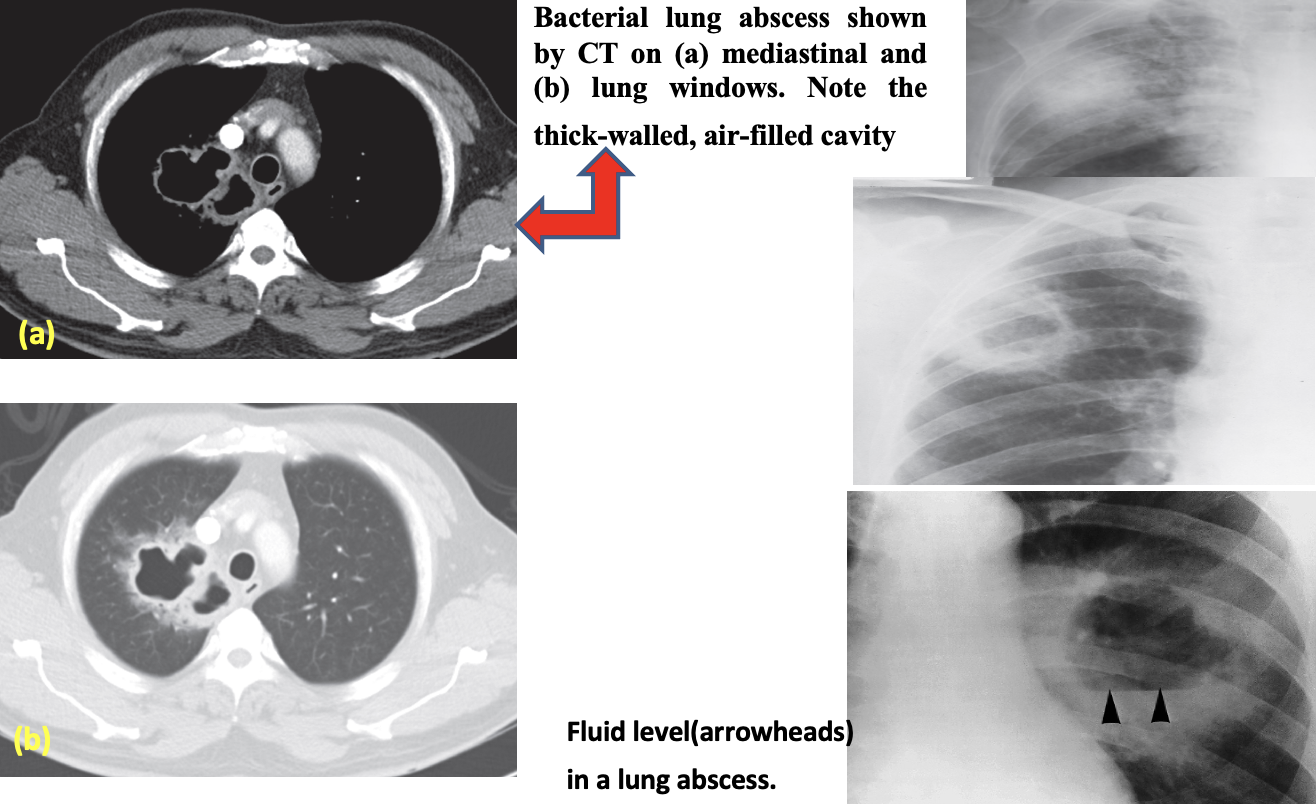
Pediatrics
Lung abscess
-
Clinical manifestations of lung abscess are nonspecific and similar to those of pneumonia
-
They include fever, cough, dyspnea, chest pain, anorexia, hemoptysis, and putrid breath.
-
The diagnosis is suggested by a chest radiograph demonstrating a thick-walled cavity with an air-fluid level and confirmed by contrast-enhanced computed tomography .
-
The most common complication of lung abscess is intracavitary hemorrhage.
-
This can cause hemoptysis or spillage of the abscess contents with spread of infection to other areas of the lung .
-
Other complications of lung abscess include empyema, bronchopleural fistula, septicemia, cerebral abscess, and inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone
Anterior view of a chest radiograph in a patient with thick-walled right lung abscess. The patient later developed a brain abscess.
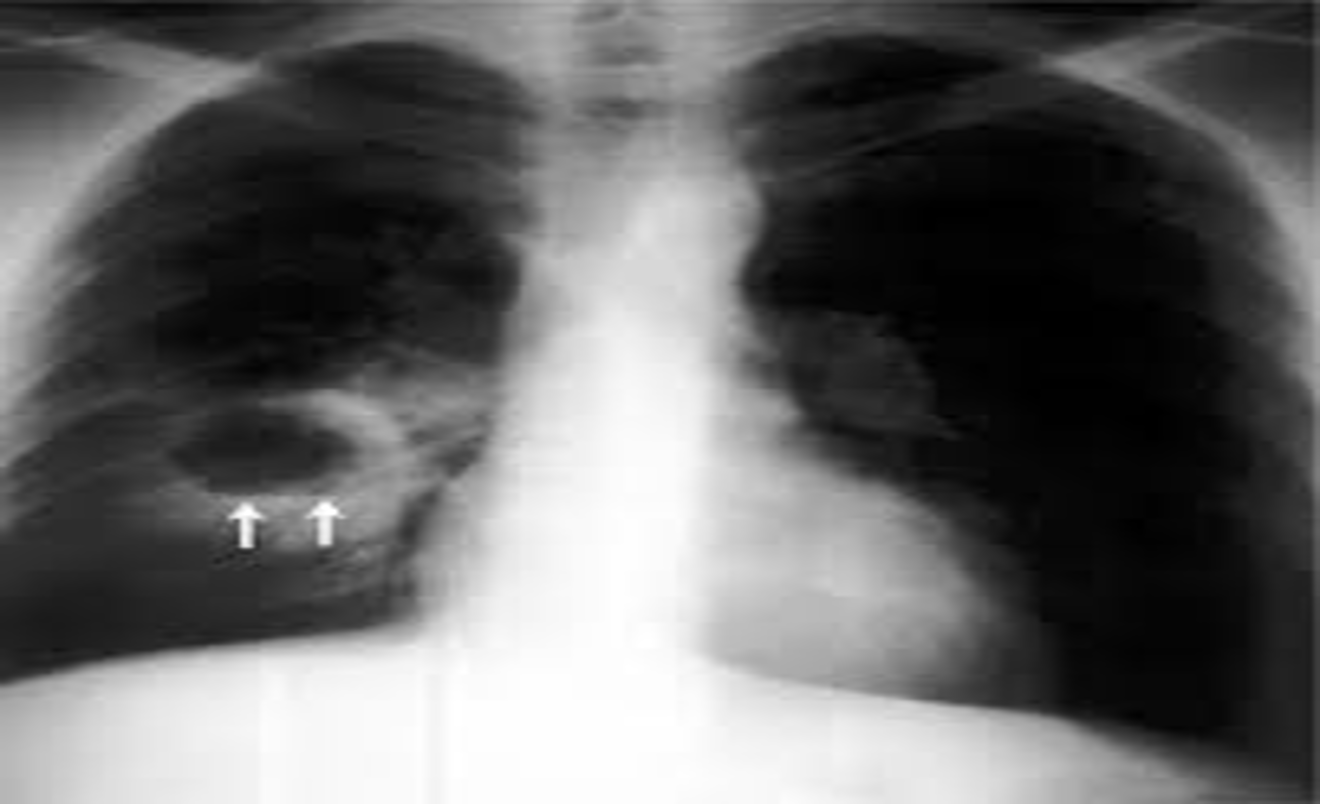 Air fluid level
Air fluid level
Radiology
Cavitation (abscess formation):
The air is then seen as a transradiancy within the consolidation and an air–fluid level may be present
CT is better and more sensitive than CXR for demonstrating cavitation