Definitions
Sustained increase of Arterial blood pressure
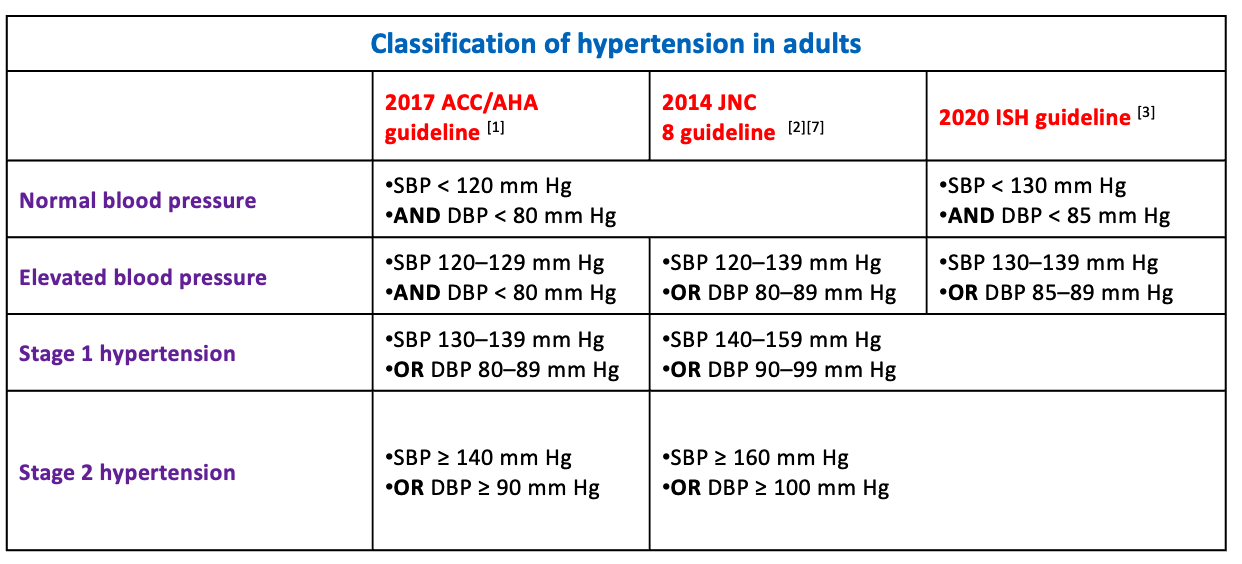
Hypertension in adults: 2020 International Society of Hypertension (ISH) and 2014 JNC 8: persistent SBP ≥ 140 mm Hg and/or DBP ≥ 90 mm Hg
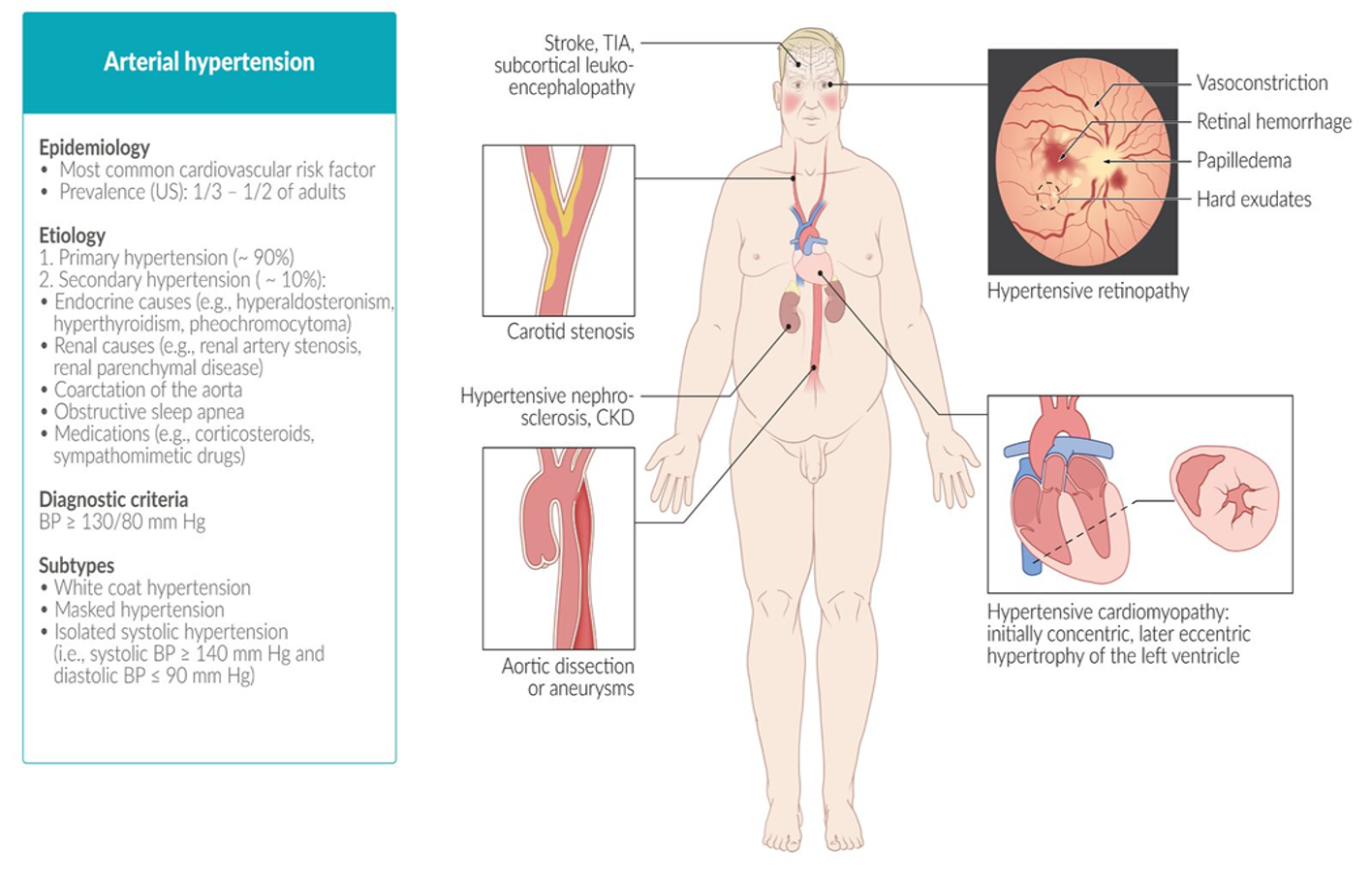
Primary hypertension: hypertension with no identifiable cause
Secondary hypertension: hypertension caused by an identifiable underlying condition
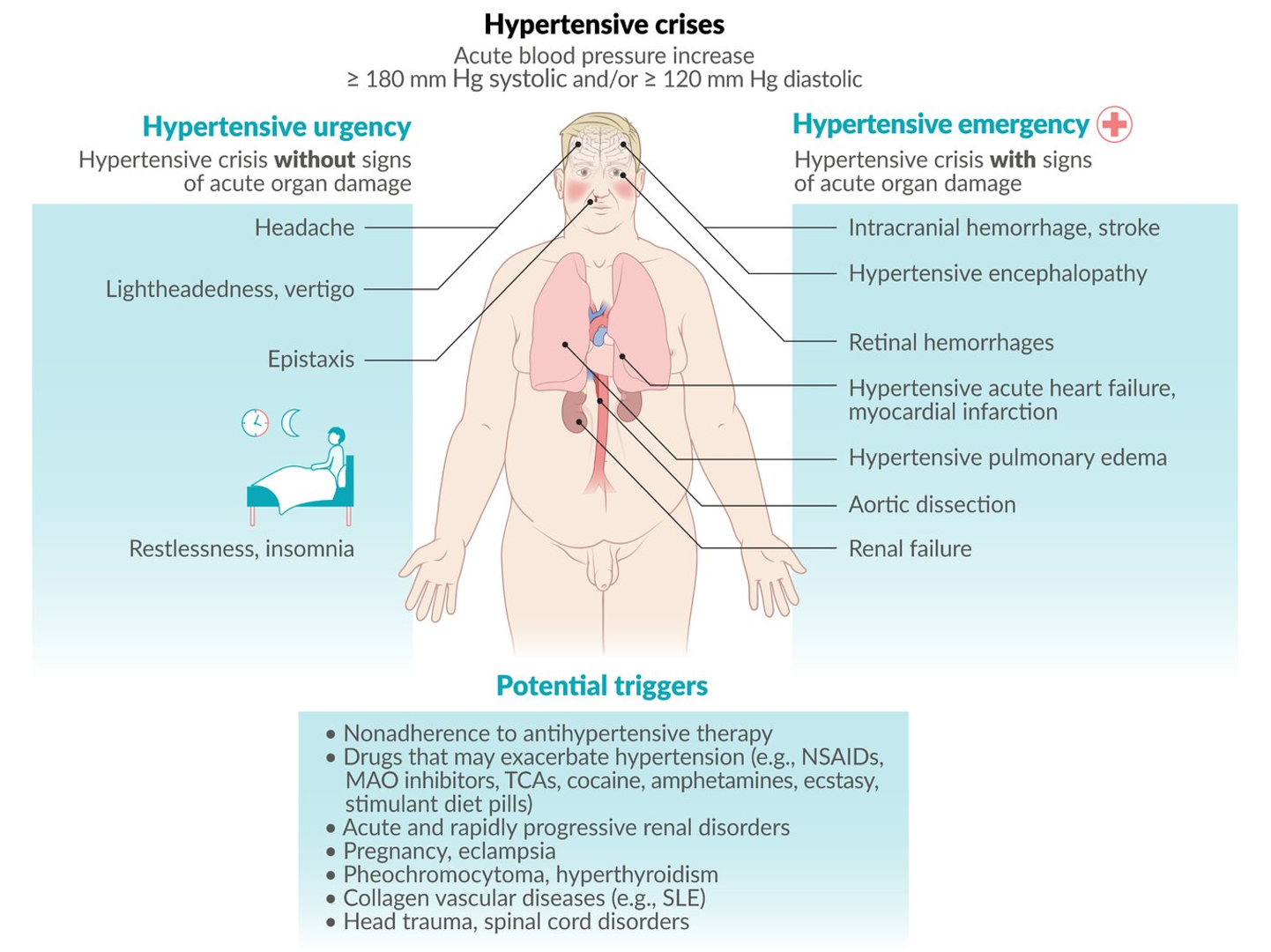
Acute severe Hypertension (Malignant HPTN): An increase in systolic blood pressure above 180 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure above 120 mmHg.
Epidemiology
Prevalence Hypertension affects between approximately one-third and one-half of adults in the US.
- Primary hypertension: 90%-95% of cases in adults .
- Secondary Hypertension: 5-10% of cases in adults
Prevalence increases with age: Approx 65–75% of adults develop it by 65–74 years of age. ∼ 60–87% of overweight & ∼ 73–95% of obese patients are affected.
Sex –♂ > ♀ below 65 years of age –After menopause, prevalence increases in women.
C.L. Features
-
Hypertension is usually asymptomatic until:
- Complications of end-organ damage arise
- Or an acute increase in blood pressure occurs (“Hypertensive crisis”)
-
Nonspecific symptoms of primary hypertension
- Headaches, esp. early morning or waking headache
- Dizziness, tinnitus, blurred vision
- Flushed appearance
- Epistaxis
- Chest discomfort, palpitations
- Strong, bounding pulse on palpation
- Nervousness
- Fatigue, sleep disturbances
- Secondary hypertension usually manifests with symptoms of the underlying disease.
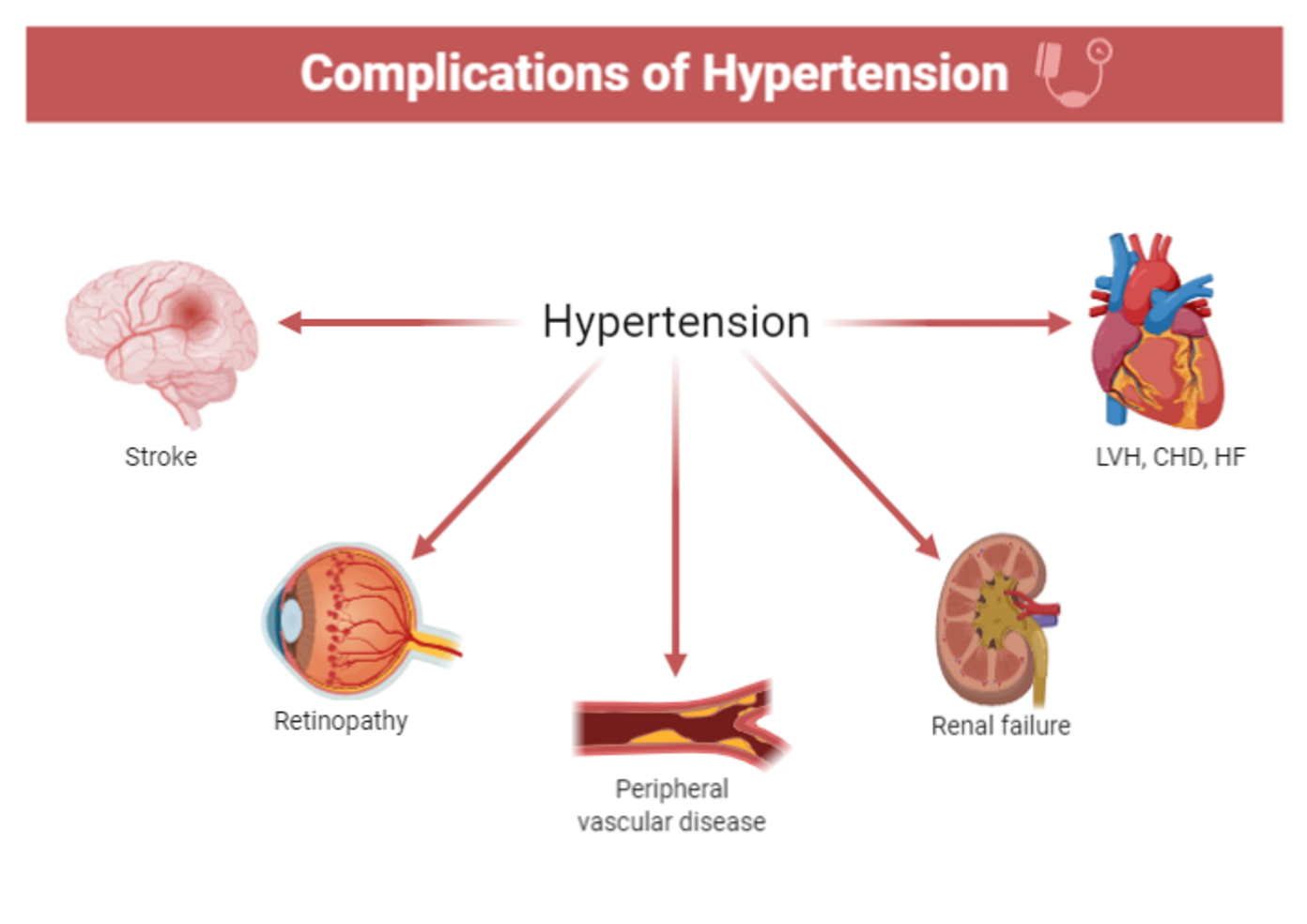
Complications
-
Arterial hypertension is the most common risk factor for cardiovascular disease
-
It leads to chronic changes in the vascular endothelium, particularly of the small vessels, and can therefore affect any organ system.
-
Acute severe hypertension causes “Hypertensive crisis”
- Vascular: - Macro-angiopathy: Atherosclrosis & - Micro-angiopathy: Arteriolosclerosis (hyaline or hyperplastic)
- Heart: LVH, Hypertensive cardiomyopathy → IHD, MI
- Kidney: Hypertensive nephrosclerosis
- Eyes: Hypertensive retinopathy
- Brain:
Cardiovascular system (hypertensive vascular disease)
- Left ventricular hypertrophy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy
- Congestive heart failure
- Coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction
- Atrial fibrillation
- Aortic aneurysm
- Aortic dissection
- Carotid artery stenosis
- Peripheral artery disease
- Atherosclerosis
Microscopy of Hypertensive vascular disease
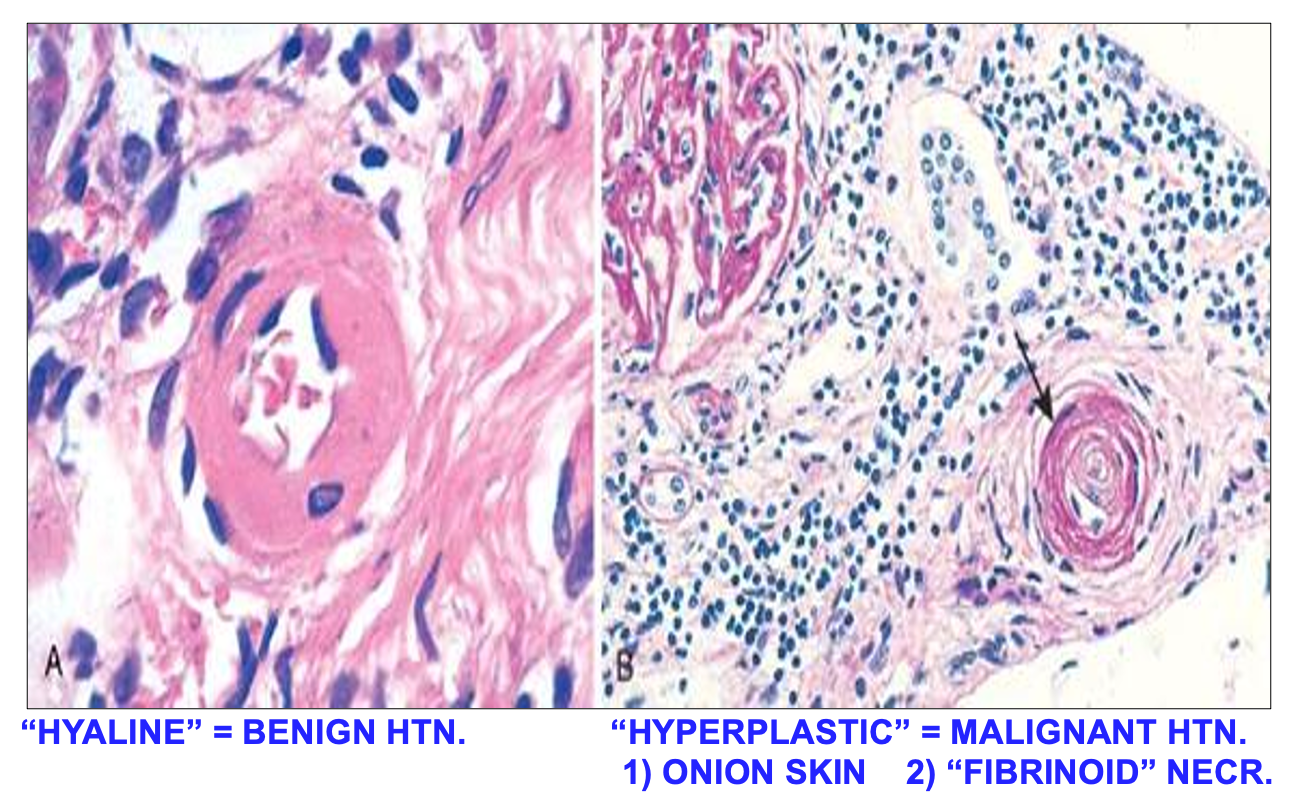
References Robbins Basic Pathology 10th edition, 2017 ( Kumar, Abbas, Aster) AMBOSS: https://next.amboss.com/us/article/Xh09cf?q=hypertension