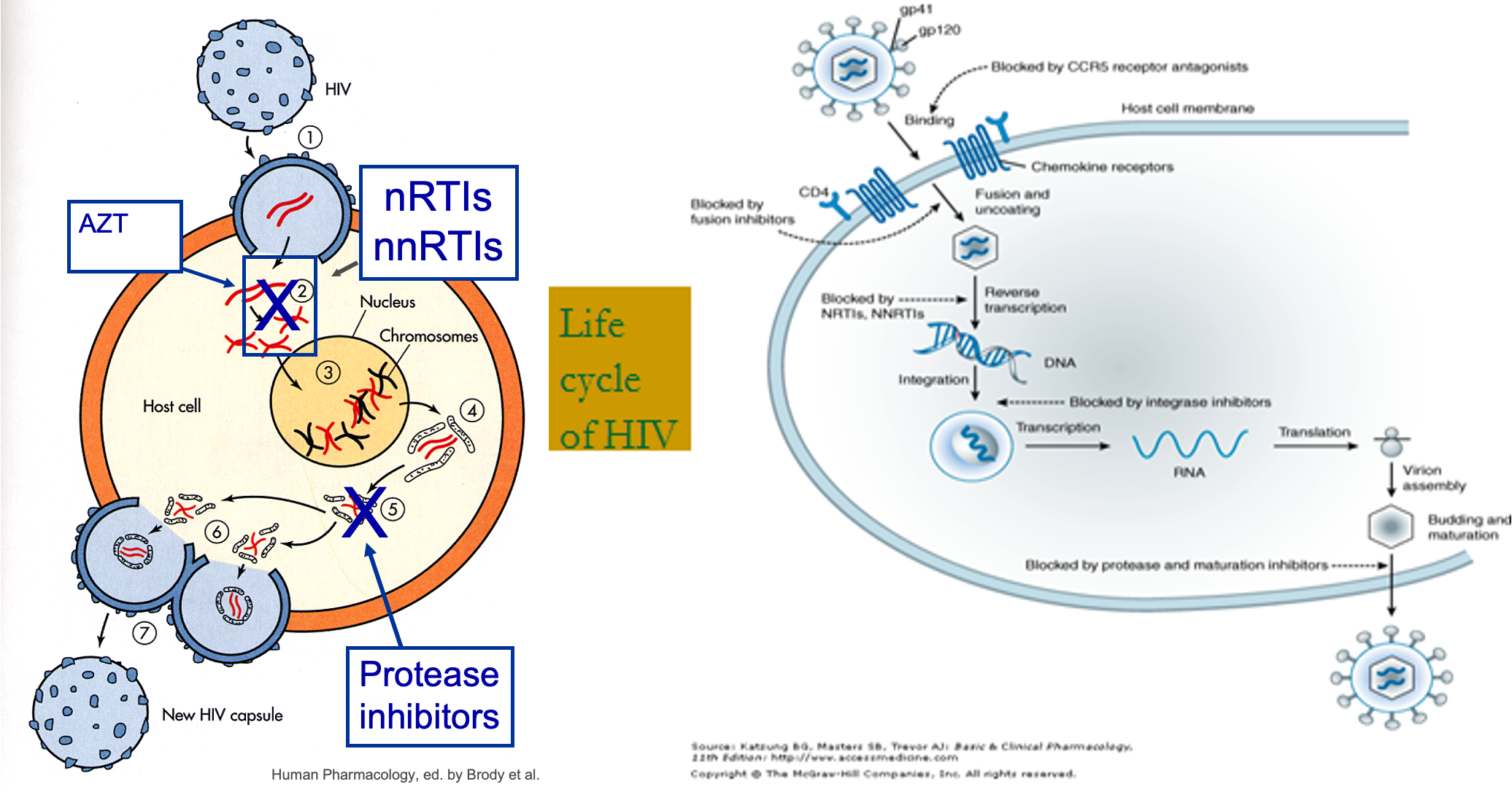
Replication of HIV
- Virion binding - CD4, chemokines
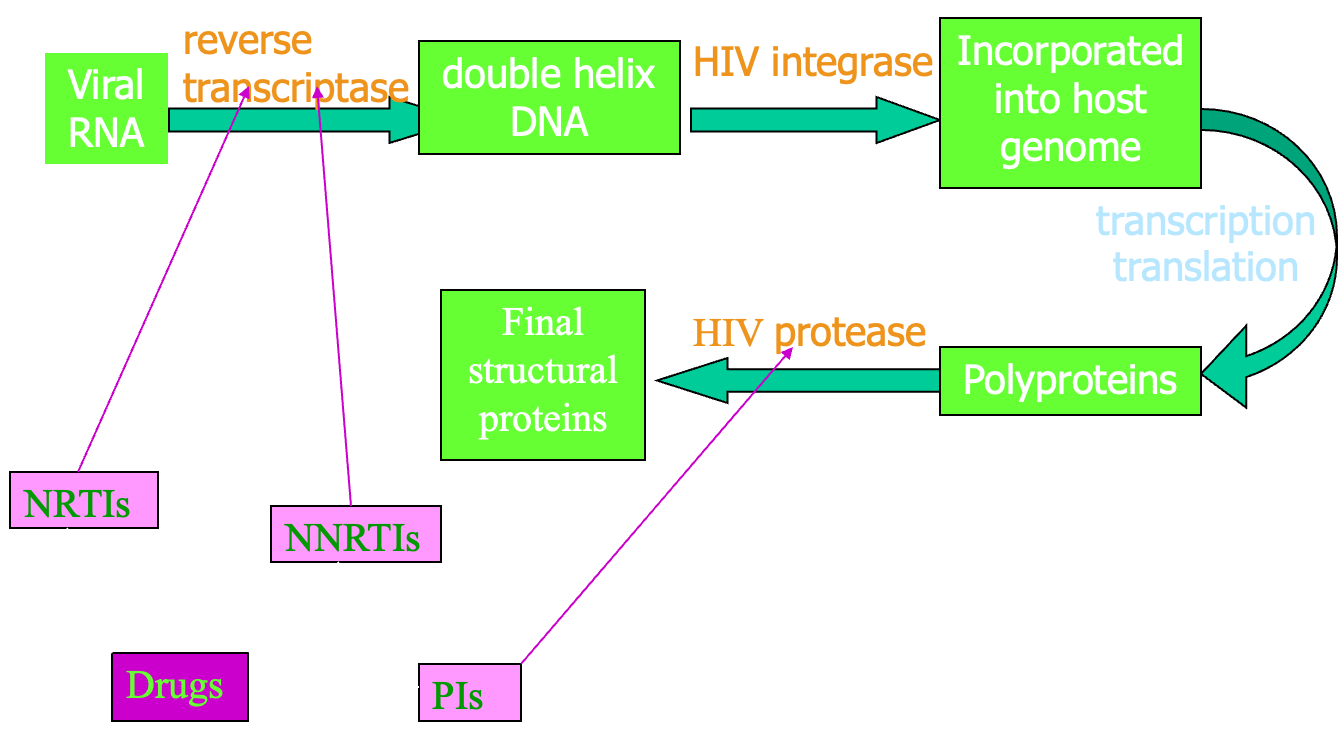
- Reverse transcriptase- RNA to DNA
- Integration of viral DNA
- Replication of viral RNA
- Protease
- Assembly of virions
- Release
Currently Available Drugs Z
| Type | Drugs… |
|---|---|
| 1. attachment - Fusion Inhibitors interfere with receptors (Enfumara) | - Enfuvirtide - Maraviroc |
| 2. Nucleoside analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitors PH3 (Vudine) | - ZIDOVUDINE first drug created for HIV - Lamivudine; used also for hepatitis - Emcitrabine - Entecavir |
| 3. Integrase inhibitors: (Ravir) | - Raltegravir |
| 4. Protease Inhibitors (Navir) | - Indinavir - Ritonavir - Saquinavir |
| Non-nucleoside; Direct reverse transcriptase inhibitors | - Nevirapine - Efavirenz |
| Nucleotide | - Tenofovir |
Why Does Treatment Fail?
- NON-ADHERENCE
- Intolerance
- Infection with a resistant virus
Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy Y
- The term Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART) is used to describe a combination of three or more anti-HIV drugs.
- Four approved classes of drugs in the HAART regimens:
- NRTI (Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors)
- NtRTI (Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors)
- NNRTI ( Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors)
- PI (Protease Inhibitors)
- Entry Inhibitors
- Integrase Inhibitors