IM
Ulcerative Colitis
Locations and Layers Involved Can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus.
-
From the rectum and spreads upwards (involves the large intestine only).
-
Only the mucosa and submucosa are affected. Affects a large area.
Pathophysiology
Interaction between genetic factors (family history + HLA DR mutation) and environmental factors like western diet (smoking reduces the risk of UC): Leads to dysregulated immune response and activation of Th2.
Th2 releases: (CONTINUOUS INFLAMMATION)
- IL4 and IL5: Recruits eosinophils and B-cells to the site of inflammation.
- IL13 is also released: Causing superficial mucosal inflammation = mucous secretion = goblet cell depletion
- IL-17 is also produced by Th17: Activates neutrophils = Polymorphonuclear cells aggregate
Histology
- Only affects mucosa and submucosa
- Goblet cell depletion
- Crypt abscess due cc
- Disturbed gland architecture
- Polymorphonuclear cells aggregate
- Continuous inflammation
Clinical Features
- Heavy bloody diarrhea
- Iron deficiency anemia: Micro Micro
- Tenesmus; urgency
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of haustra of the large colon
- Toxic megacolon
- Increased risk of large intestinal cancer
Z Top diff for jaundice + UC - Autoimmune liver Chronic = colorectal cancer ± metasteses to liver
Specific Investigations
- Antibodies: P-ANCA found also in Churg-Strauss syndrome RR
- Barium SBFT/enema: Lead pipe sign; dont use during flare
- Colonoscopy and biopsy: Friable mucosa, pancolitis, submucosal ulcers, and continuous lesions
- MRI:
- Loss of architecture, lead pipe appearance
- X-Ray: 1st prior to enema to r/o obstruction/flare
- Dilated colon ≥ 6 cm or pneumoperitoneum to rule out toxic megacolon.
Treatment of UC
-
Mild to moderate disease:
- Induce remission with 5-ASA or budesonide and maintain remission with 5-ASA or 6-MP or AZA if no response to 5-ASA.
-
Moderate to severe disease
- Induction of remission with prednisone then maintain remission with AZA or 6-MP or we can use infliximab; r/o TB
-
Severe/ refractory disease:
- Induce the remission with methylprednisolone or infliximab then maintain remission with Vedolizumab
Induction treatment: ciprofloxacin; DNA Gyrase inhibitor | Metrindiazole (giving to CD only in fistulating crohns, abdominal abcess; otherwise it will increase intestinal obstruction due healed fibrosis)
Surgery
is surgically curable generally performed for patients with toxic megacolon, patient with fulminant colitis and patients with precancerous lesions.
Imaging
PAIN ABDOMEN AND BLOODY DIARRHEA - ULCERATIVE COLITIS
- Occur usually after the age of 40 yeas
- disease always involves the rectum. When more extensive it extends in continuity around the colon, sometimes affecting the whole colon.
- Formation of mucosal ulcers (The cardinal radiological sign is widespread ulceration)
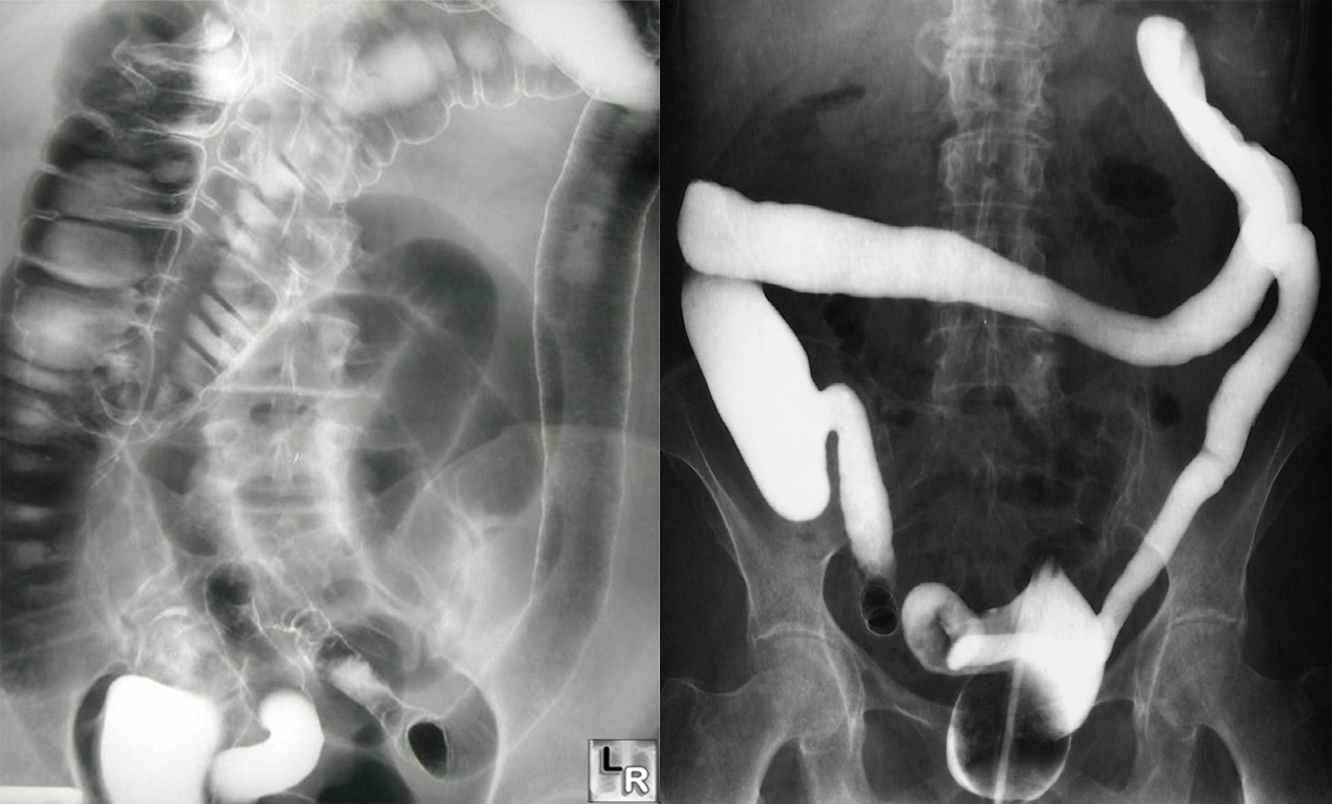
- Narrowing and shortening of colon
- Featureless colon give lead pipe appearances
- Carcinoma of colon in long standing cases.
Ulcerative colitis. With longstanding disease, the haustra are lost and the colon becomes narrowed and shortened, coming to resemble a rigid tube. Reflux into the ileum through an incompetent ileocaecal valve has occurred.
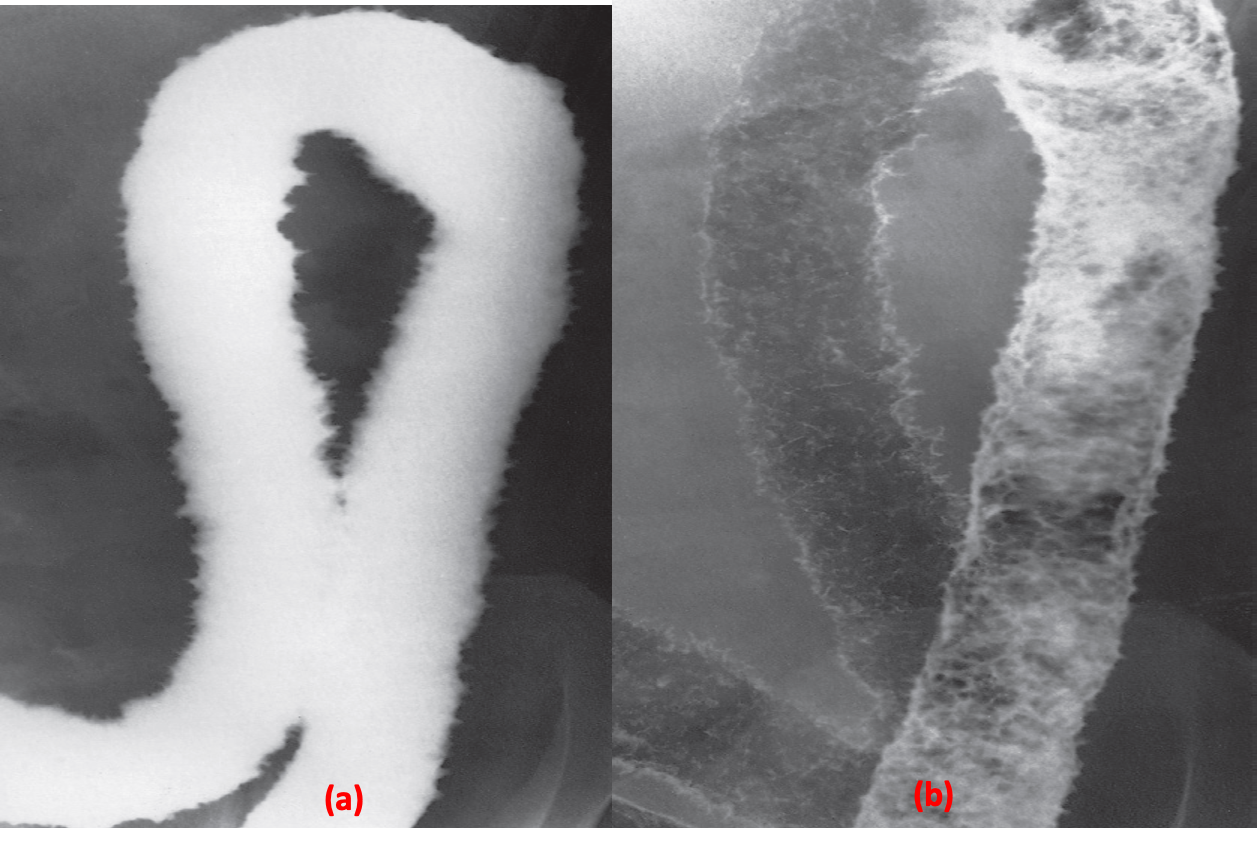
Ulceration. (a) Single contrast. (b) Double contrast.
In this case of ulcerative colitis, the ulceration causes the normally smooth outline of the colon to be irregular