Pediatrics Rickets
Dr Faten Zaidan
Introduction
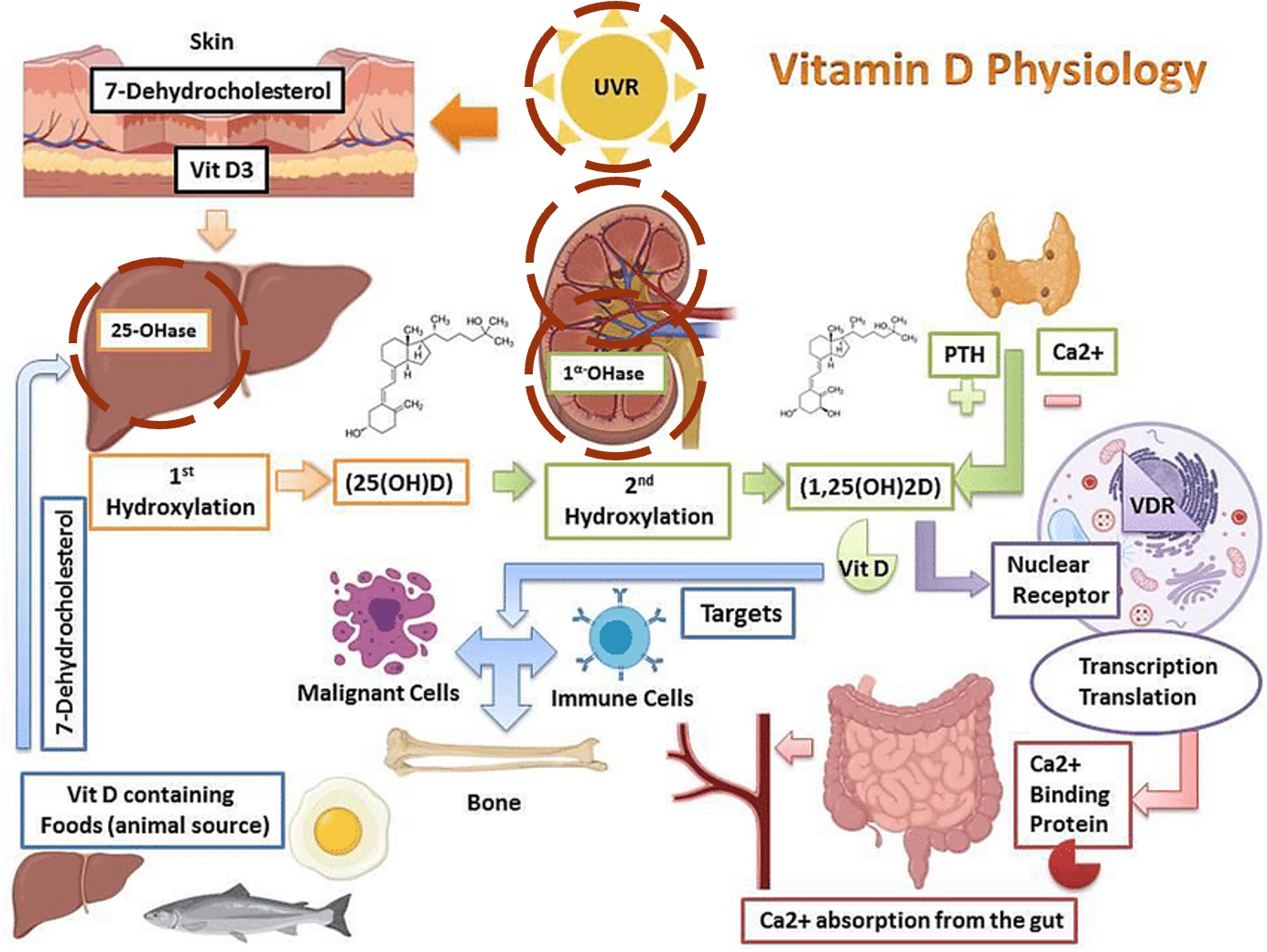
Calcium balance is achieved by calcium transport across three organ systems: intestines, kidney, bone through the effect of two hormones:
- PTH and 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D
A fall in calcium level is detected in parathyroid glands and renal tubules therefore increasing PTH and active Vitamin D. This leads to:
- Increased renal tubular reabsorption of calcium and decreased tubular reabsorption of phosphate and increased phosphate excretion. This is called the phosphaturic effect.
- Increased bone resorption leading to calcium release from bone into circulation.
- Stimulation of 1 alpha hydroxylase activity at the proximal renal tubule which results in increased secretion of 1.25(OH)2D and increased reabsorption of intestinal calcium.
Hypocalcemia can result from three categories of disorders:
-
Disorder of PTH secretion and action
- Congenital hypoparathyroidism
- Chromosome 22q11.2 deletion: DiGeorge Syndrome (calcium supplementation treatment)
- Acquired causes such as parathyroidectomy
-
Disorders of vitamin D deficiency or action
- Renal disease > 1 alpha hydroxylase deficiency or renal disease
- 25-hydroxylase deficiency or liver disease
- Vitamin D resistance
-
Abnormality of calcium sensing receptor
Causes of Hypocalcemia as per Age
Neonatal
-
Early (0-72 hours)
- Preterm
- LBW
- RDS (initially only)
- Asphyxia
- Acidosis
- Infants of diabetic mothers
- Exchange plasma transfusion
-
Late (after 72 hours)
- High phosphate milk
- Vit D deficiency
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Maternal hyperparathyroidism
- Mg deficiency
Later in Childhood
- VD Deficiency
- VD Metabolism Problems
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Calcium Deficiency
- Hypomagnesemia
- High Phosphate (e.g., enemas/tumor lysis syndrome)
Presentation of hypocalcemia
Type of rickets
Rickets is under-mineralization of the growth plate of a growing bone due to abnormality in the production or excretion of calcium and phosphate.
-
Calcipenic Rickets: Due to calcium and/or Vitamin D deficiency regardless of the cause
-
Phosphopenic Rickets: Due to Renal Tubular phosphate deficiency due to either renal loss or nutritional defect
Orthopedics
Rickets & Osteomalacia
Overview
- Same disease process affecting different age groups:
- Rickets: Children (growing skeleton)
- Osteomalacia: Adults (mature skeleton)
- Pathophysiology: Inadequate absorption and/or utilization of
- Common causes:
- Lack of Vitamin D → Severe deficiency
- Hypophosphatemia
- Result: Loss of mineralization of bone matrix
RicketsZ
Pathology
- Matrix forms but is not calcified (soft bone)
- In growing physis:
- Widened physis (epiphyseal growth plate)
- Cupping of metaphyseal end (weak new bone)
- Irregular metaphyseal end
- In all bone:
- Osteopenia (decreased bone density)
- Thin cortex
- Deformity

Clinical PictureZ
Skeletal Manifestations
- Enlarged ends of long bones:
- Wrists and knees most prominent
- Rickety rosary: Enlarged costo-chondral junctions
- Harrison’s sulcus: Horizontal groove at lower border of thorax
- Frontal bossing: Prominent forehead
Lower Limb Deformities
- Bowing of legs: most common presentation
- Localized – distal tibiae most affected
Systemic Symptoms (in severe cases)
- Tetany and convulsions (due to hypocalcemia)


Additional Clinical Signs

Harris’s sign (subluxation of costochondral junctions)

Rickety Rosary




Radiological Features
Primary X-ray Findings
- Widened physis (first and most prominent finding)
- Metaphyseal changes:
- Cupping (due to weak new bone)
- Irregular margins
- Deformed bones





Laboratory Results
| Parameter | Expected Findings |
|---|---|
| Serum Calcium | Slightly low or normal |
| Serum Phosphate | Slightly low or normal |
| Serum Alkaline Phosphatase | High (increased bone turnover) |
| Serum Vitamin D | Low |
| Serum PTH | Increased (secondary effect to maintain serum Ca) |
| Urinary Calcium | Very low |
Treatment
Primary Management ✓
- Vitamin D supplementation
- Calcium supplementation
Management of Deformities
- Most deformities correct gradually with medical treatment
- Severe deformities may require surgical correction


Hypophosphatemic Rickets
Overview
- Vitamin D resistant rickets
- Familial, X-linked inheritance
- Renal tubular acidosis → need very high doses of Ca2+
Pathophysiology
- Impaired renal tubular reabsorption of phosphate
Laboratory Results
| Parameter | Finding |
|---|---|
| Serum Phosphate | Low |
| Urinary Phosphate | High |
Treatment
- High dose Vitamin D
- Phosphate supplementation