Parasitic Infestations CS-OSPE
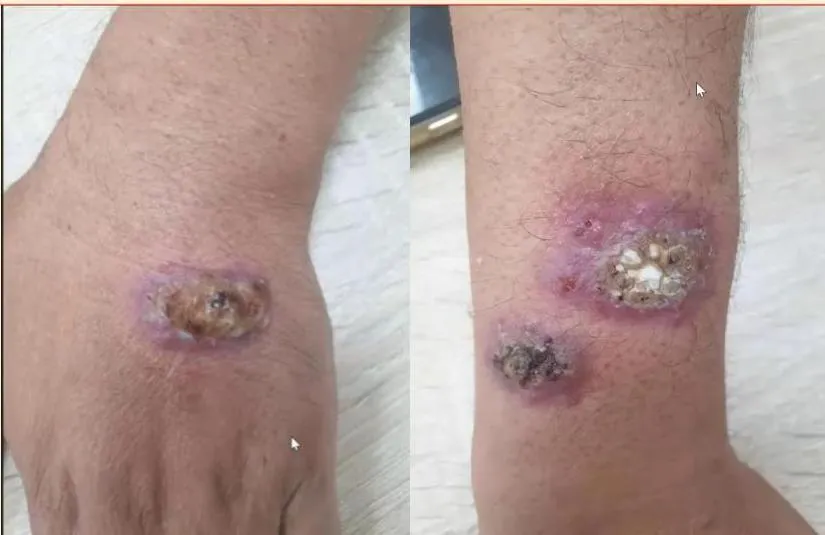
Cutaneous leishmaniasis Z
Working in King Salman forest, developed this lesion from Sandfly bite
diff basal cell carcinoma
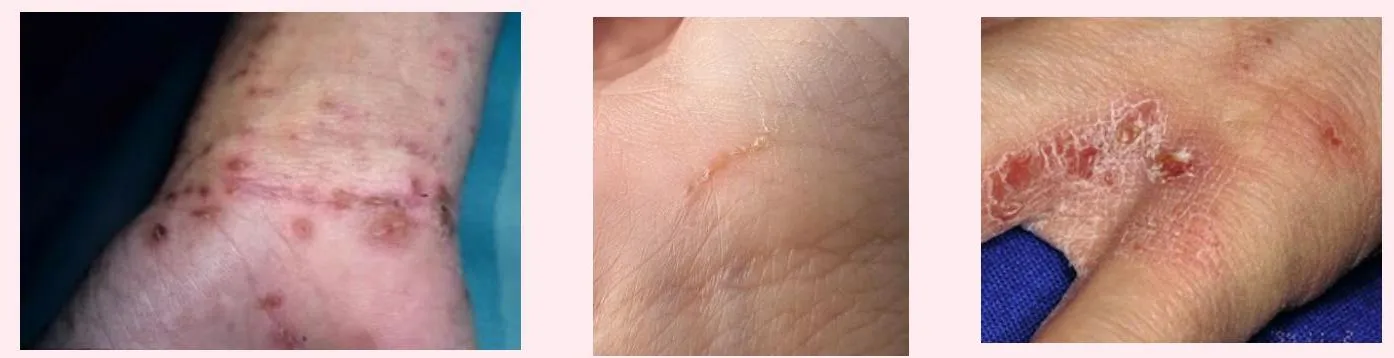
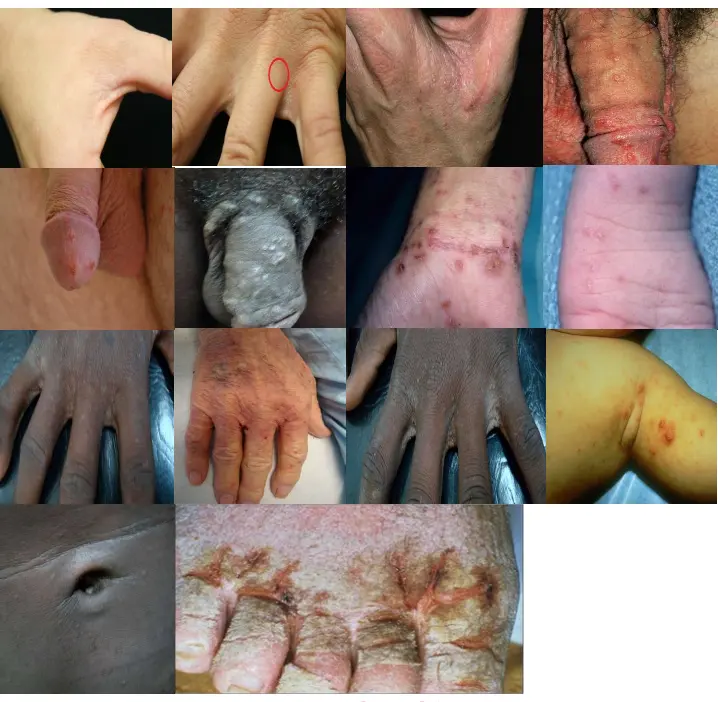
Scabies
A 27-year-old man presents with severe itching, that started two weeks ago and has progressively worsened. He reports that his roommates have similar symptoms.
What is the diagnosis?
- Scabies.
Describe the morphology / Clinical Presentation:
- Linear burrows, papules, or vesicles with intense pruritus.
- Pruritic itching which increases at night.
- Burrows.
- Commonly involves the axillae, breasts, umbilicus, penis, scrotum, finger webs, and wrists.
Causative organism? / Pathology:
- Sarcoptes scabiei – scabies mite / Host-specific mite, Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis.
Name two types of this disease? / Types:
- Classical.
- Crusted: Usually affects immunocompromised individuals or the elderly.
What other sites should be examined to support the diagnosis?
- Wrist (flexor aspect)
- Interdigital web spaces
- Groin (genital area)
- Axillae
- Breasts
- Umbilicus
- Penis
- Scrotum
- Finger webs
What investigation is done to confirm the diagnosis? / What in-office procedure would best help to confirm the diagnosis of scabies?
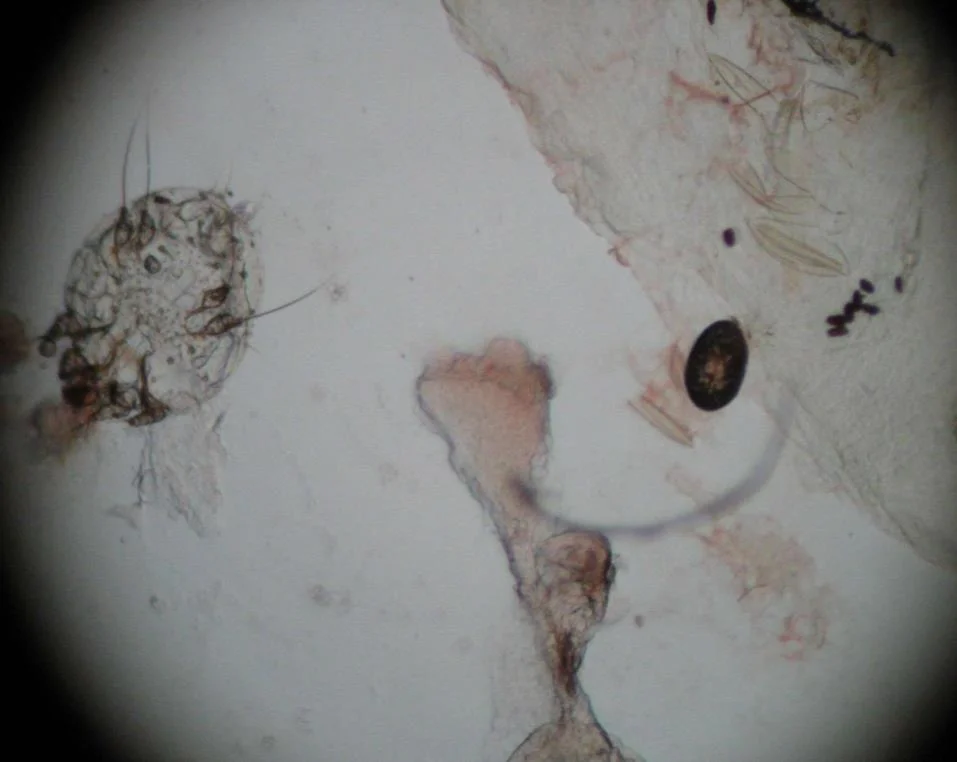
- Skin scraping (mineral oil preparation) + microscopic examination.
What will you see?
- Mites, eggs, and scybala (feces).
Treatment options? / First line of treatment is?
- Scabicidal agents:
- 5% permethrin cream (1% and 5% cream).
- Must be applied 10 minutes after shampooing and drying hair completely.
- No hair washing for 24 hours.
- Sulfur
- Lindane (gamma benzene hexachloride): Has potential neurotoxicity if abused.
- Crotamiton (Eurax) 10% cream or lotion.
- Malathion 0.5% lotion: Protecting against re-infection for 6 weeks.
- 5% permethrin cream (1% and 5% cream).
- Oral treatment: Ivermectin.
- Antipruritic agent (e.g., sedating antihistamine).
- Antimicrobial agent if secondarily infected.

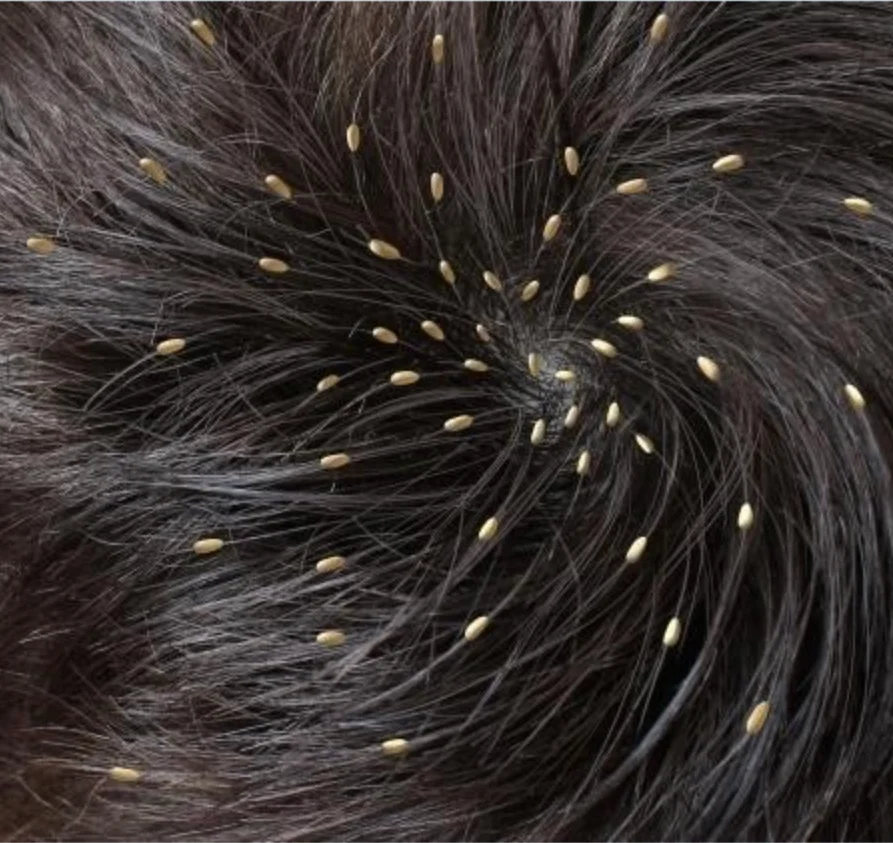

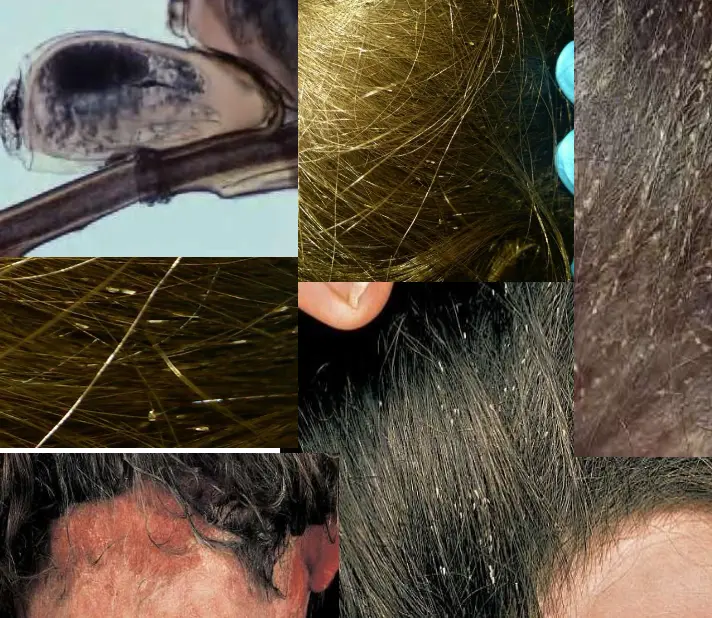
Pediculosis Capitis
This kid came with itchy scalp, reported one of her family member has the same. A 10-year-old schoolgirl presented with itchy scalp and when you examined her hair you found this picture.
What is the diagnosis?
- Pediculosis Capitis (head louse) / Head lice (Pediculosis Capitis)
To confirm this diagnosis?
- Seeing nits on the scalp in clinical exam
What are the clinical presentations?
- Pruritic eruption on back of scalp and nape.
- Excoriations & secondary infections (lice dermatitis).
- Multiple nits present. No lice noted.
- May also have posterior cervical lymphadenopathy.
What is the pathology?
- Pediculus humanus capitis.
Treatment options?
- Permethrin:
- 1% and 5% cream.
- Must be applied (10 min) after shampooing and drying hair completely.
- No hair washing for 24 hours.
- Pyrethrin
- Malathion 0.5% lotion:
- Protecting against re-infection for 6 weeks.
- Lindane (gamma benzene hexachloride):
- Has potential neurotoxicity if abused.
- Crotamiton (Eurax) 10% cream or lotion.
- Oral Ivermectin
- Head lice (Pediculosis Capitis)
- Children
- Body lice (Pediculosis Corporis)
- Homeless people and vagrants
- Public lice (Pediculosis Pubis)
- STD (partner should be treated)
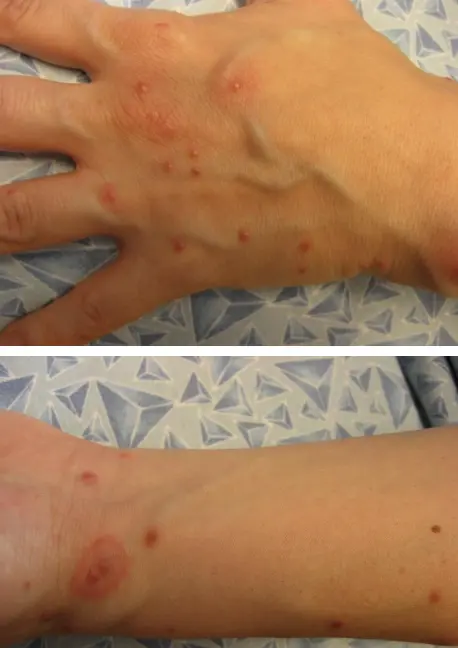
Bedbug bites
What is the diagnosis?
- Bedbug bites.
What is the clinical presentation?
- Edematous papules scattered over the body, some are excoriated.
What is the pathology?
- Cimex Lectularius.
What investigations are done?
- Skin scraping (mineral oil preparation).
What is the treatment?
- Typically resolve within 1-2 weeks.
- For symptomatic relief, treat with potent topical steroids and antihistamines.