Macular Diseases
- Age-related macular degeneration
Age-Related Macular Degeneration
- The incidence increases with each decade over age 50
- Main blind-causing disease in elderly
- Severe central visual loss
Etiology:
- Long-term chronic macular light damage, heredity, metabolism, nutrient factors
Mechanism:
- Decreased phagocytosis of RPE leading to drusen.
- Drusen can cause damage of Bruch’s membrane, CNV and fibrocyte proliferation
- Destruction of choroidal capillary, Bruch’s membrane, RPE and photoreceptor
Clinical Presentation
-
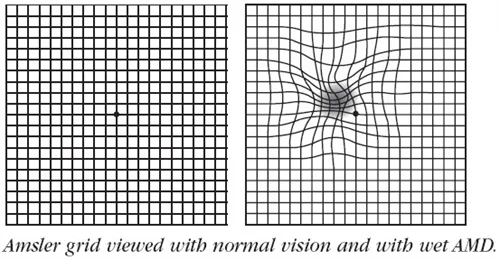
Visual acuity: decreased VA, metamorphopsia, micropsia
-
Visual field: central scotoma
-
Fundus:
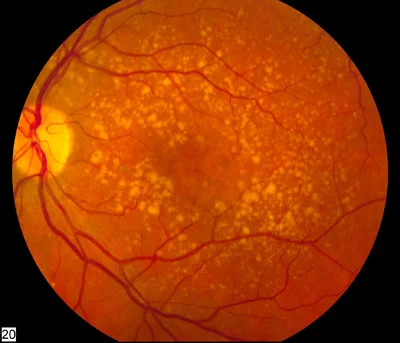
- Dry: drusen (yellow or white deposits that form between the retina and Bruch’s membrane.), RPE (Retinal Pigment Epithelium) change
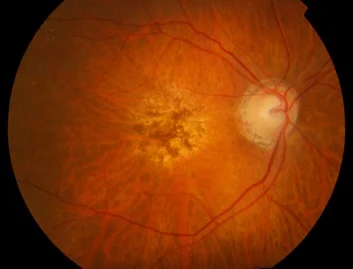
- Wet: gray-yellow CNV (Choroidal Neovascularization) under retina of posterior pole, associated with dark red subretinal hemorrhage, which covers CNV sometimes
-
FFA: CNV leakage, bleeding
-
Nonexudate:
- Drusen
- RPE atrophy
- Degeneration of photoreceptor
- Choroid capillary atrophy
- Exudate:
- Drusen
- Damage of Bruch’s membrane
- CNV - corroidal new vessels
- Disciform scar formation under macula, bleeding and leakage of CNV
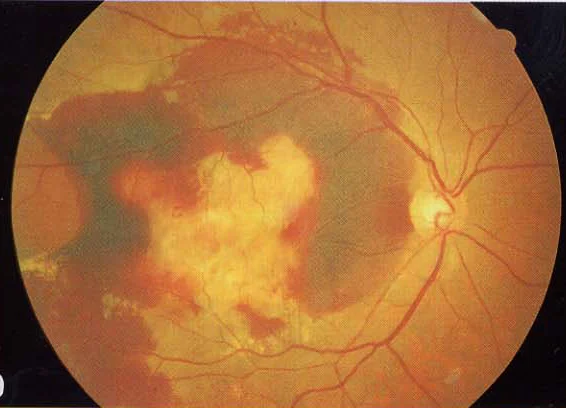
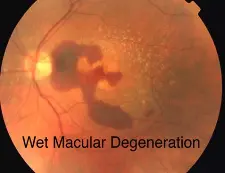
Exudative AMD
- Amsler grid viewed with normal vision and with wet AMD.

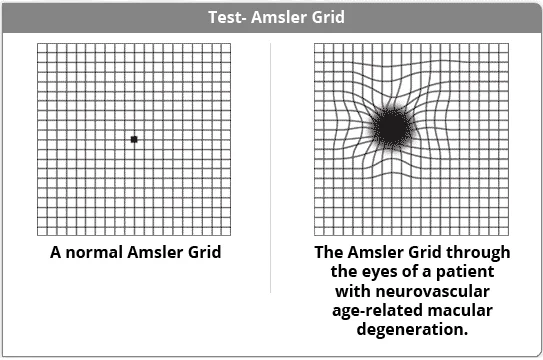
Test - Amsler Grid
-
A normal Amsler Grid
-
The Amsler Grid through the eyes of a patient with neurovascular age-related macular degeneration.
-
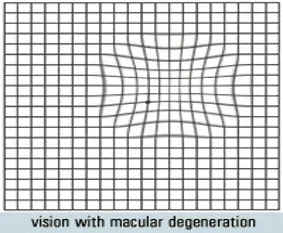
Vision with macular degeneration
FL,oct,Grid inv