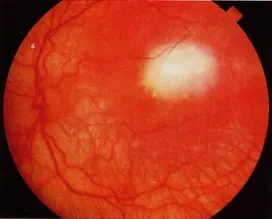
Retinoblastoma
- Retinoblastoma is the most common intraocular tumor of childhood.
Clinical Manifestations
- Leukocoria (60%)
- Strabismus (20%)
Other - Uveitis, Orbital cellulitis, Hyphaema, Heterochromia, Glaucoma, Bupthalmos



- Calcification is another feature of retinoblastomas, usually occurring in necrotic areas.
- Calcium stains with H&E. It is worth identifying calcium in suspect eyes by ultrasound or CT scan to differentiate retinoblastomas from other tumors.

Management
-
Empirical Genetic Counselling
-
Enucleation
- Unilateral, poor visual prognosis
-
Plaque
- 4-12mm +/- vitreous seeding
-
External Beam
-
12mm, multiple foci, only eye
-
-
Laser
- Consider - indirect, xenon arc
- Cryotherapy if <2dd in size
-
Chemotherapy, if intracranial extension
-
Retinal Tumor
Retinoblastoma
- Heritable (AD) or sporadic
Z
1- The most common primary intraocular malignant tumor in children, of which 90% are younger than 3 yrs
2- adult = childhood choroidal melanoma
3- extraocular/orbital malignant tumor most common in children rhabdomyosarcoma
4- most common extraocular vascular tumor in children capillary hemangioma
5- most common extraocular vascular tumor in adults cavernous hemangioma
Etiology
- Parents are affected or gene carriers, or germ cell mutation
- Autosomal dominant 40%
- Patient with retinoblast mutation
- Uninherited 60%
- Patient with autosomal chromosome mutation
- RB, complicated with intelligence and growth retardation.
Study shows:
Loss of or unactivated RB gene is the key factor of RB
Best INV: Ocular US - CT - MRI to finally confirm indicated treatment of excision Z
Staging
- Intraocular stage
- Glaucomatous stage
- Extraocular stage
- Metastasis stage
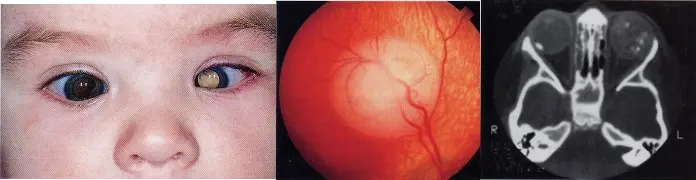
Differential Diagnosis
| RB | Coats disease | |
|---|---|---|
| Onset age | 90%<3 yrs | >6-8 yrs |
| Eyes involved | 30% both | 95% single |
| Microcirculation abnormality | none | Diffuse microaneurysm |
| Cholesterol cystal | none | Subretinal, obvious |
| Calcification | + | - |
| B-us | Solid tumor | Without solid tumor |
RB vs. Coats Disease
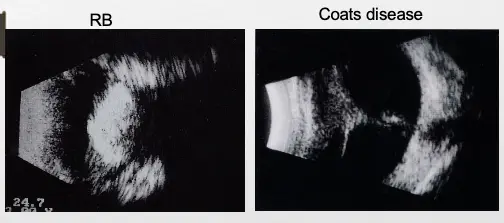
Treatment
- Small tumor localized in central retina can be effectively treated with photocoagulation
- Small tumor localized in peripheral retina can be treated with cryotherapy
- Moderate localized tumor: Plaque radiation therapy
- Big tumor: Enucleation Z ; removal of eye if large tumour
- Extraocular stage: enucleation + chemotherapy + radiation (bad prognosis)
- Metastasis: no specific treatment
Right After Laser Photocoagulation
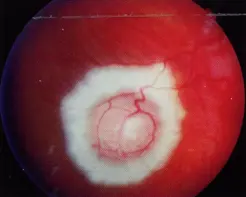
6 Months After Photocoagulation
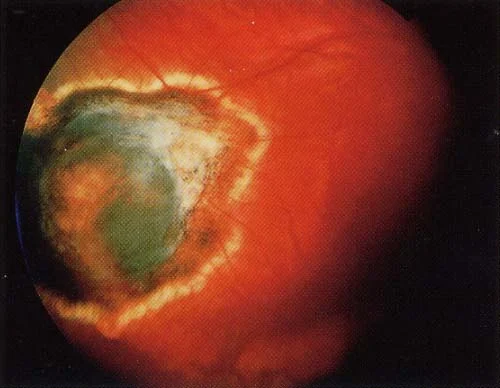
RB
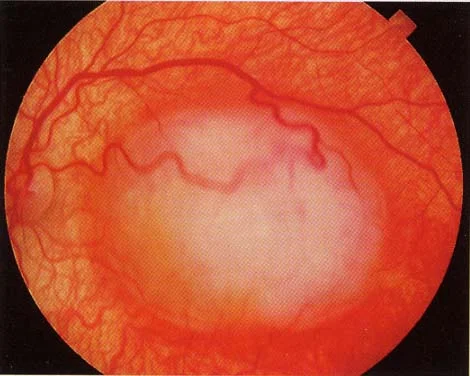
After plate radiation therapy