Cholangitis
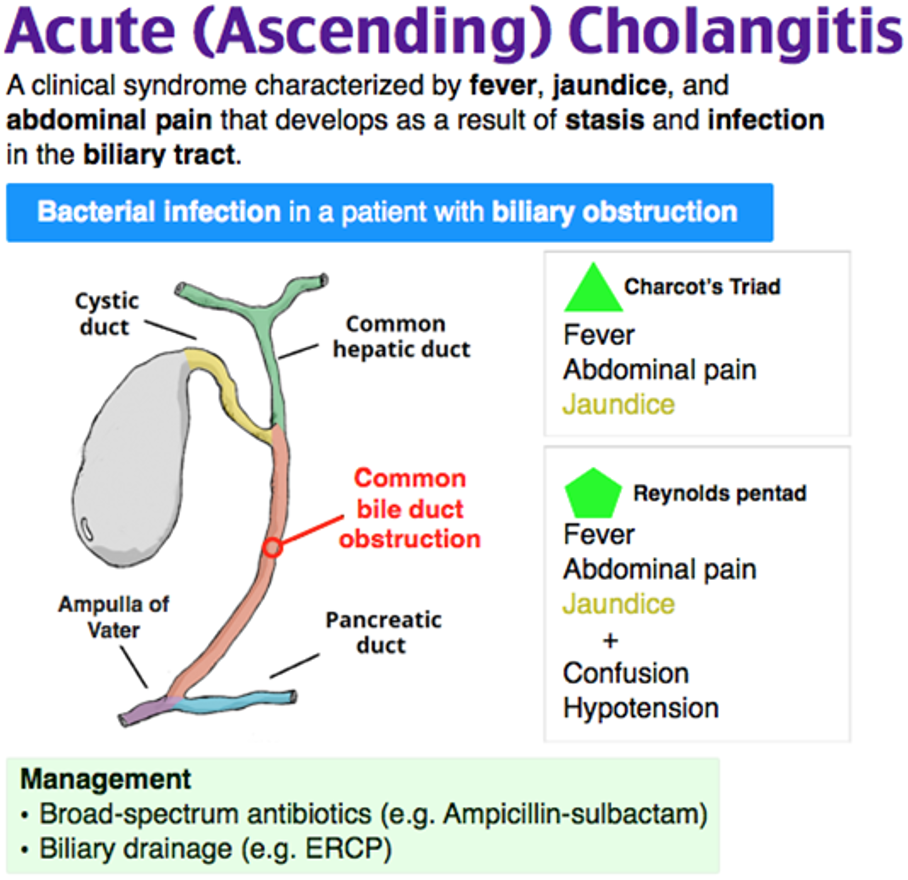
Systemic infection of acute inflammation & infection of bile ducts resulting from combination of biliary obstruction and bacterial bile growth.
Symptoms:
Charcot’s triad Fever, Abdominal Pain, Jaundice RUQ Abd Pain, pyrexia
((bacteria biliary system to systemic - Reynolds pentad develops))
Reynolds Pentad. Fever, Abdominal pain, Jaundice + Confusion & Hypotension
Signs:
Pyrexia, tachycardia, possibly hypotension, jaundice and mild right upper quadrant tenderness.
Investigations
Blood tests: will show high LFT like obstructive jaundice with leukocytosis
Imaging: Ultrasound abdomen will show dilated extra-hepatic biliary system, possibly will show gallstone and the stone in the common bile duct.
Treatment
- Admission to the hospital
- Nothing given by mouth
- Intravenous fluids infusion
- Intravenous broad spectrum antibiotics
- Analgesia
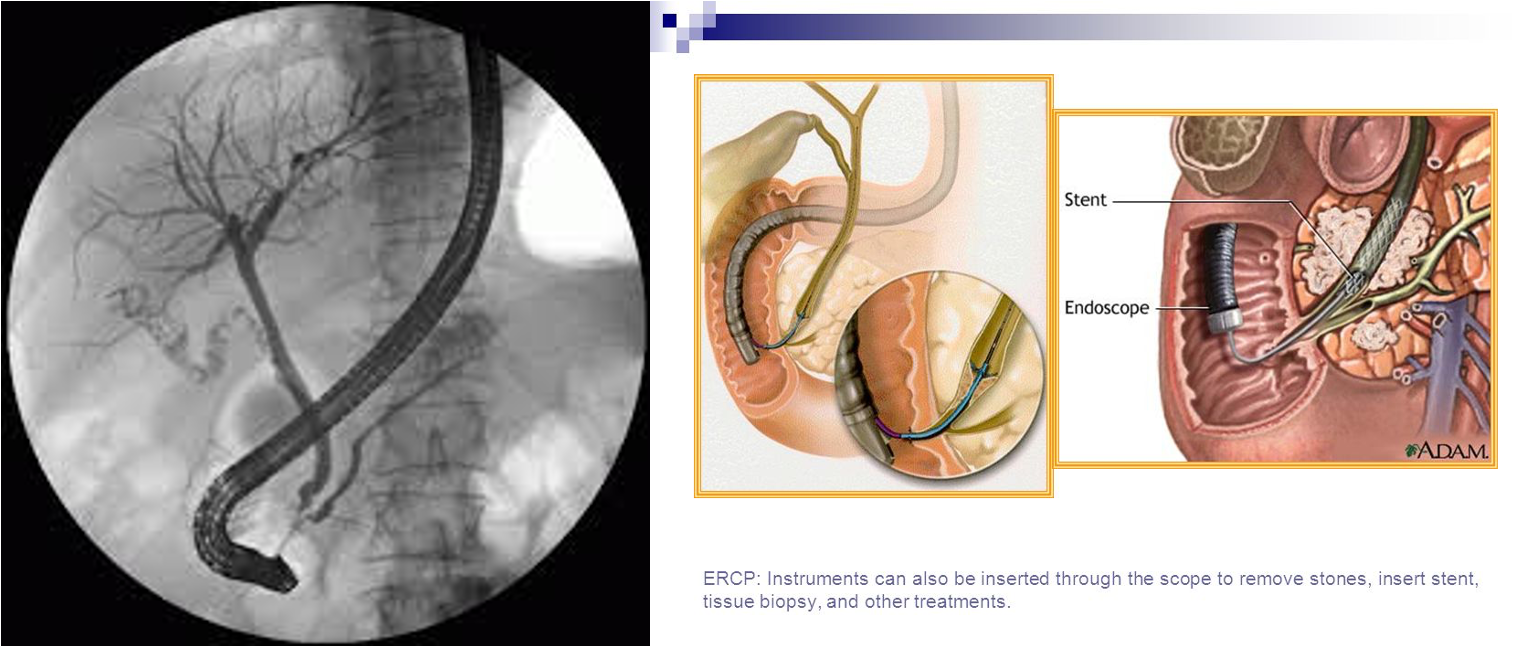
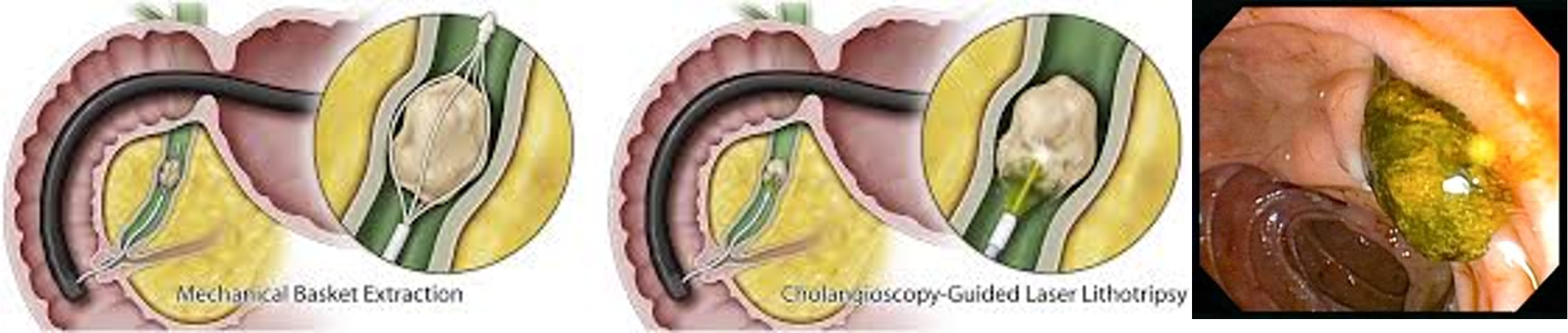
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with stone extraction from the bile duct followed by laparoscopic cholecystectomy if the gallbladder containing stones.
Cholangio-venous and cholangio-lymphatic reflux Z
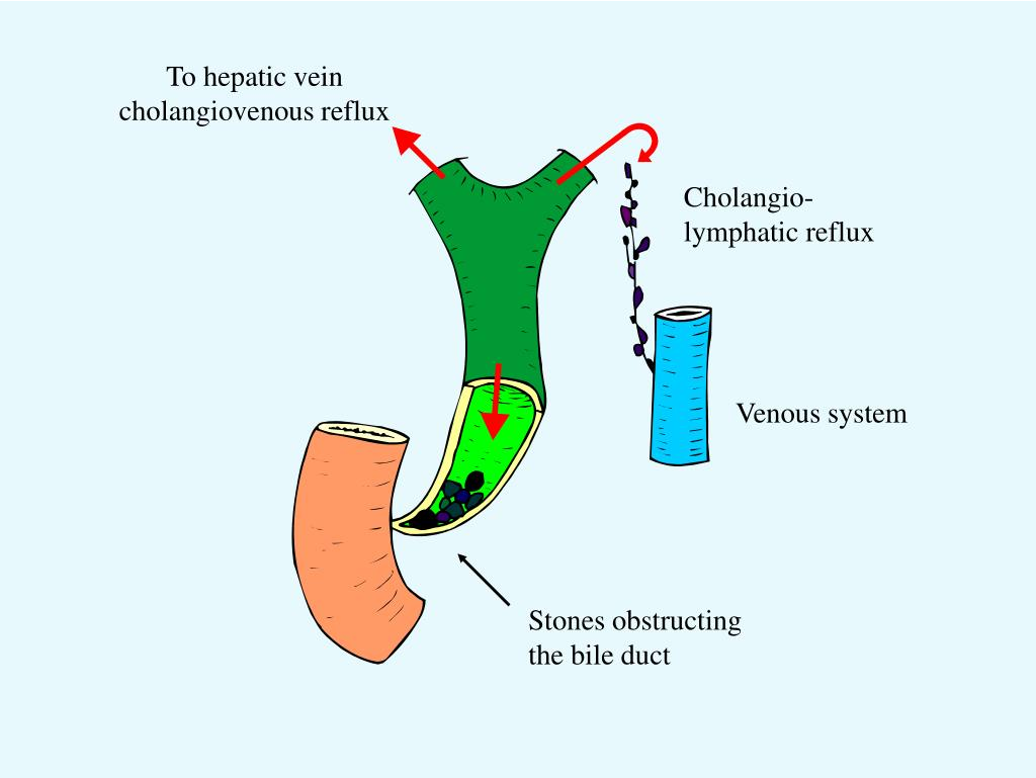 what is most important therapeutic intervention in this case Z
Remove stone to alleviate pressure from reflux
what is most important therapeutic intervention in this case Z
Remove stone to alleviate pressure from reflux
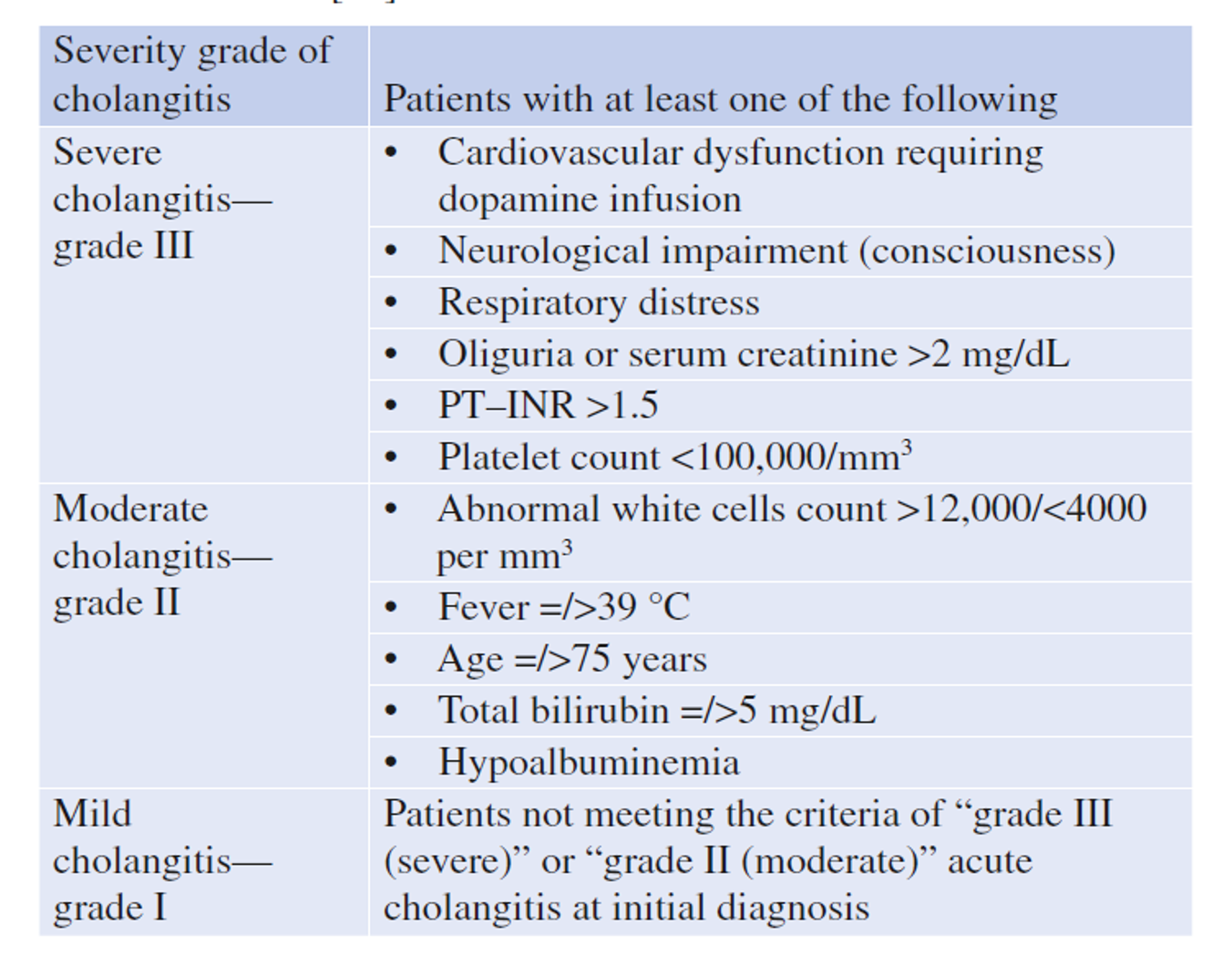
Severity assessment of cholangitis according to Tokyo - Guidelines TG13 Y
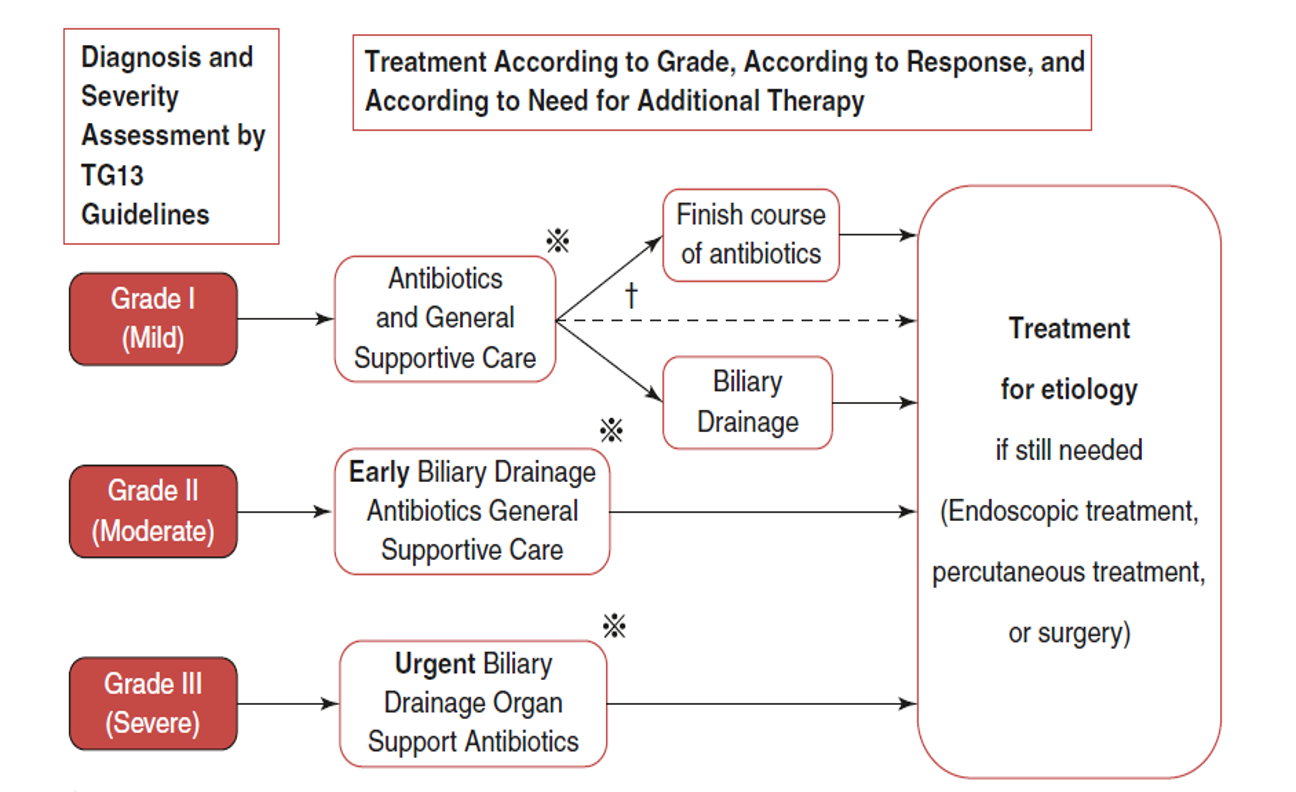
Comprehensive algorithm for the treatment of cholangitis from the TG13 guidelines for diagnosis and severity grading of acute cholangitis Y
(Table) Which Antibiotics Z
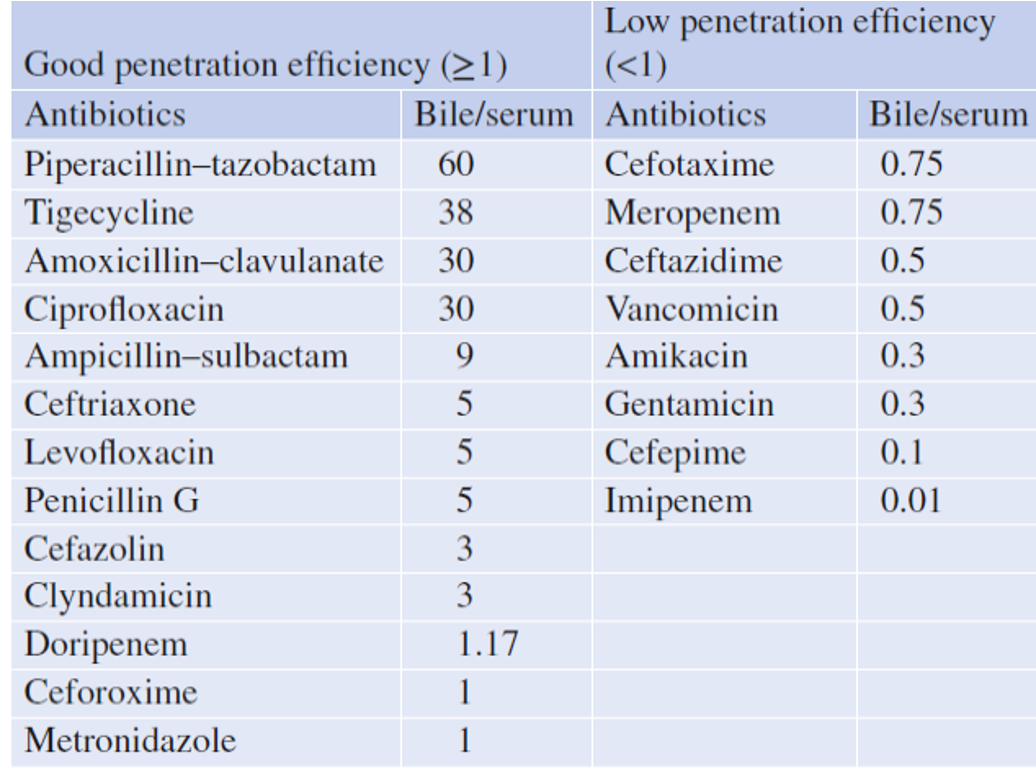 Piperacillin - Tazobactam best for cholangitis
Tazocin? - CC
Piperacillin - Tazobactam best for cholangitis
Tazocin? - CC
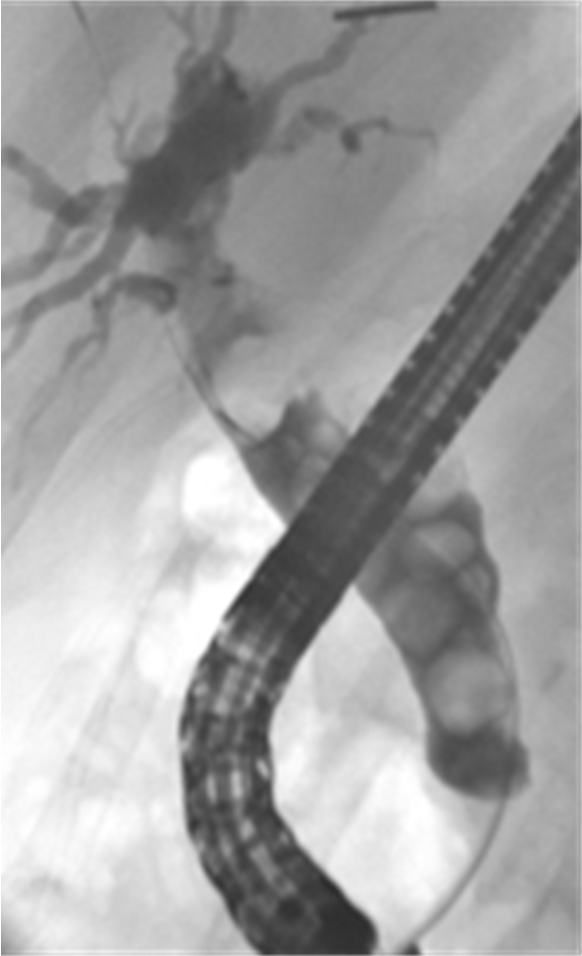
Percutaneous Transhepatic cholangiogram (PTC)
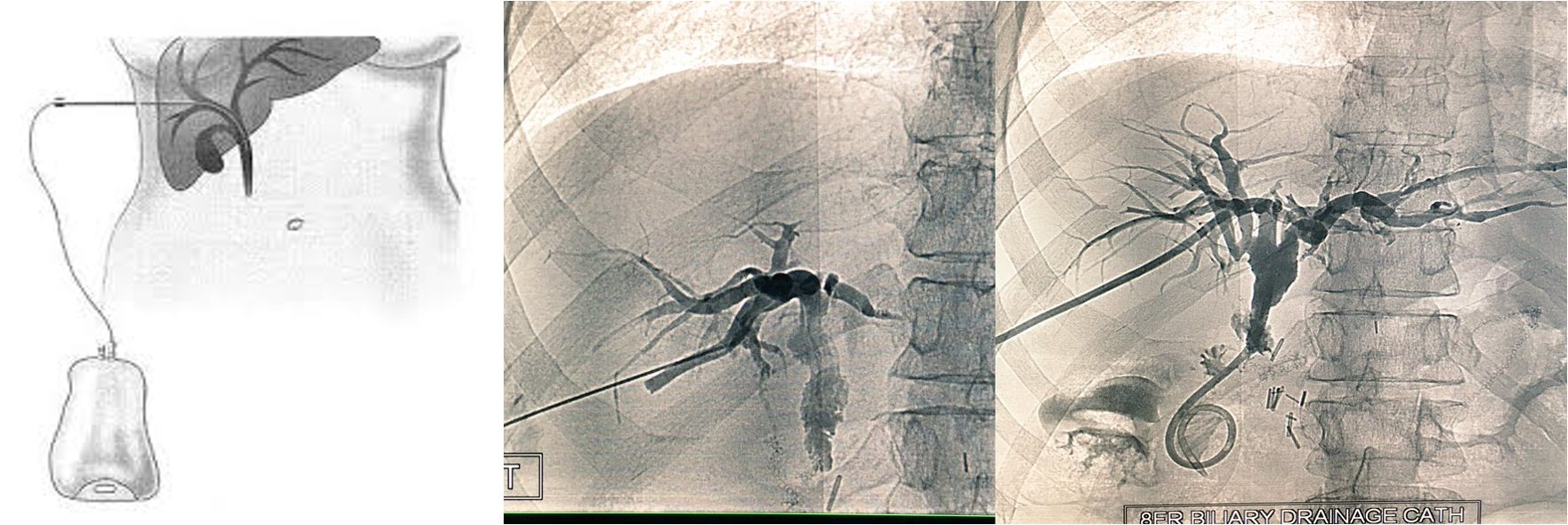
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)