Common Pediatric Fractures
Prof. Mamoun Kremli Dr. Tarif AlAkhras
Objectives
- How are children’s fractures different
- Discuss common fractures in children
- X-ray diagnosis
- Principles of management
- Identify Epiphyseal injuries
- Precautions
Treatment Approaches in pediatric fractures
Common Pediatric Injuries
-
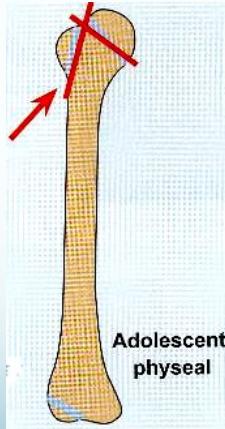
Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries
-
Clavicle Fractures
-
Supracondylar Humerus Fractures
-
Forearm Fractures - Radius and Ulna
-
Femur Fractures
-
Non-accidental injuries
Summary
- Fractures in children are common
- Closed reduction is good
- Surgery might be needed
- Supracondylar humerus needs urgent attention
- Epiphyseal injuries ⇒ Growth Arrest
- Beware: Non-accidental injuries & Tumors
How Children’s Fractures Differ from Adults
Anatomical Differences
- Ends of long bones have thick cartilage:
- Not seen on x-rays
- Growth plate:
- Good remodeling. Special injuries
- More elastic, more cancellous:
- → Incomplete fractures, simple fractures
- Periosteum:
- Thick, good blood supply → Heal well & quickly
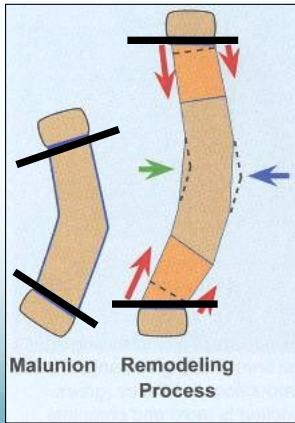
The Power of Remodeling
- ✓ Accept more angulation and displacement
- Better remodeling near growth plates
- Rotational mal-alignment does not remodel
Femoral Shaft Displacement Example
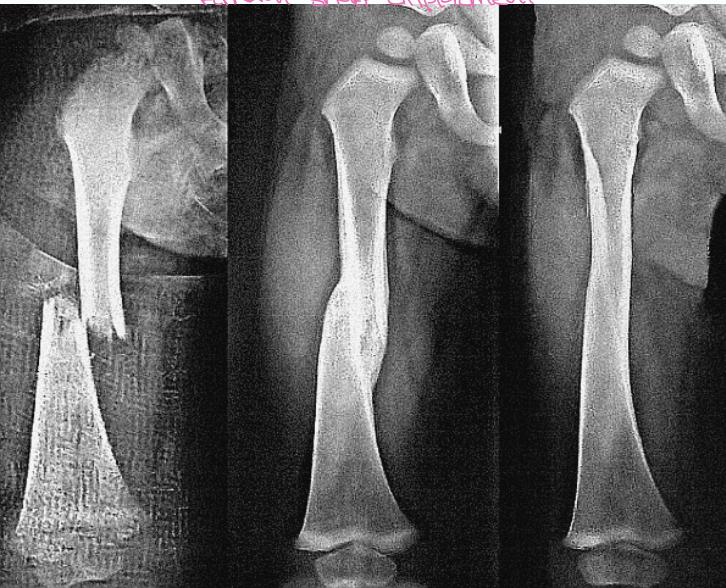
“We accept it in children, but in adults we don’t”
Age-Specific Fracture Patterns
- Varies in various age groups
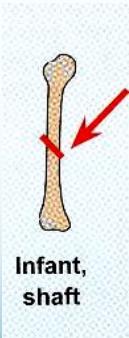
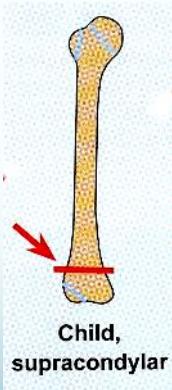
Fracture Types Specific to Children
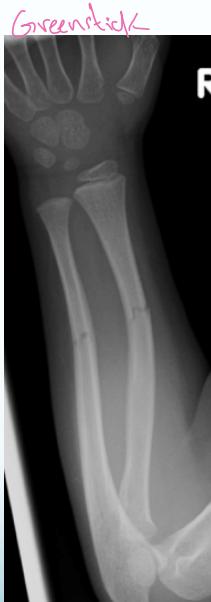
- Greenstick - only on cortex
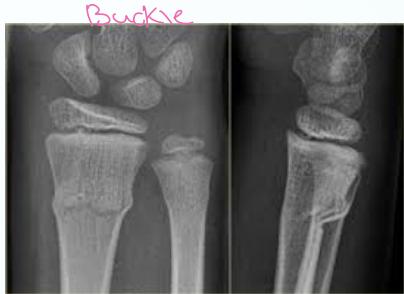
- Torus (buckle) - Compression on one side
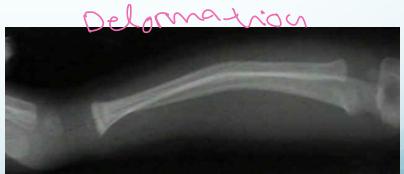
- Plastic deformation - abnormal shape without fracture line
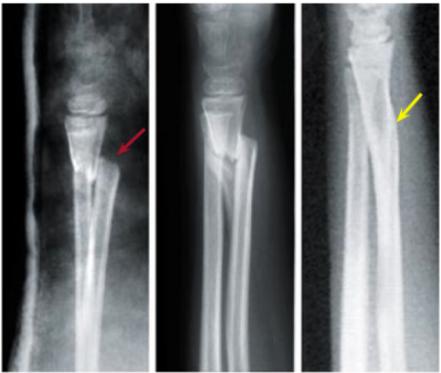
- Physeal injuries
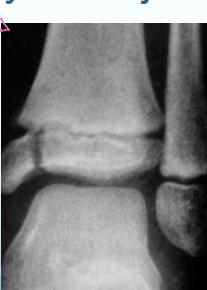 phyuseal injuries
phyuseal injuries