Choice of Treatment
Conservative treatment
Stable Fractures - Incomplete
- Greenstick
- Buckle (Torus)
- Plastic deformation
Stable Fractures - Complete
- Undisplaced
- Displaced, reducible
Operative treatment
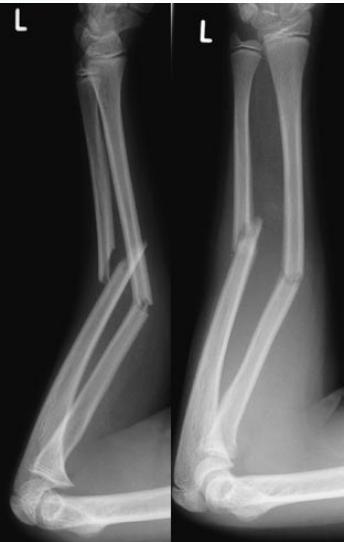
Unstable Fractures
- Both bones at same level (ex: forearm)
- Oblique fractures
- Comminuted fractures (difficult in healing)
Closed Reduction and Casting
- The commonest approach
- Good remodeling power
- Needs close monitoring:
- Must re-check within days
- Regular follow-ups
- If swelling subsides:
- ✓ Cast becomes loose
- ✓ Fracture may displace
Age consideration: 4-5 years may accept conservative but if 6-10 years → do surgery
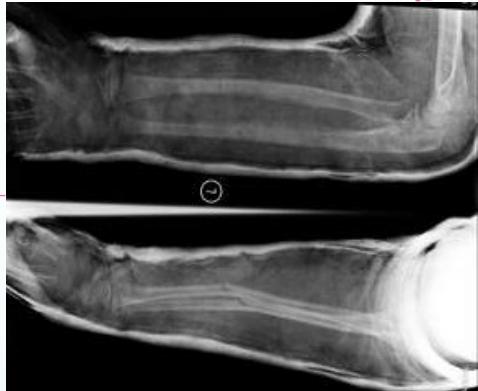
Surgical Treatment Options
K-Wires
- The commonest in children
- Effective:
- Prevents displacement
- Application:
- Percutaneous
- Open
- Needs additional casting
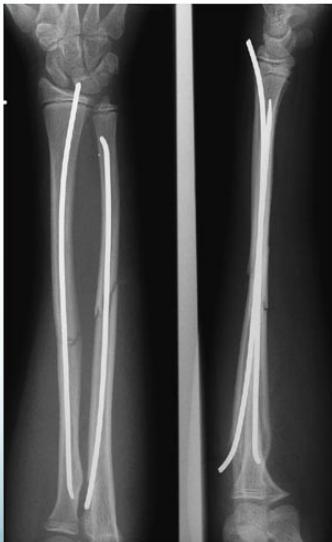
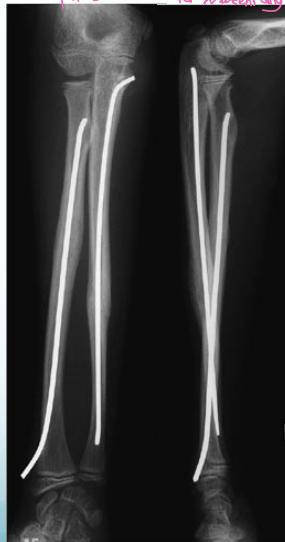
Elastic Intramedullary Nails
- For unstable fractures – minimal surgery
- Put back slab for 2 weeks only
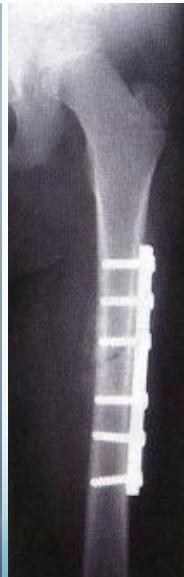
Plating
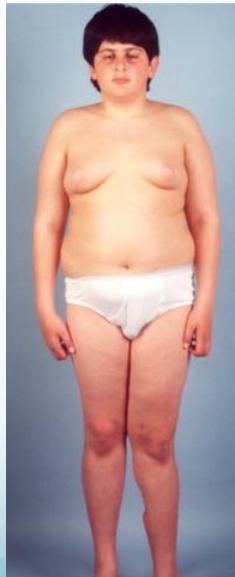
- For overweight children
- Problems:
- Large scars
- Needs removal
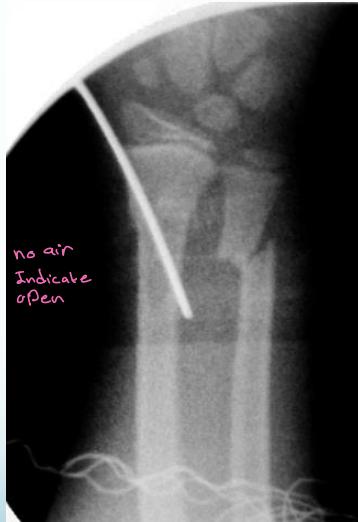
External Fixator
- Open (compound) fractures
