Case 1 Z
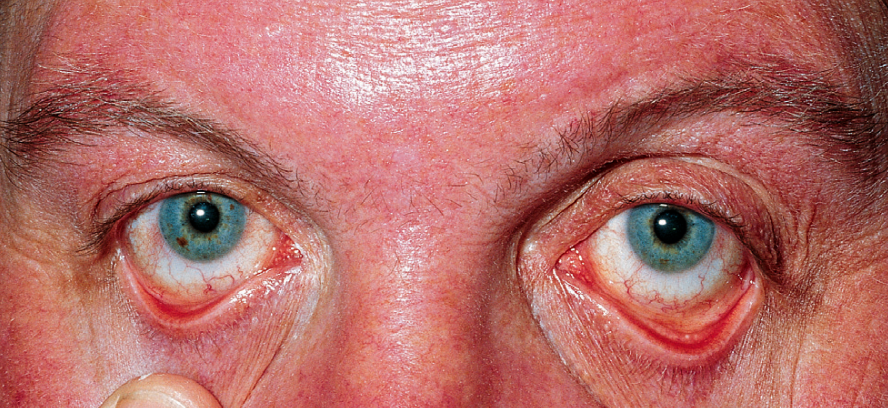 1. What is your clinical diagnosis?
Polycythemia
1. What is your clinical diagnosis?
Polycythemia
-
Mention 2 abnormal findings in the CBC of these patients? high hemoglobin, high WBC and platelets
-
What is the genetic abnormality which causes this condition? JAK 2 Mutation
-
In this patient, what will be the blood erythropoietin level, high or low? Erythropoietin low
-
Mention 2 treatment options for this disease? Venesection to remove blood and Aspirin
-
Mention 1 symptom of this disease? Visual disturbances and Claudication
-
Mention 2 other etiologies of high RBC count in the blood, besides this condition? Hypoxia and Tumor
Case 2
A 20 years old male comes with fever since 5 days. Fever is episodic. The peripheral blood film is shown below.
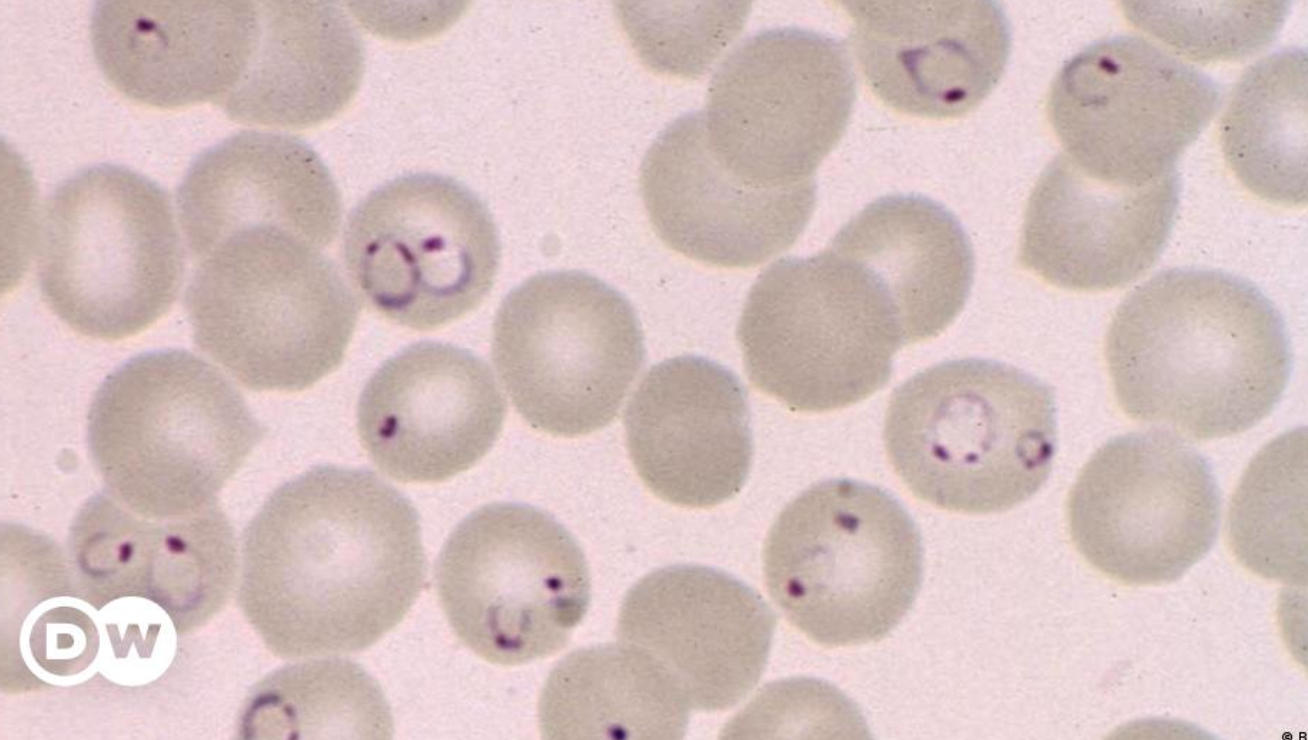
-
What abnormality (Micrograph name) do you see in this smear?
- Ring form - Malarial parasite inside RBCs Z
-
What is your diagnosis?
- Malaria
-
Mention 2 causes of anemia in this infection? Z
- **Mechanical destruction of RBCs
- Reduced erythropoiesis in the bone marrow
-
Mention 3 features of severe form of this infection? Z
- **Cerebral malaria
- Blackwater fever
- Hypoglycemia
- Renal involvement DIC
-
Mention 4 species of the parasite which cause this infection?
- **Plasmodium
- P. Vivax, P. ovale, P. Falciparum and P. Malariae**
-
Mention 3 drugs used to treat this infection?
- Mefloquin / amodiaquin/ lumifantrire
- Artemisinin compounds/ Chloroquin / quinine
- For pregnancy; Hydroxychloroquine
- To prevent relapse; Primaquine
-
Name the 4 species of the parasite which cause this infection in humans?
- **a) Plasmodium Vivax
- b) Plasmodium Ovale
- c) Plasmodium Falciparum
- d) Plasmodium malariae
-
Name any complication which can occur in severe form of this disease?
- a) Cerebral involvement / renal involvement DIC/
Case 3
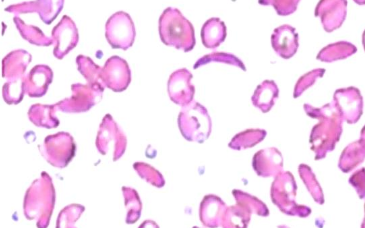 This is the peripheral smear of a 14 year old patient who gets frequently admitted to the hospital due to bone and joint pain
This is the peripheral smear of a 14 year old patient who gets frequently admitted to the hospital due to bone and joint pain
Q1: Describe the abnormal findings in this smear? Sickle cells.
Q2: what’s your diagnosis? Sickle cell anemia.
Q3: Name any type of crisis which can occur in this disease? Aplastic crisis, acute chest syndrome.
Q4: What are the ttt options for this disease? Hydroxyurea, blood transfusion, folic acid (not sure).
Case 4
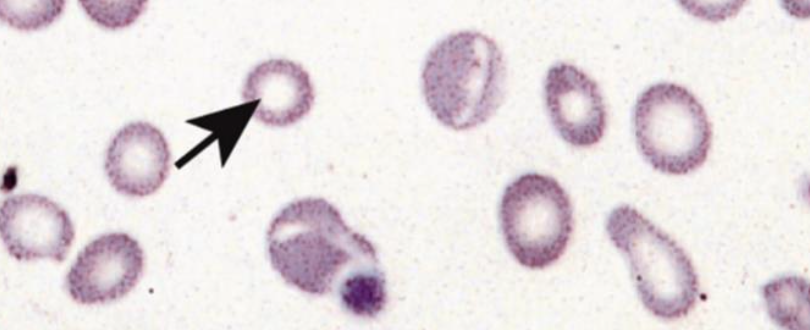 1- Diagnosis?
Iron deficiency anemia.
1- Diagnosis?
Iron deficiency anemia.
2- Give 2 investigation? Serum ferritin level, Total iron binding capacity (TIBC).
3- Causes? Decrease iron intake in diet, chronic GI bleeding or heavy menses.
Case 5
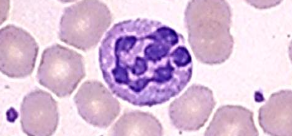
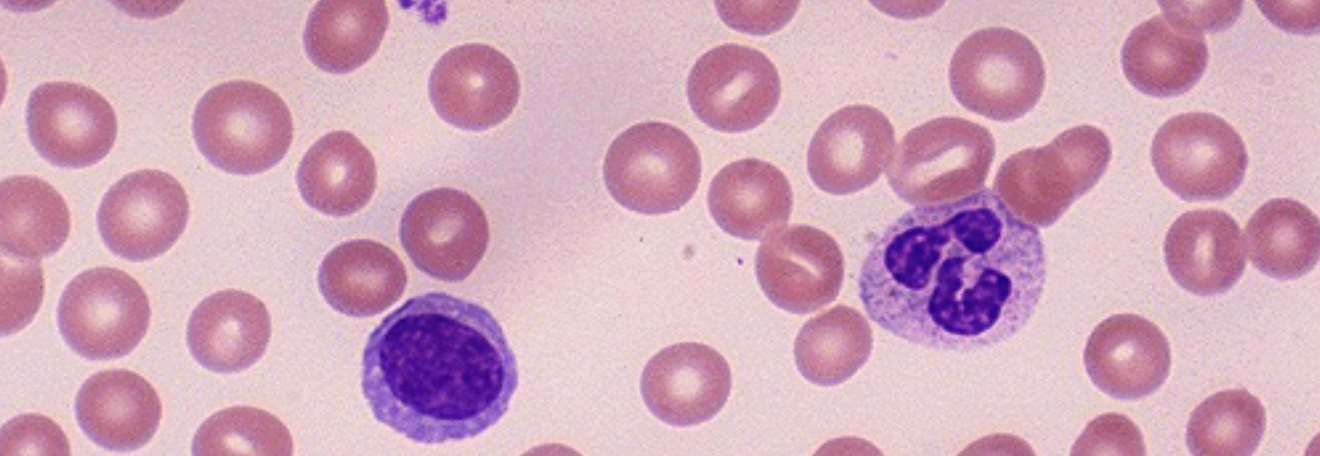
A 40 year old man complains of fatigue, tiredness and clumsy walking (ataxia) since few months. He has very pale conjunctiva. Peripheral blood smear is shown above.
Q1: What’s your diagnosis? Megaloblastic anemia.
Q2: What abnormality do you see in this picture? Neutrophil with hyper segmented nucleus.
Q3: Name 2 conditions which can cause this type of peripheral smear? Vitamin B12 deficiency, folic acid deficiency.
Q4: Name the blood test which you will do in this pt to confirm the diagnosis? Vitamin B12 level.
Q5: What treatment will you give to this pt? Replacement of Vitamin B12.
Q6: Name 2 neurological features seen in this condition? Z Peripheral neuropathy, numbness.
Q7: Test to confirm diagnosis? Z - Serum vit b 12 - Serum autoantibodies
Case 6
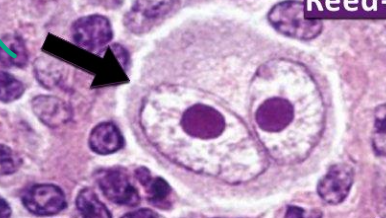
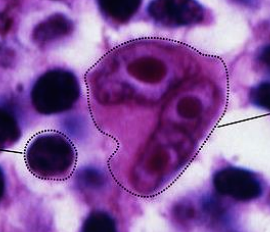 A 50-year-old male had cervical lymph node enlargement for 2 months. Biopsy of the nodes shows.
A 50-year-old male had cervical lymph node enlargement for 2 months. Biopsy of the nodes shows.
-
Name of the cell? Z Reed-Sternberg cell.
-
Diagnosis?
Hodgkin’s lymphoma. -
Mention 4 clinical features that may be presenting symptoms of this disease?
- B Symptoms (Fever, night sweats, and unintentional weight loss)
- Regional lymphadenopathy
- Bone pain
- Pruritus
- SVC syndrome (Superior Vena Cava Syndrome)
-
Diagnostics investigations
- Bone marrow; Cytology and histology
- CXR
- ESR
-
Staging tests
- PET
- CT
-
Mention 2 treatment options for this disease?
- Regional radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy; rituximab, methotrexate
- surgical resection
Case 7
A 48 year old female is concerned about her several episodes of fainting. Brief clinical examination reveals pallor of her skin. Her blood is:
- Hb 8.7 g/dl
- MCV 64.5 fl
- Plt 556 x 109/l
- WBC 7.7 x 109/l
- Serum iron 6 μmol/l (NR: 65-180 μg/dL )
- Ferritin 10 μmol/l (NR: 12-300 ng/mL)
- TIBC 90 μmol/l (NR: 45-85 μmol/L)
- Vitamin B12 221 ng/l (NR: 130-700 ng/L)
- Folate 9.2 μg/l (NR: 7-36 nmol/L
How would you interpret these results?
hypochromic microcytic anemia
How would you proceed with investigations?
a. fecal occult blood test
b. —angiography—
Case 8 Z
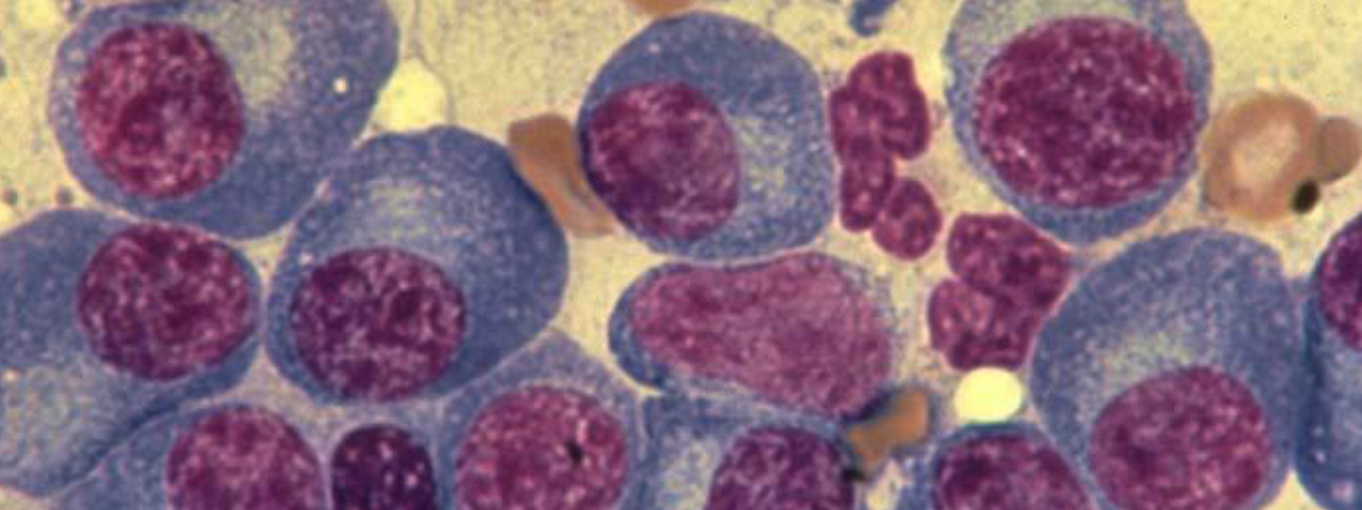 Bone marrow aspirate of patient with multiple myeloma
Bone marrow aspirate of patient with multiple myeloma
-
Describe the morphology of the cells shown?
---plasma cell tumor--- -
What other conditions these cells are present?
---plasma cell leukemia---
Case 9
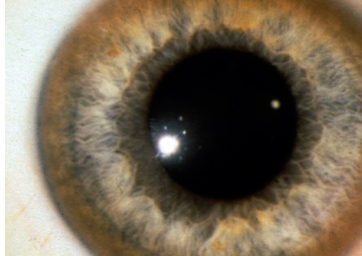 A 26 years old female presented with dystonia. O/E is found to have ascites due to portal hypertension & asymptomatic golden brown rings around the corneo-scleral junction (limbus) of the eyes as shown
A 26 years old female presented with dystonia. O/E is found to have ascites due to portal hypertension & asymptomatic golden brown rings around the corneo-scleral junction (limbus) of the eyes as shown
-
What you see in Pic ? Kayser Fleischer
-
Diagnosis?: Wilson’s Disease
-
Treatment: Z
Penicillamine -
What is the type of inheritance for this disease?
- Autosomal recessive
-
Mention 2 recognized hepatic complications of this disease?
- Chronic active hepatitis
- Liver cirrhosis
-
Mention 2 tests commonly used for diagnosis of this disease? Z
- Serum ceruloplasmin
- Urine copper
-
Mention 2 neurological manifestation of this disease? Dystonia, Spasticity, grand mal seizure, wing beating tremor
-
Name a drug commonly used for the treatment of this disorder? Use of chelating agent for lifelong (penicillamine trientine)
-
Name a life threatening complication of this disease? Fulminant hepatic failure, Liver cirrhosis
Case 10
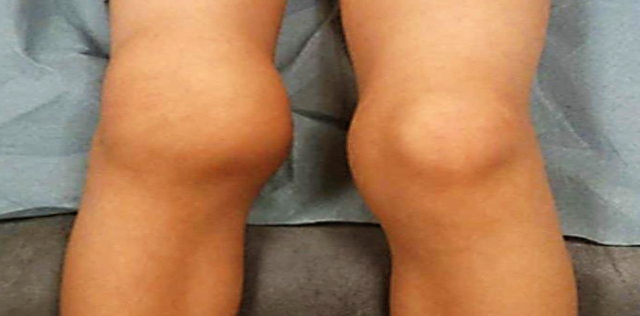 A 14 year old boy, who is a known case of hemophilia, presented with acute right knee pain and swelling.
A 14 year old boy, who is a known case of hemophilia, presented with acute right knee pain and swelling.
Q1: What’s the likely cause of his knee pain? Z Hemarthrosis
Q2: what’s the mode of inheritance of hemophilia? X-linked recessive.
Q3: what’s the recommended ttt of hemophilia? Z Factor 8 or factor 9
Q4: What’s the likely cause of failure of ttt in some pt? Z Antibodies formation against the factors.
Case 11 Z
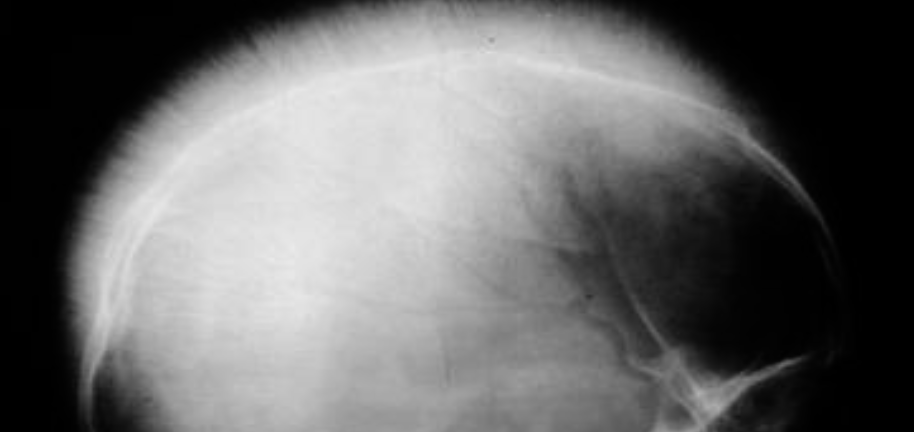
-
Describe and explain radiological changes seen in the X-ray?
Hair on end appearance -
Causes of severe hemolytic crisis?
1.Acute splenic sequestration 2.Transient Red cell aplasia 3.Hyperhemolysis due to infection -
What is best treatment of acute chest syndrome?
Oxygen – Transfusion – Antibiotic -
What investigation will you suggest to prevent stroke in children 2 – 16 years age?
Doppler US -
What drug treatment is commonly recommended for these patients?
Hydroxycarbamide
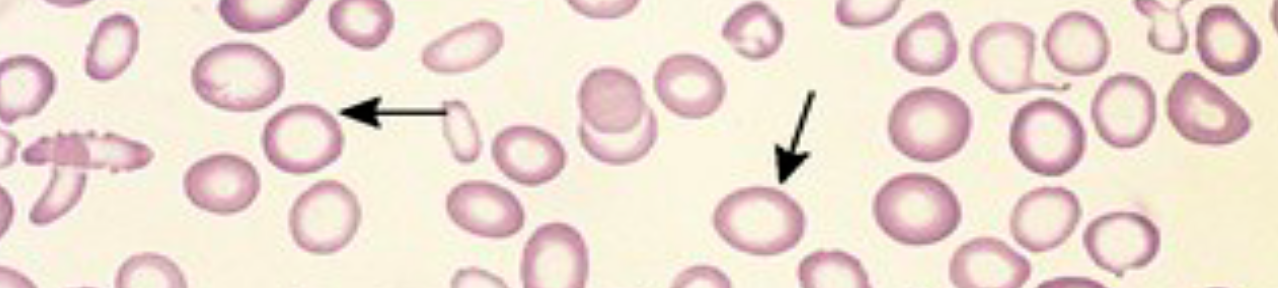
Peripheral smear
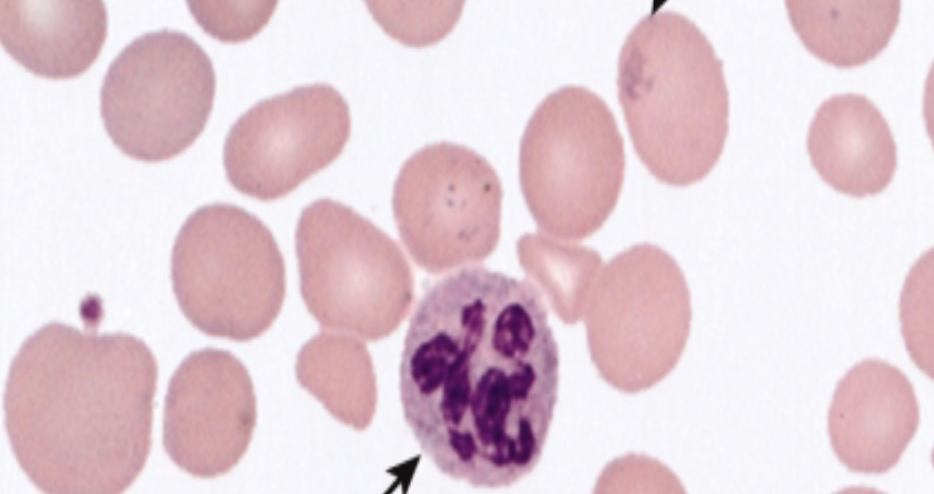 Note the large RBCs & Large Neutrophil with Multilobed nucleus
Note the large RBCs & Large Neutrophil with Multilobed nucleus
Iron deficiency anemia - Hypochromic, microcytic
Normal Peripheral Smear
Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma
Mycosis Fungoides
Angioimmunoblastic Lymhoma
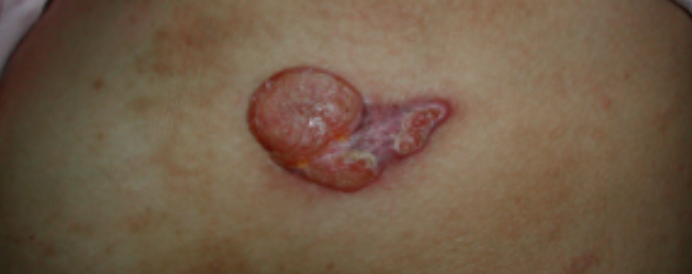
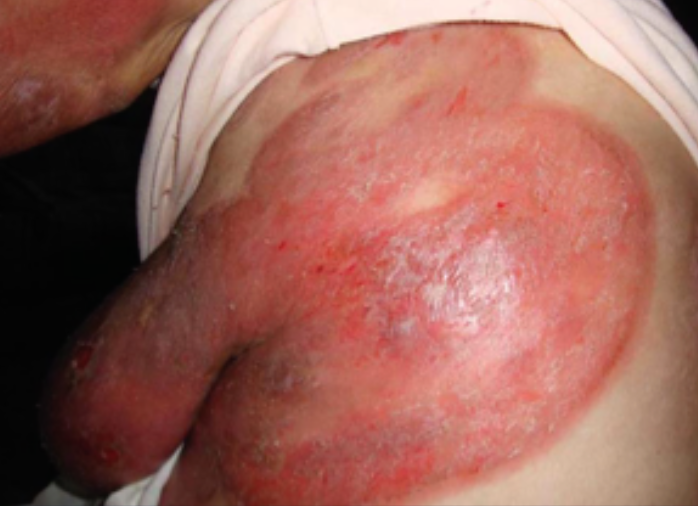
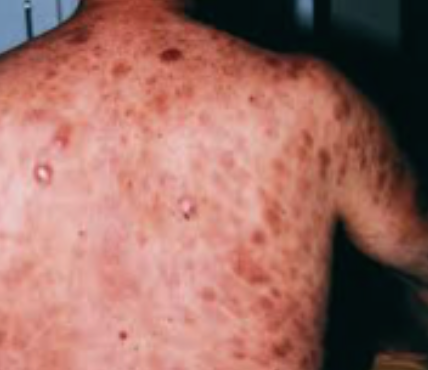 SKin lesions: associated with coetaneous T-cell lymphoma
SKin lesions: associated with coetaneous T-cell lymphoma