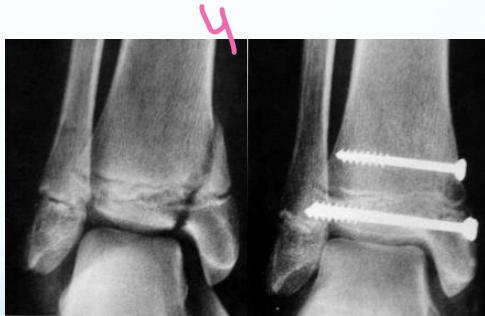 growth plate through and through epiphysis
growth plate through and through epiphysis
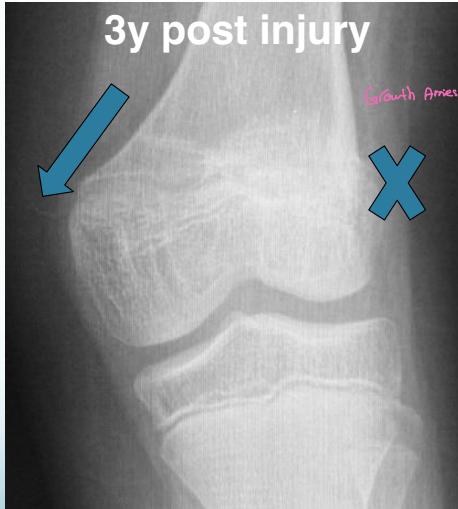
Compressed Type (Type V)
- Doesn’t appear on x-ray at first
- Cast & healed but prognosis is unpredictable
- Usually causes affection of growth arrest
- Diagnosed in retrospect!
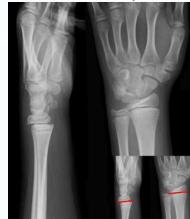
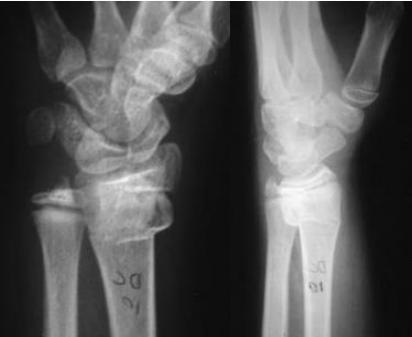 Injury films
Injury films
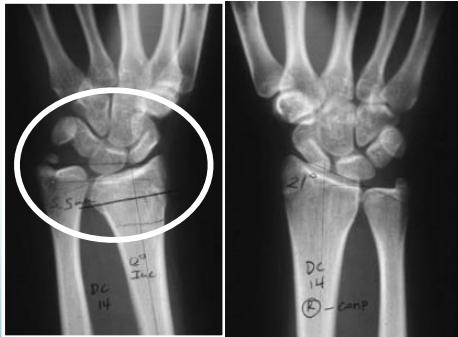 Injured and uninjured wrists after premature physeal closure
Injured and uninjured wrists after premature physeal closure
Asymmetrical Physeal Affection
- Seen on x-ray
- One side grows more than the other
- Causing an increasing deformity
- Oblique Park-Harris growth arrest/recovery line (white arrows)
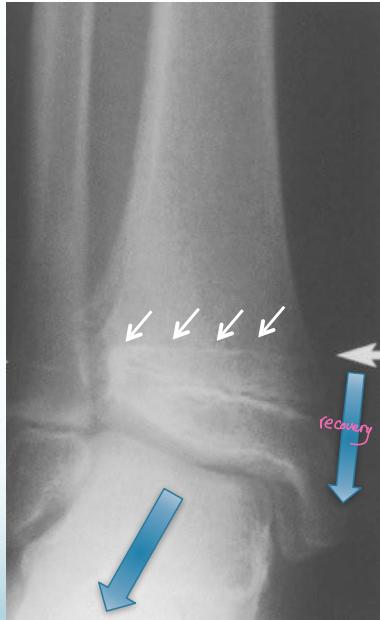
Case Example: 12-year-old male, Salter-Harris Type II