ER
- Definition: serum calcium < 8.5 mg/dL
- Causes:
- Hypoalbuminemia
- Hypoparathyroidism (neck irradiation / parathyroidectomy)
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Hyperphosphatemia
- Hypomagnesemia
- Severe pancreatitis
- Certain drugs (bisphosphonates, phenytoin, phosphate, calcitonin)
- Rhabdomyolysis
Clinical features
-
Muscular: weakness, fatigue, spasms, cramps
-
Neurologic: seizures, tetany, perioral/finger paresthesias, confusion, hallucinations
-
Cardiovascular: heart failure & ventricular arrhythmias
Signs
-
Trousseau’s sign: induction of carpopedal spasm by inflating cuff above SBP for 3 minutes → adduction of thumb, flexion of MCP joints, extension of IP joints, fl exion of wrist.
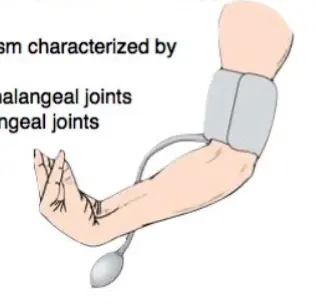
-
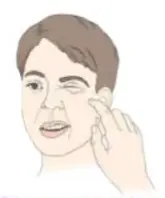
Chvostek’s sign: contraction of ipsilateral facial muscles when tapping facial nerve anterior to ear → twitching of lip or facial muscles.
ECG changes
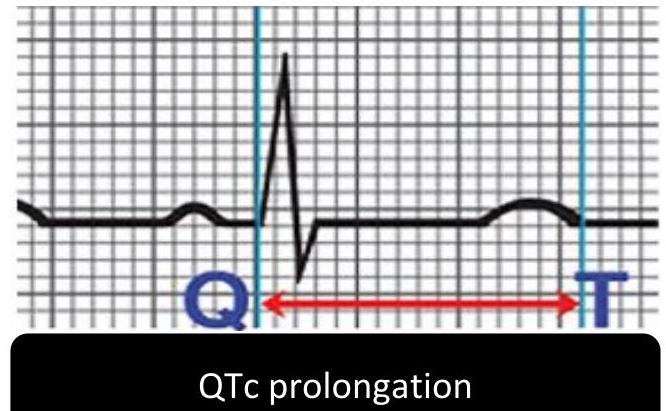
QTc prolongation
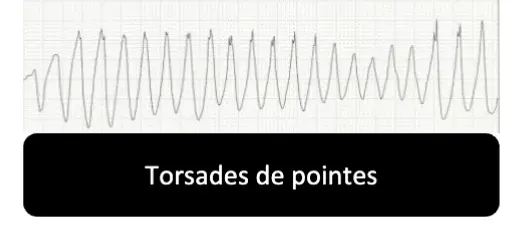 Torsades de pointes
Torsades de pointes
Treatment
| Therapy | Dose | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Oral calcium supplementation (calcium carbonate) | 500–3000 mg elemental Ca2+ PO daily (1 dose or up to 3 divided) | For asymptomatic/mild patients |
| IV calcium gluconate or calcium chloride | 10–30 mL of 10% calcium gluconate or 10 mL of 10% CaCl2 | Indicated for moderate–severe symptoms; CaCl2 caustic to veins (use central access unless critical); continuous ECG monitoring required |
| Magnesium sulfate | 2 g over 10 min then 1 g/hr | Indicated if hypomagnesemia |
Pediatrics
Hypocalcemia is defined as:
- Infant: total serum calcium concentration of less than 1.8 mmol/L
- Older children: total serum calcium concentration of less than 2 mmol/L
Presentation:
- Stridor
- Paresthesia and tingling sensation around the mouth, fingers, and toes
- Tetany with carpopedal spasms
- Seizures
- Chvostek sign
- Trousseau sign
Two Signs You Need to Remember
Chvostek Sign
Tap on the zygomatic branch of the facial nerve (zygomatic bone) and observe the twitching of the mouth
Trousseau Sign
Carpopedal spasm occurs when BP cuff is inflated above systolic pressure 160 mmHg for 3 minutes