Internal Medicine
IBD
By Isra Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Introduction
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is an idiopathic disease caused by a dysregulated immune response to host intestinal microflora. The two major types of inflammatory bowel disease are:
Although UC and CD have distinct pathologic findings, approximately 10%-15% of patients cannot be classified definitively into either type; this is labeled as indeterminate colitis.
Both UC and CD usually have waxing and waning intensity and severity.
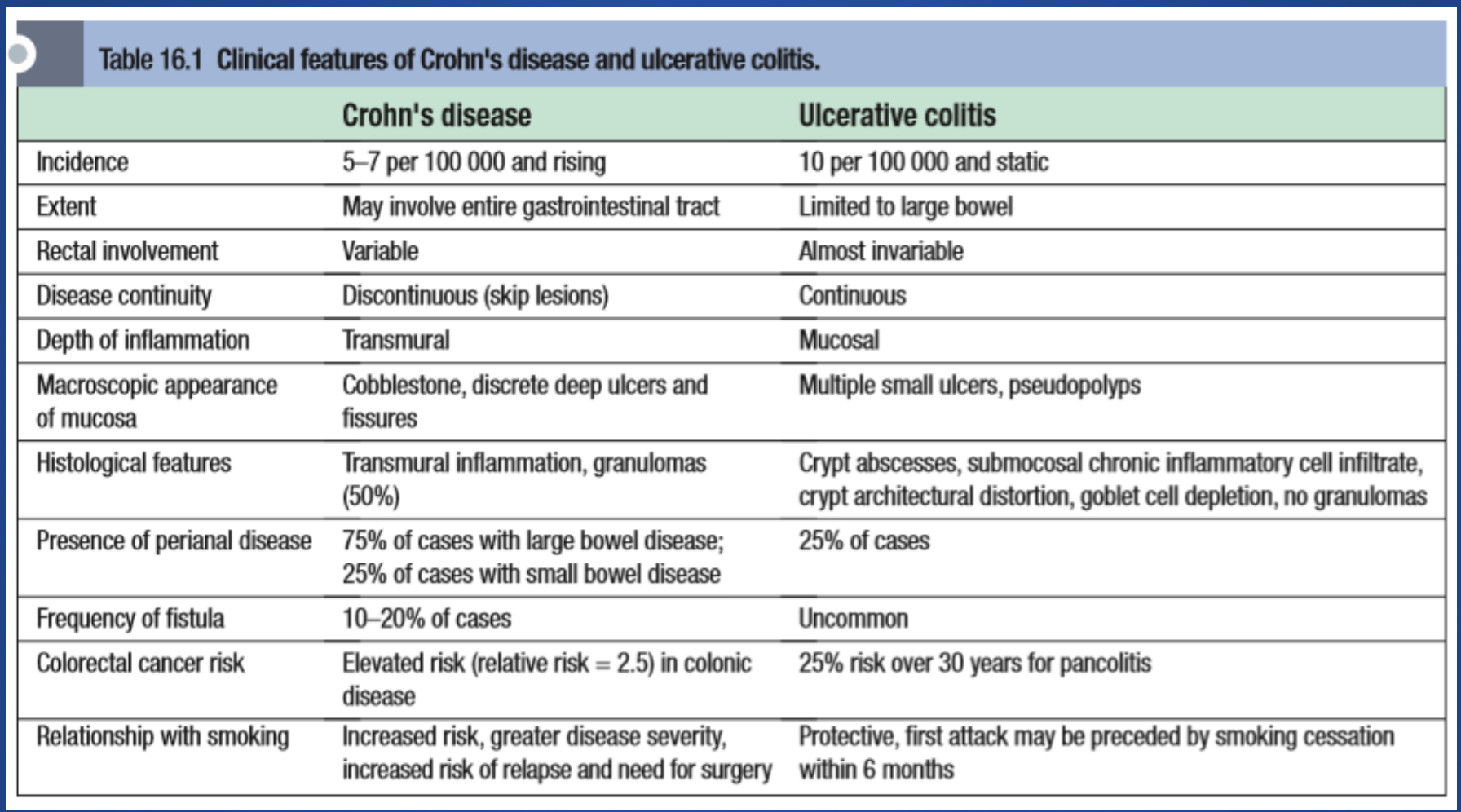
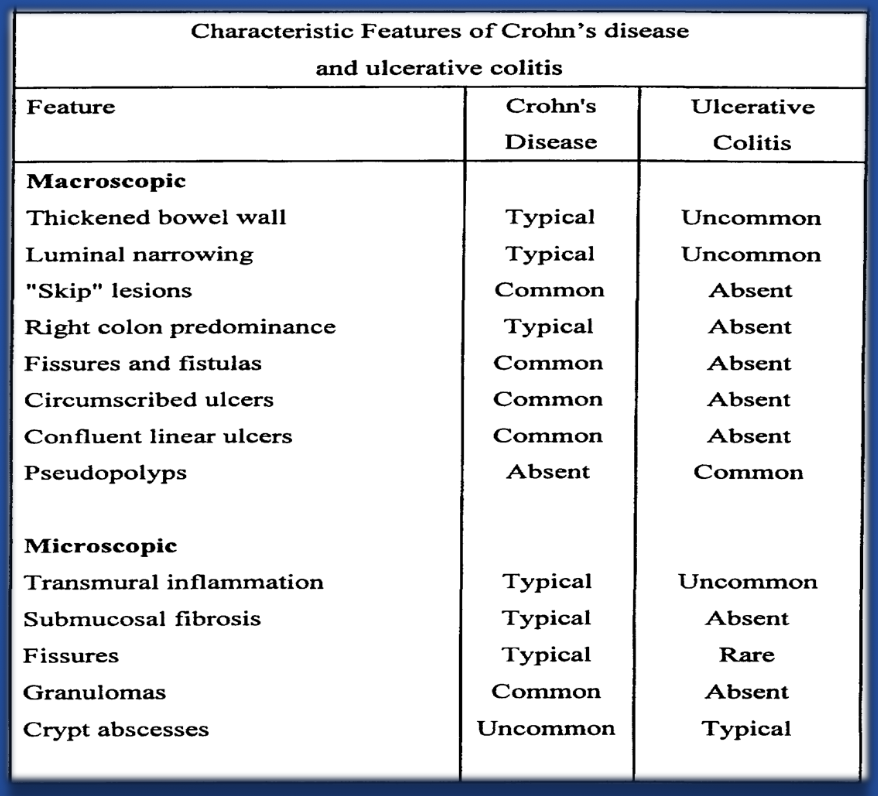
Comparison of Crohn’s Disease (CD) and Ulcerative Colitis (UC)
| Feature | Crohn’s Disease (CD) | Ulcerative Colitis (UC) |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Any part of the GI tract, mouth to anus, skip lesions | Colon and rectum only, continuous lesions |
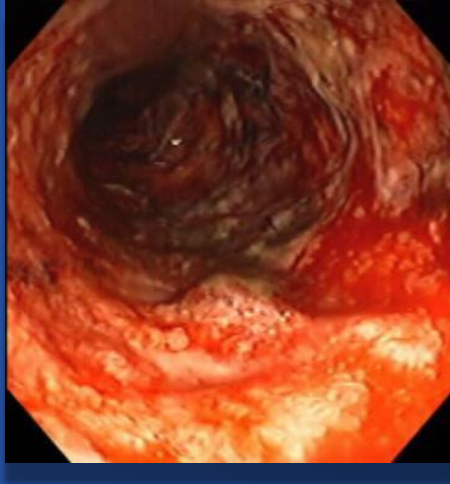
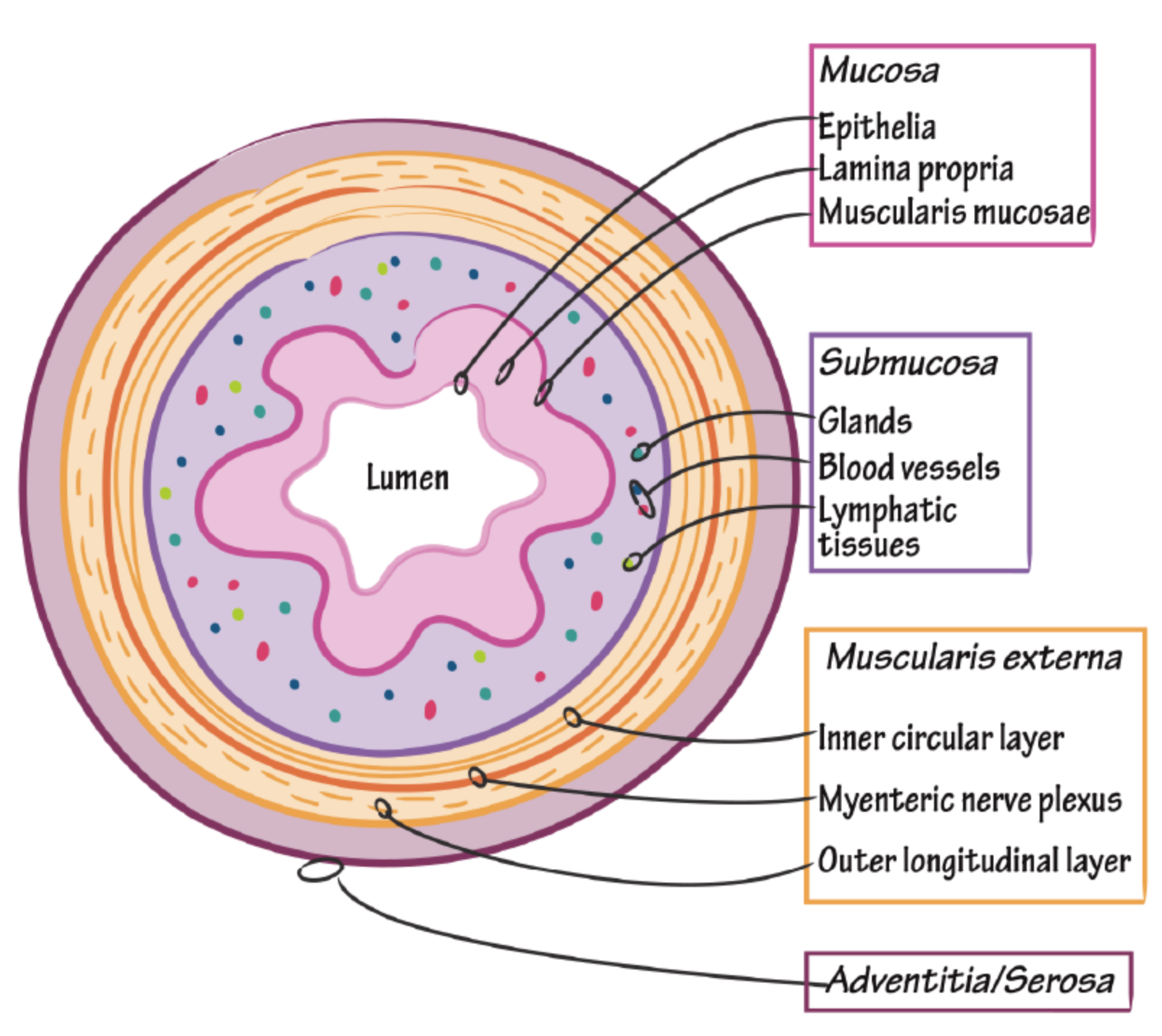
| Depth | Transmural (all layers of bowel wall) may result in ulcers, transmural ulcers, resulting in fistula formation | Mucosa and submucosa only - rarely presents as feature of fistula formation |
| Inflammation | Patchy, granulomatous | Diffuse, continuous |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, fatigue, fever | Bloody diarrhea, urgency, tenesmus, abdominal pain |
| Complications | Strictures, fistulas, abscesses, perianal disease | Toxic megacolon, perforation, colorectal cancer risk |
Etiopathogenesis & Pathogenesis of IBD
IBD results from unregulated immune responses to gut commensals in genetically susceptible individuals. Cytokines, released by macrophages in response to various antigenic stimuli, cause differentiation of lymphocytes into different types of T cells.
- Helper T cells, type 1 (Th-1): Principally associated with Crohn disease.
- Th-2 cells: Principally associated with ulcerative colitis.
The immune response disrupts the intestinal mucosa and leads to a chronic inflammatory process.
\
Extraintestinal Manifestations of IBD Z
- Arthritis: Peripheral arthritis, sacroiliitis (bamboo sign) - more in UC, spondylitis.
- Skin: Erythema nodosum + pyoderma gangrenosum around stoma, extensor surfaces, injury sites - more in Crohn’s.
- Mouth: Aphthous ulcers, stomatitis - more in Crohn’s.
- Eyes: Anterior uveitis, scleritis, episcleritis - more in Crohn’s.
- Anemia: Anemia of chronic disease in both.; microcytic
- Clubbing
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis: Associated with UC.
General Investigations for IBD
- CBC: Anemia + leukocytosis - FLARE
- High ESR and CRP: Especially with disease flare. -
- Fecal calprotectin: To rule out IBS - C. deficille w/ antibiotic hx usage cc
- Stool for ova and parasites, stool culture: To rule out infectious agents.
Top DIFF IBS, celiac, gastrointestinal infection
Specific Investigations: CD vs. UC
| Investigation | Crohn’s Disease (CD) | Ulcerative Colitis (UC) |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ASCA positive | P-ANCA positive |
| Barium SBFT/enema | String sign | Lead pipe sign found also in Churg-Strauss syndrome |
| Colonoscopy/Biopsy | Skip lesions, cobblestoning, transmural ulcers | Friable mucosa, pancolitis, submucosal ulcers, continuous lesions |
| MRI | Creepy appearance of fat | Loss of architecture, lead pipe appearance |
| X-Ray | Air-fluid level, dilated loops (rule out SBO) | Dilated colon ≥ 6 cm, pneumoperitoneum (toxic megacolon) |
Treatment
| Disease Severity | Crohn’s Disease (CD) | Ulcerative Colitis (UC) |
|---|---|---|
| Mild to Moderate | Ileal: Oral budesonide → 6-MP or AZA Colonic: 5-ASA → 5-ASA | 5-ASA or budesonide → 5-ASA or (if no response to 5-ASA) 6-MP or AZA |
| Moderate to Severe | Prednisone → AZA or 6-MP or Infliximab | Prednisone → AZA or 6-MP or Infliximab |
| Severe/Refractory | Methylprednisolone or Infliximab → Vedolizumab or Ustekinumab | Methylprednisolone or Infliximab → Vedolizumab |
Surgery: CD vs. UC
| Feature | Crohn’s Disease (CD) | Ulcerative Colitis (UC) |
|---|---|---|
| Curative? | No | Yes |
| Indication | Complications (strictures, fistulas, perianal disease); short bowel syndrome | Toxic megacolon, fulminant colitis, precancerous lesions |
| Type | Conservative resection | Total colectomy with ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA) |
Surveillance
- 8-10 years after diagnosis in all patients to stage histologic activity and guide future surveillance.
- At diagnosis in primary sclerosing cholangitis = MOST LIKELY COLERECTAL CANCER.
- Targeted to biopsy the suspicious mucosal abnormalities to rule out dysplasia.
- Next colonoscopy is planned according to the degree of dysplasia: either annually, after 3 years, or after 5 years.
SURGERY
Idiopathic disease caused by a dysregulated immune response to host intestinal microflora.
Major types:
-
Ulcerative colitis (UC), which is limited to the colonic mucosa
-
Crohn disease (CD), which can affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract from the mouth to the anus
-
Manifestations depend on the area of the intestinal tract involved
-
Not specific
World Gastroenterology Organization WGO
- Diarrhea: Possible presence of mucus/blood in stool; occurs at night; incontinence
- Constipation: May be the primary symptom in UC limited to the rectum
- Bowel movement abnormalities: Possible presence of pain or rectal bleeding, severe urgency, tenesmus
- Abdominal cramping : Commonly present in the RIF in CD; occur in the periumbilical or in the left lower quadrant in UC
- Nausea and vomiting: More in CD than in UC
Diagnosis:
- Labs: CBC, Serology (Perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA), anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies (ASCA), Nutritional
-
Radiology:
- Barium double-contrast enema radiographic studies
- Abdominal ultrasonography
- CT/MRI
-
Investigation procedures:
- OGD/Colonoscopy, with biopsies
- Capsule enteroscopy
Management:
Medical approach for symptomatic care, & mucosal healing
Surgical:
- Resection is not curative in CD
if complications:
- Perforation
- Stricture
- Fistula
- Malignancy
- Abscess/ collection
Table Comparision
| Feature | Ulcerative Colitis | Crohn Disease |
|---|---|---|
| Extent | Only colon involved | Panintestinal |
| Inflammation Pattern | Continuous, extending proximally from rectum | Skip-lesions with intervening normal mucosa |
| Depth of Inflammation | Mucosa and submucosa | Transmural |
| Perianal Lesions | Absent | Present |
| Granulomas | Absent | Noncaseating granulomas present |
| Bleeding | Common | Uncommon |
| Fistulae | Rare | Common |