All T4 & small amount of T3 are synthesized in the thyroid.
All steps Stimulated by TSH
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Uptake of iodide (Dietary sea shores vegetables & fruits or iodinated table salts) from plasma by thyroid gland actively by Na iodide transporter. |
| 2 | Oxidation of iodide to iodine by thyroid peroxidase |
| 3 | iodination of tyrosine: on thyroglobulin of the colloid of thyroid follicles to form monoiodotyrosine (MIT) & diiodotyrosine (DIT). |
| 4 | Coupling of DIT & DIT to form tetraiodothyronine (Thyroxine or T4) & Coupling of DIT & MIT to form triiodothyronine (T3). |
| 5 | Storage: MIT, DIT, T3 & T4 are stored in colloid bound to thyroglobulin Tg (120 Tyr/6 only). |
| 6 | Release: Thyroglobulin colloid is taken into the cells by endocytosis then by protease enzyme ⇒ release of T4, T3, MIT & DIT. |
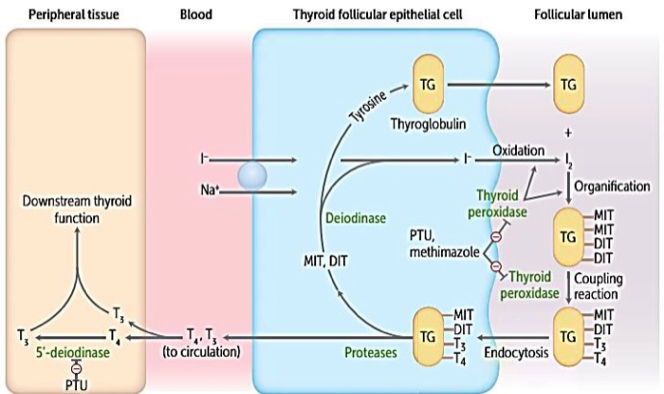
Thyroid peroxidase TPO is the enzyme responsible for oxidation and organifcation of iodide as well as coupling of monoiodotyrosine (MIT) and di-iodotyrosine (DIT).
Antibodies against thyroid peroxidase are present in more than 90% of patients with autoimmune (Hashimoto’s) thyroiditis.
Antithyroid Drugs
- Thiocyanate and perchlorates inhibits iodine uptake
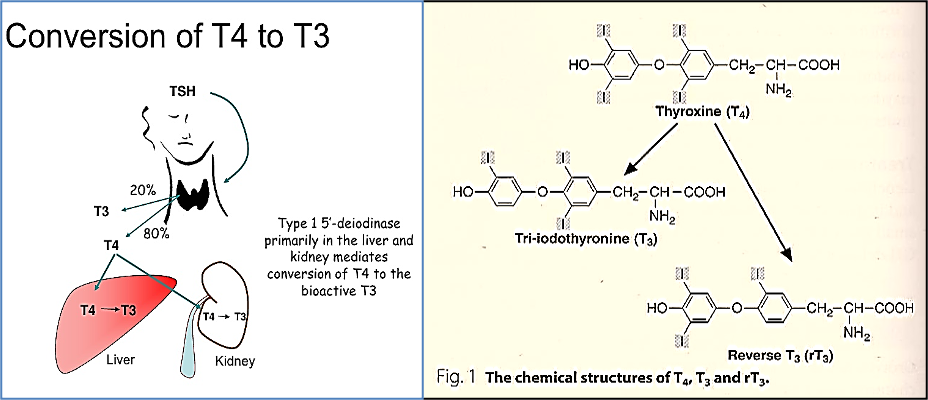
- Propylthiouracil (PTU) inhibits both thyroid peroxidase and 5′-deiodinase
- Methimazole inhibits thyroid peroxidase only.
- Potassium iodide inhibit the process of proteolysis of thyroglobulin
- Glucocorticoids inhibit peripheral conversion of T4 to T3.