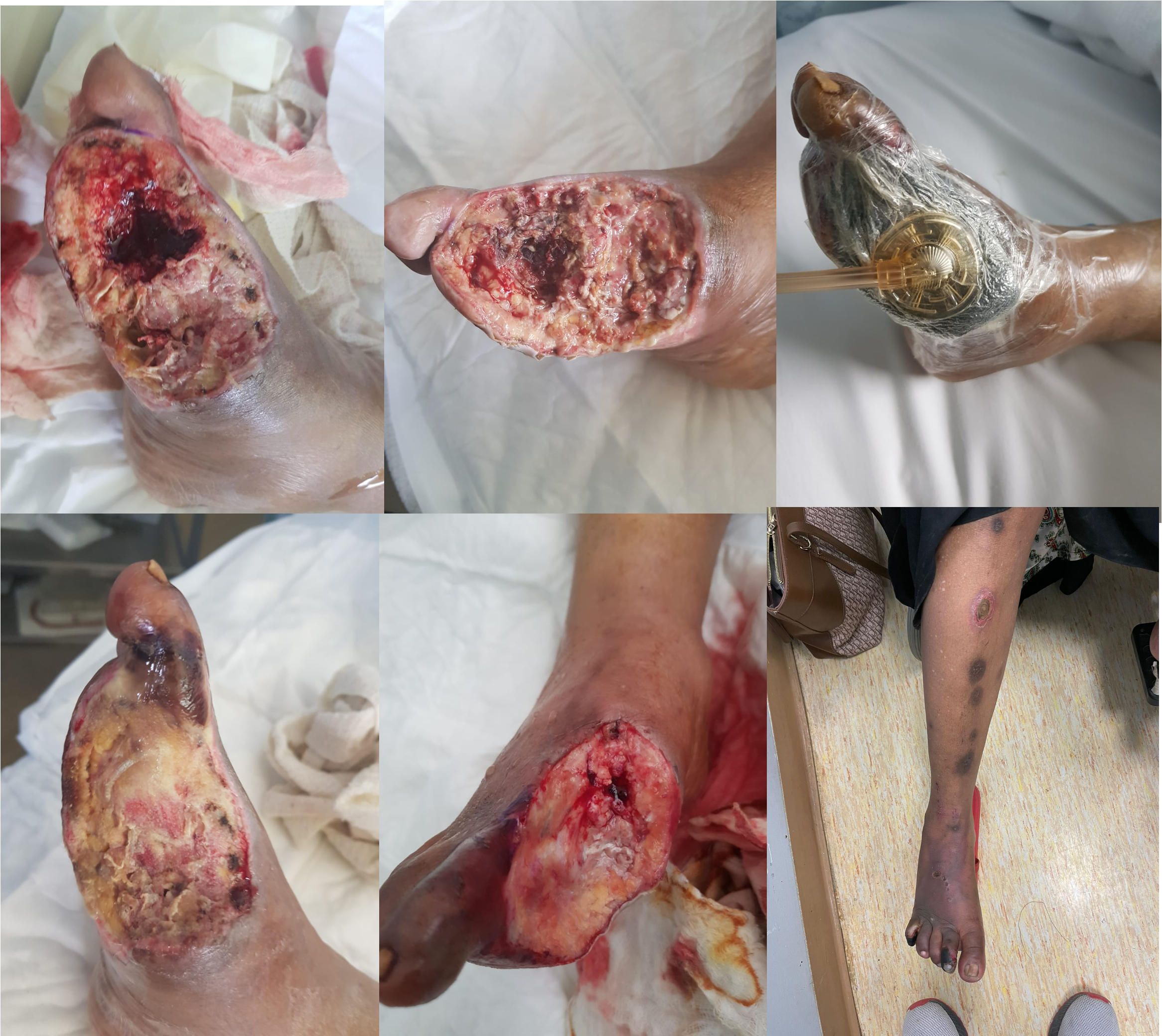
Diabetic Ulcer
Dr Shaher Abbarah
Hx & Exam
Diabetic Foot History & Examination
Presentations
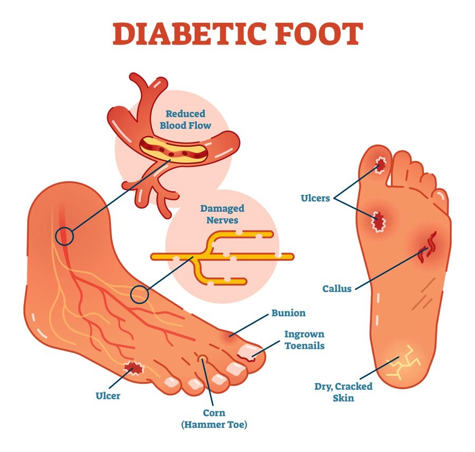
Diabetic Foot
All diabetes people should be examined at least annually for the presence of peripheral neuropathy, and peripheral arterial disease, two of the most important risk factors for developing foot ulcers.
The history of symptoms of peripheral neuropathy (a burning sensation, pins and needles in the lower extremities, shooting, sharp or stabbing pains, muscle cramps), usually neuropathic symptoms are worse during the night, at rest).
Loss of vibratory sensation and altered proprioception (affecting balance and causing numbness and tingling) and light touch reflect large‐fiber loss, whereas impairment of pain and temperature sensation occur secondary to the loss of small fibers.
Decreased or absent ankle reflexes occur early in the disease,
Diabetic neuropathy is also a major contributor to falls and fractures through loss of protective sensation (LOPS), proprioception, temperature discrimination, and pain, all ultimately leading to unsteadiness, recurrent minor injuries, and an increased risk of falls.
Management:
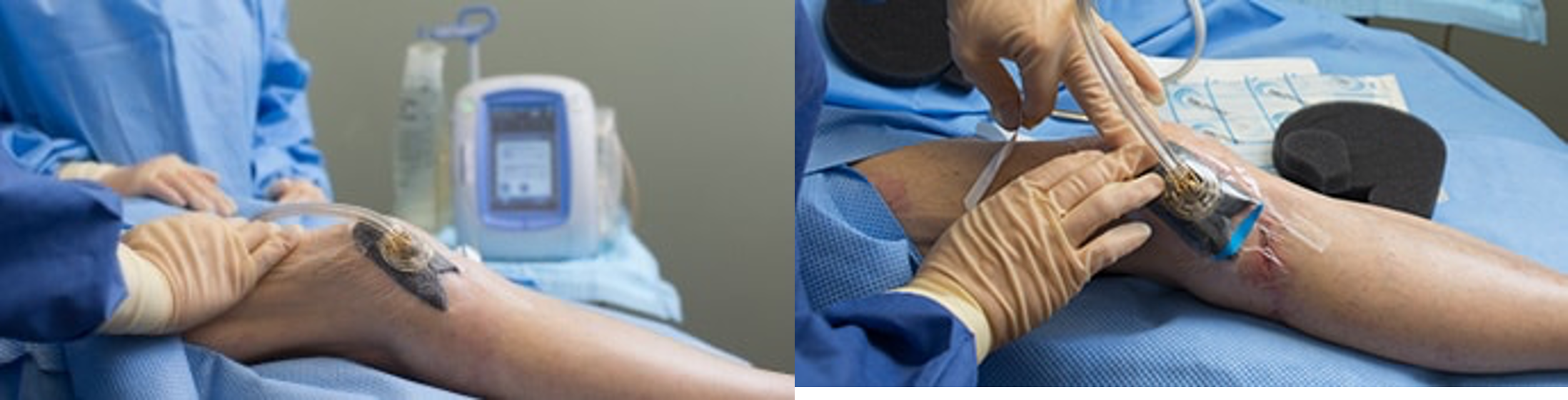
Local wound care:
- Clean
- Debride infected necrotic devitalized tissue
- Wet dressing
- ?VAC
Investigation
- Blood test (CBC, KFT, Alb, C-RP, ESR, culture)
- Wound Culture
- X-ray
- MRI
- ABI
- Angiography
Read about Diabetic Foot Infection (P.58 principle & practice of Surgery)Z
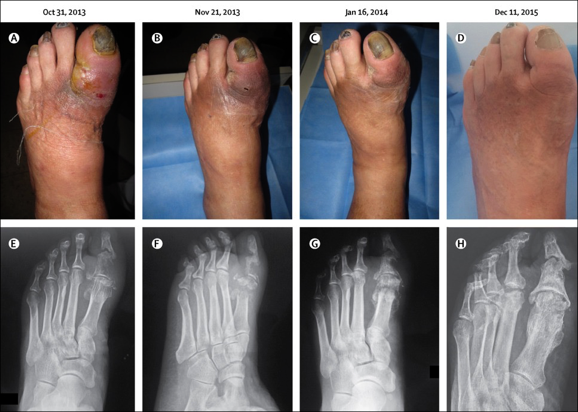
Xray findings of Osteomyelitis:
- periosteal reaction / elevation
- cortical irregularity / thickening
- Demineralization, osteopenia
Treatment -
Anti-biotics: (Target ?, Duration?, route)
- Broad spectrum, covering G+ve, -ve & Anareobic
- In case of mild infection, duration of 1-2 weeks.
- In case of sever infection, duration of 2-4 weeks.
- In case of Osteomylitis, duration of 4-6 weeks IV.
- Control sugar, blood pressure, lipids
- Prevention (proper shoes, instructions, … )
Patient education and routine foot care
- Wear comfortable, supportive footwear
- Avoid walking ‘barefoot’
- Wash the feet once a day in warm (not hot) soapy water
- If the skin is dry, use a regular emollient to reduce risk of fissuring
- Never fail to remove a foreign body from the shoe immediately after it is noticed
- Do not warm the feet using hot water bottles or by direct contact with a radiator
- Never attempt to ‘self-manage’ callosities using sharp paring instruments
- Do not apply adherent dressings such as corn plasters to the feet
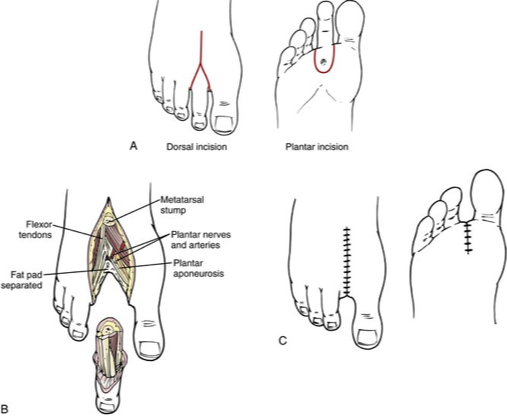
Amputations:
- Types ? Ray amputation, which involves the excision of the toe and part of the metatarsal
Home message
10-25% of DM patient has risk to develop ulcers. Main pathophysiology are peripheral neuropathy, peripheral vascular disease and immunodeficiency. Patient education, medical management and early detection of foot problems play important roles in improving chances of limb preservation.
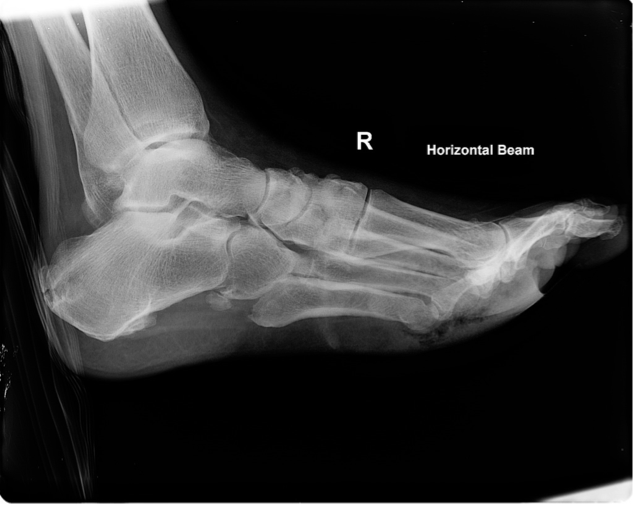
Subcutanous emphysema
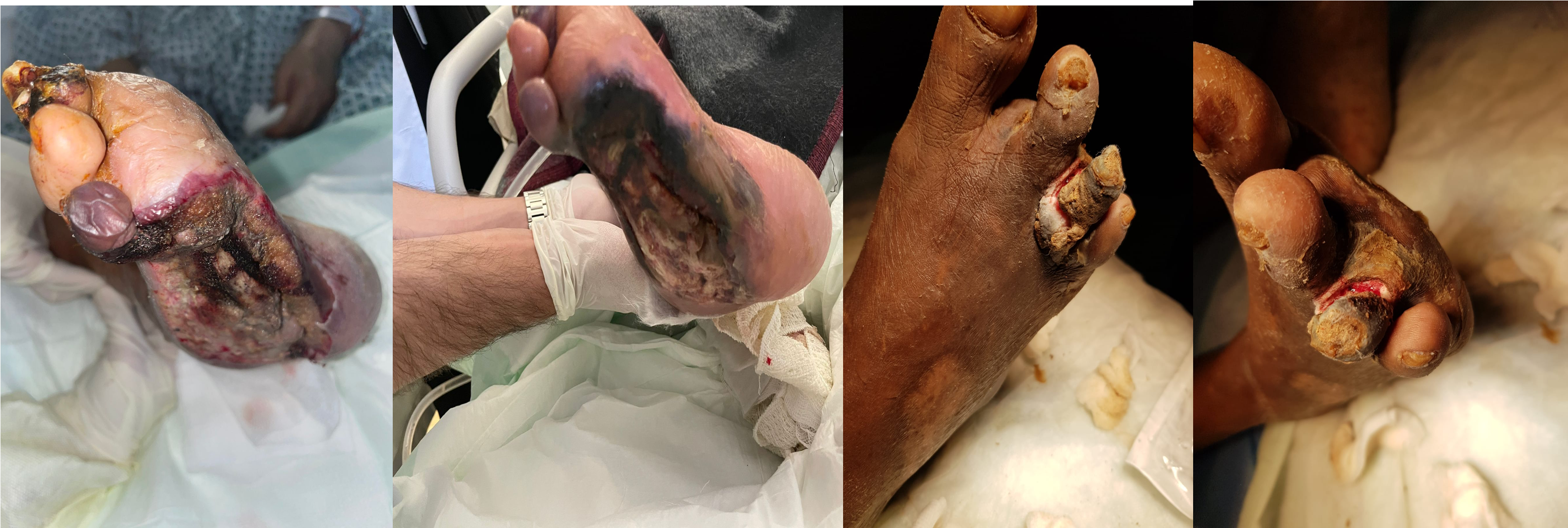
- Ulcer in sole of foot, 8x8 cm, granulation, necrotic tissue and wet gangeren, bone, irregular margins,