Case 1 Z
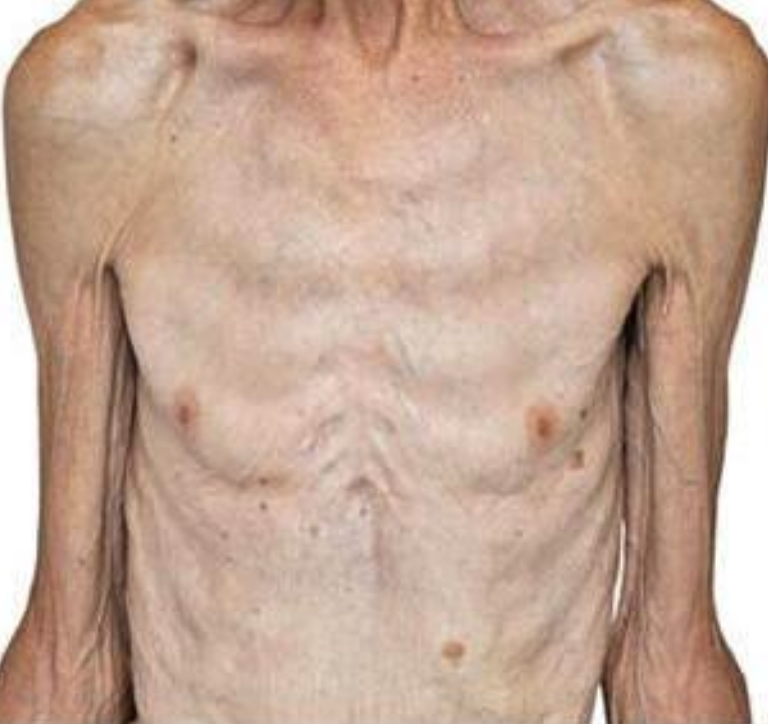 Patient with weight loss and diarrhea. Suspected of having malabsorption syndrome.
Patient with weight loss and diarrhea. Suspected of having malabsorption syndrome.
++ Female patient with diarrhea
Biopsy show: destructive intestinal mucosa..
And 20g. lipid in stool
-
Name any 2 etiologies of fat malabsorption? Celiac disease, pancreatitis.
-
Which serologic test will you do for the diagnosis of celiac disease? Serum anti-gliadin and anti-endomysial antibodies.
-
Name any imaging study which is used in the workup of malabsorption? CT Abdomen, Endoscope with biopsy.
Case 2
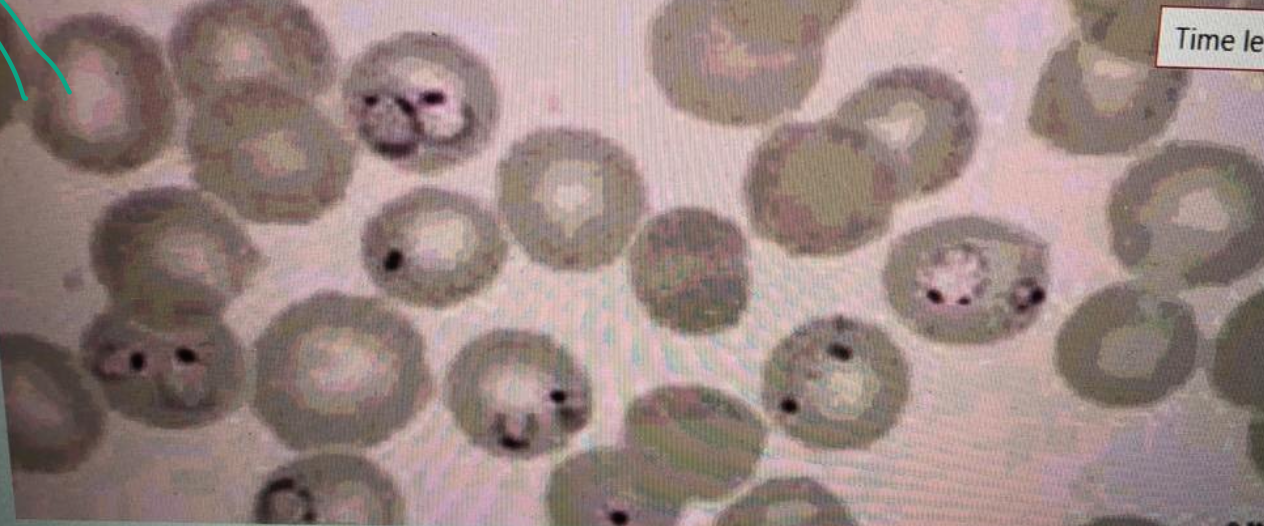 A 20-year-old male comes with fever since 5 days. Fever is episodic. The peripheral blood film is shown below.
A 20-year-old male comes with fever since 5 days. Fever is episodic. The peripheral blood film is shown below.
- What is your diagnosis based on the abnormality on the slide?
- Malaria.
- Outline 2 causes of anemia in this infection?
- Mechanical destruction of RBCs, reduced erythropoiesis in the bone marrow.
- Outline any 3 features of severe form of this infection? Z
- Cerebral malaria, blackwater fever, hypoglycemia
- Name any 2 medicines used to treat this infection, and one of them used during pregnancy?
- Hydroxychloroquine (Pregnancy), mefloquine.
Case 3
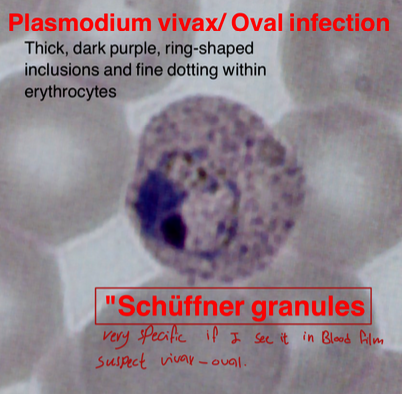 Thick, dark purple, ring-shaped inclusions and fine dotting within erythrocytes.
“Schüffner granules” (very specific if seen in blood film, suspect vivax-oval)
Thick, dark purple, ring-shaped inclusions and fine dotting within erythrocytes.
“Schüffner granules” (very specific if seen in blood film, suspect vivax-oval)
- Name the cause: Vivax - Oval
- Treatment: Primaquine
- What is the specific name? Schüffner granules
Case 4
 Ascites in liver cirrhosis
Ascites in liver cirrhosis
findings:
- Skin pigmentation
- Abdominal distention
- Visible vessels
Lab test:
- Saag
- Chemistry
- LFT
- U/S
Q&A
- Causes: Liver Cirrhosis - CHF
- Infectious Complication: Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
- What is SAAG? Serum Albumin to Ascites Albumin Ratio
- Diagnosis: Ascites
Case 5
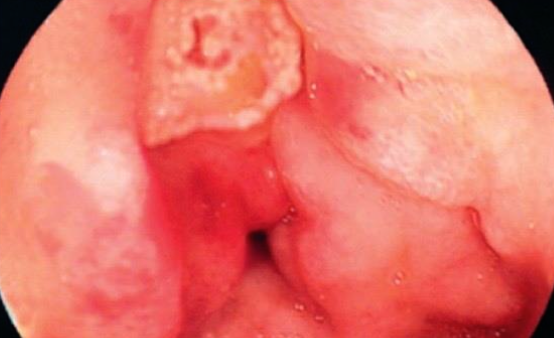 25 year old patient. Complaining of epigastric pain and dyspepsia since 1 month. Upper endoscopy showed duodenal ulcer as shown & H.pylori test was positive.
25 year old patient. Complaining of epigastric pain and dyspepsia since 1 month. Upper endoscopy showed duodenal ulcer as shown & H.pylori test was positive.
-
Name any 2 investigations used to diagnose H. pylori? Stool antigen test Urea breath test Z
-
Which combination of medicines is used to treat H. pylori infection?
- PPI’s - Omeprazole
- Clarithromycin
- Amoxicillin
-
Name any 1 complication of duodenal ulcer? Perforation
Case 6
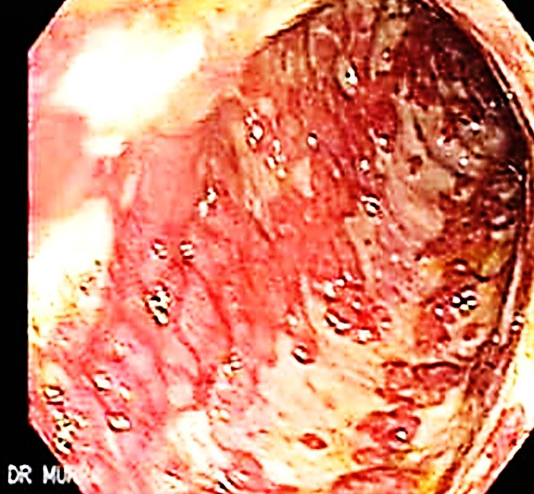 This is an endoscopic image of colon affected by ulcerative colitis. The mucosa is blotchy and broken in many places.
This is an endoscopic image of colon affected by ulcerative colitis. The mucosa is blotchy and broken in many places.
Q1: Name 3 common clinical symptoms of ulcerative colitis?
Lower abdominal pain, diarrhea, blood and mucus with the stool.
Q2: Name 2 features of a severe episode of UC?
Leukocytosis, increase frequency of the stool more than 6 times in the day, anemia.
#Z
Q3: Name 2 ttt options for UC?
5-ASA, Corticosteroids.
#Z
Q4: Name 3 extracolonic manifestations of UC?
Arthritis, Ancylosing spondylitis, Uveitis, Episcleritis
CASE 7
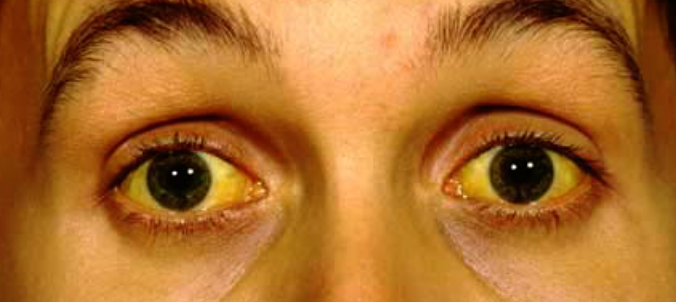 Q1: JAUNDICE
Q1: JAUNDICE
Q2: Mention 4 risk factors. Hemolytic Anemia. Alcohol - drugs: Paracetamol - GB stones
Q3: 4 Signs.
- Yellowish skin
Q4: Investigations. Serum Bilirubin, Urine Bilirubin, LFT
Q5: Treatment. Treat the cause
Case 8

A 47 year old woman complains of generalized tiredness, low mood, altered bowel habits and more recently generalized itching. O/E she has 4 cm hepatomegaly and xanthelasma around her eyes.
Her liver function tests show:
- Total bilirubin 60 μmol/l
- AST 35 IU/l
- ALT 34 IU/l
- ALP 180 U/l
- GGT 90 U/l
- Albumin 39 g/l
- AMA titer 1:140
-
Describe the abnormalities present?
a. Increases bilirubin, ALP, GGT, AMA -
Suggest 2 possible causes of this diagnosis? Z
1- Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
2- sclerosing cholangitis
Case 9
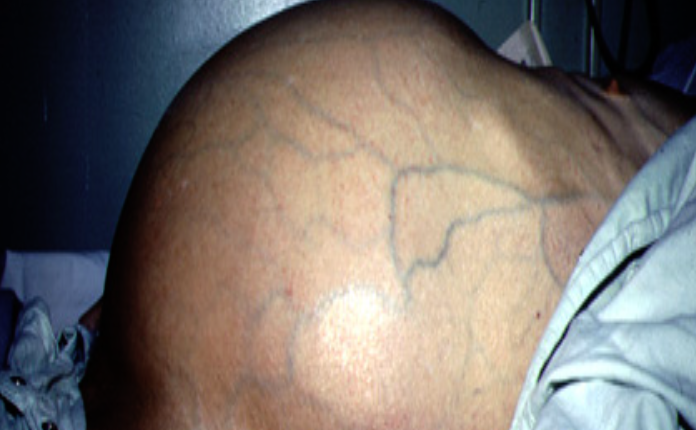
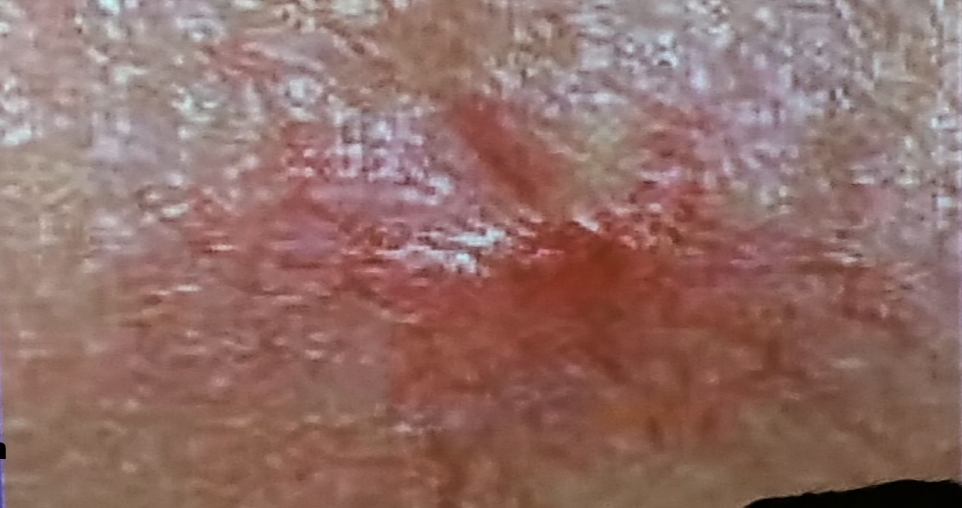 This lesion was found on routine medical examination of military recruit who was fit and has been medically free.
This lesion was found on routine medical examination of military recruit who was fit and has been medically free.
-
What is the lesion?
a. Spider-angioma -
Name 2 clinical conditions in which this lesion may be seen?
1-Cirrhosis (partial-HTN)
2-increase portal hypertension #Z -
What advice will you to this person?
a. Reassure
Peritoneal dialysis catheter
A 43 year old woman presented with diarrhea
The following results were obtained:
3 day fecal fat 30 mmol/day
Jejunal biopsy subtotal villous atrophy
#Z
-
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Celiac Disease -
What treatment is recommended?
Gluten-free diet