Dr. Alaidaroos
Hernia History & Examination
Abdominal wall hernia
DEFINITION: Hernia is an abnormal protrusion of a part or whole of the viscus through a normal or abnormal opening through the wall of the cavity that contains it. Risk factors:
- Chronic cough, obesity,
- Straining (constipation),
- Repeated pregnancy,
- Family history,
- Ascites,
- Defective collagen synthesis,
- Heavy lifting,
- RLQ incision.
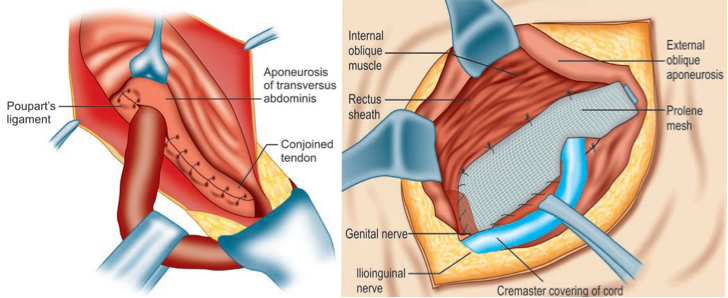
The ilioinguinal nerve, encountered during an incisional appendectomy, provides motor innervation to muscles around the conjoint tendon??? near the ligament. Damage to this nerve could lead to muscle weakness, potentially resulting in an abdominal hernia.
Additionally, the ilioinguinal nerve carries sensory information from the thigh and ant testicle + root penis, which may be affected during hernia surgery, but not typically during an appendectomy.
Types of Hernias
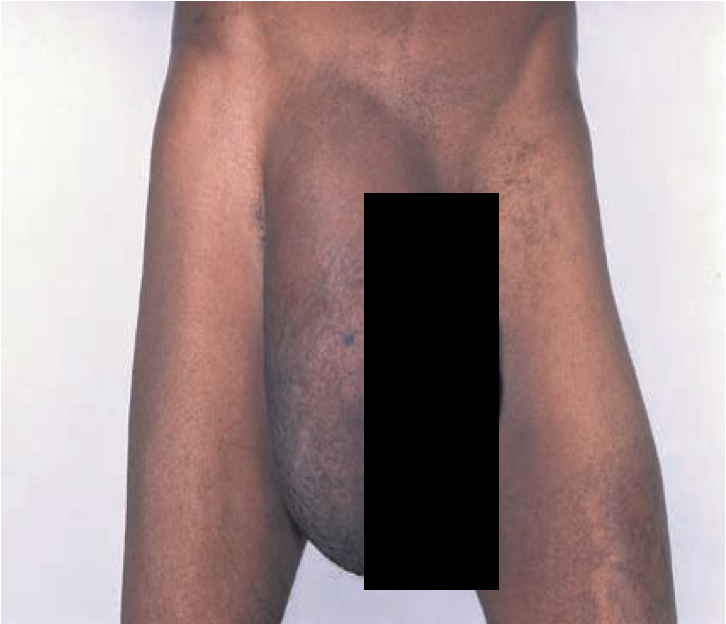
- Groin hernias: Inguinal (direct/ indirect) , femoral hernia
- Umbilical & Para-umbilical hernia
- Epigastric hernia
- Incisional hernia
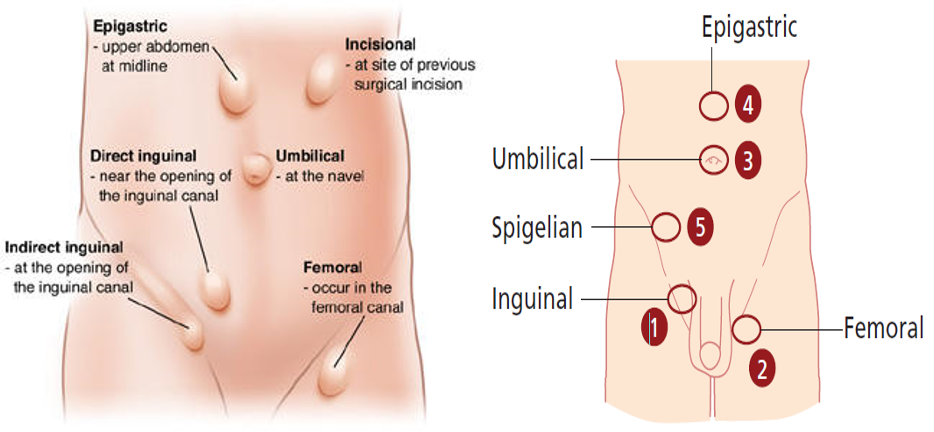
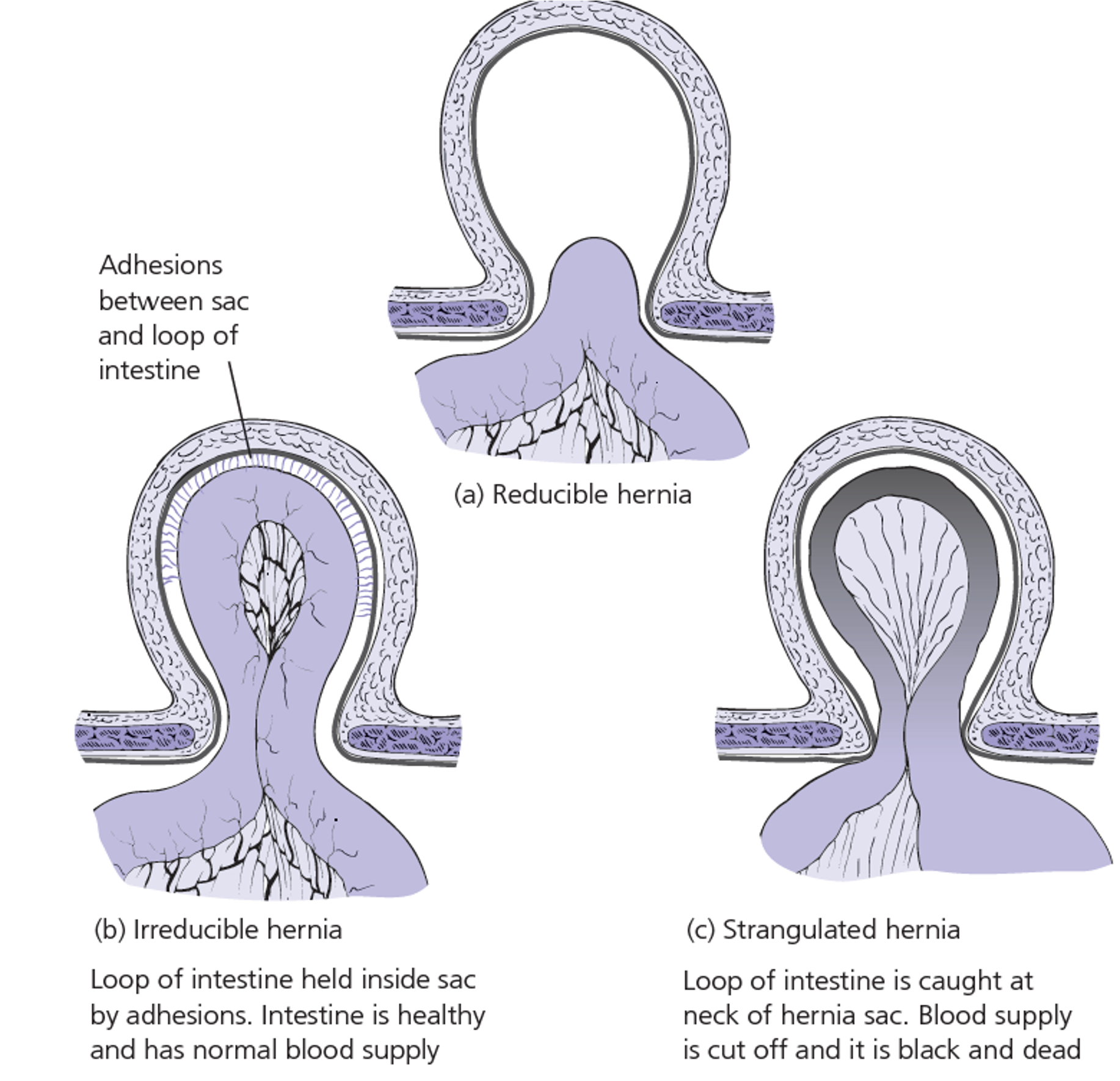
Each type can be:
- Reducible: may result in adhesion resulting in irreducible (longstanding)
- Irreducible/ incarcerated;
- Complicated: Obstructed; bowel & strangulated; artery veins
Uncommon Hernias
-
Richter’s hernia: Z Partial thickness of bowel trapped within sac leads to partial bowel obstruction with vomiting but the patient continues to pass flatus. (contents of mickel’s diverticulum colon)
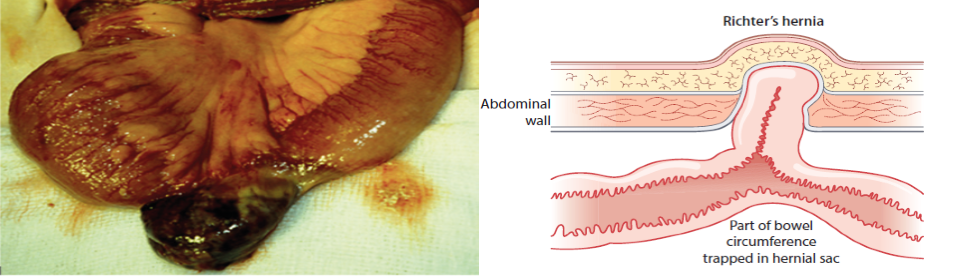
-
Sliding hernia: A peritoneal covered structure such as the colon or urinary bladder slides down extra-peritoneally with the peritoneum adjacent to it and forms the wall of the hernial sac.
-
Littre’s hernia: Hernial sac containing Meckel’s diverticulum as the content is called Littre’s hernia.
-
Pantaloon/ Dual hernia: A pantaloon hernia is described as having both a direct and indirect inguinal hernial sac lying - On either side of inferior epigastric vessels.
-
Amyand’s hernia: incarcerated appendix
Rare external hernias
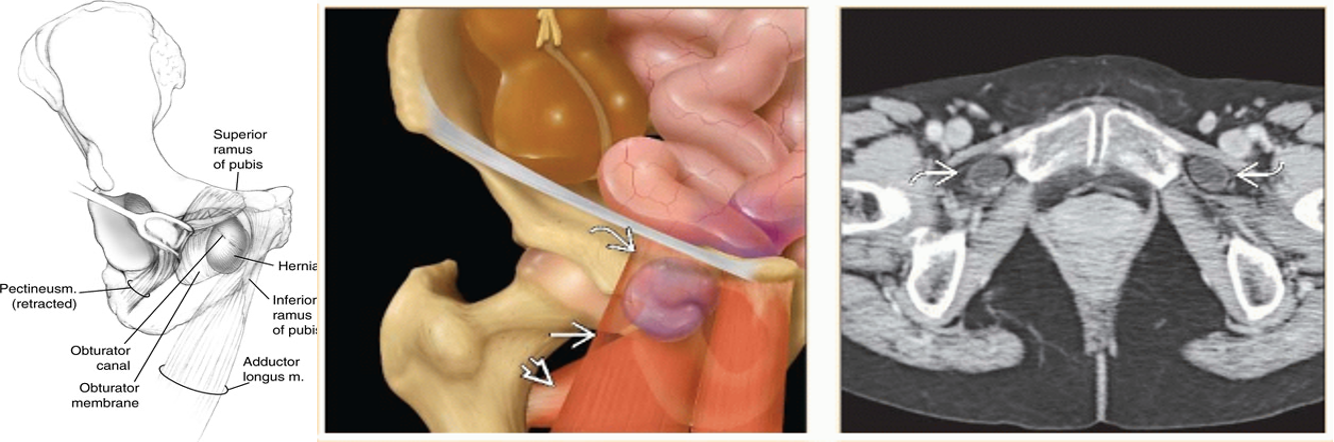
-
Obturator hernia: through obturator canal. Common in female. Diagnosis- usually at laparotomy for intestinal obstruction due to strangulated hernia.
-
Spigelian hernia: through linea semilunaris at the lateral border of rectus abdominis. Surgical repair
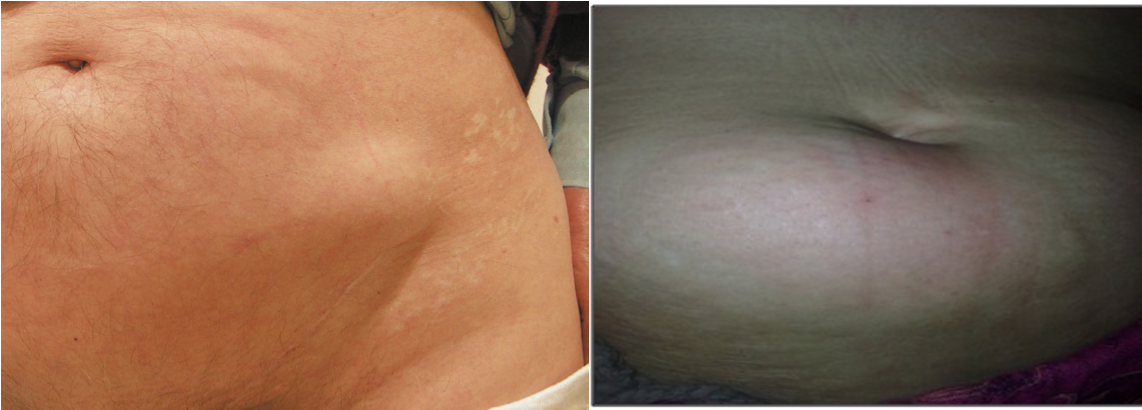
-
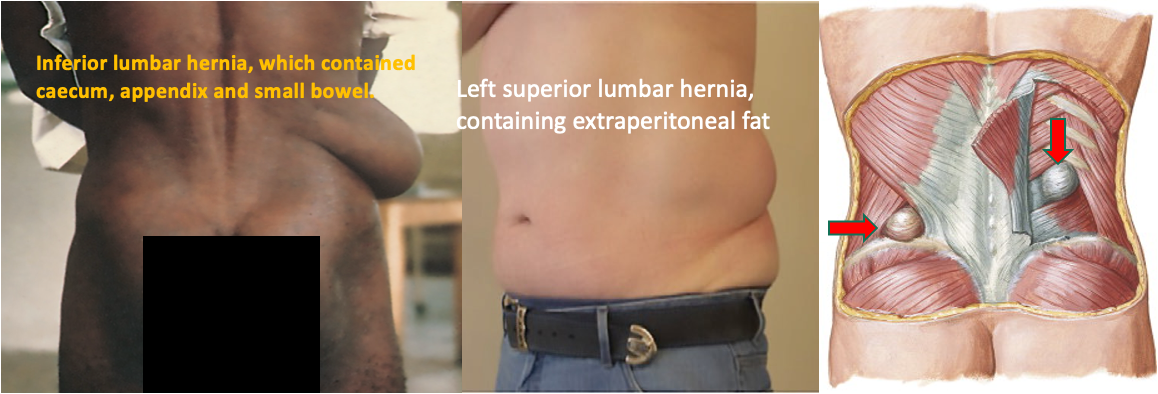
Lumber hernias:
- Superior lumbar triangle: Hernia bulges below 12th rib between sacrospinalis and posterior border of internal oblique
- Inferior lumbar triangle: Hernia bulges above iliac crest between posterior border of ext. oblique & latissimus dorsi.
Complications of Hernia
- Incarcerated: Hernia contents are irreducible due to adhesion. May obstruct or strangulate.
- Obstructed: Irreducible hernia presenting with intestinal obstruction.
- Strangulated: When blood supply to the contents is jeopardized in an irreducible hernia.
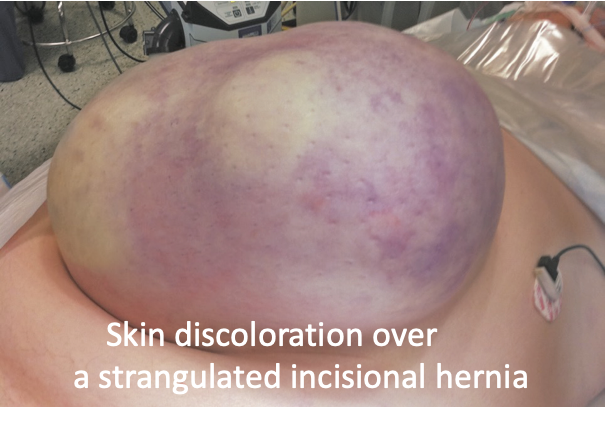
Complications of hernia surgery
| Intraoperative | Immediate postoperative | Late complications |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Injury to the blood vessels (inferior epigastric and femoral) | 1. Urine retention | 1. Recurrence |
| 2. Injury to bowel and bladder | 2. Hematoma | 2. Numbness over the local region if the nerve was cut |
| 3. Injury to ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerves | 3. Infection | |
| 4. Injury to cord structures | 4. Periostitis of pubic tubercle (as the stitch is taken from periosteum) | |
| 5. Postherniorrhaphy hydrocele (due to obstruction of lymphatics at deep ring when narrowed tightly) |
INVESTIGATIONS
I. Routine
- Hemoglobin
- Bleeding time/Clotting time
- Total count, differential count, ESR
- Urine—albumin, sugar deposits
- Blood—urea, sugar
- Blood grouping/typing—for irreducible hernia/huge hernia
II. Anesthetic Purpose
- X-ray chest (Chronic TB, Asthma—precipitate hernia)
- ECG all leads
III. USG Abdomen and Pelvis
- In old age group—to find benign prostate hyperplasia calculate post-voidal residual urine. If >100 ml it is significant
- To find any mass
TREATMENT:
A. Treat the precipitating cause of hernia first e.g.
- Benign prostate hypertrophy
- Tuberculosis
- Stop smoking
B. Conservative management is indicated only in cases of very old man with direct hernia; since there is no chance of obstruction.
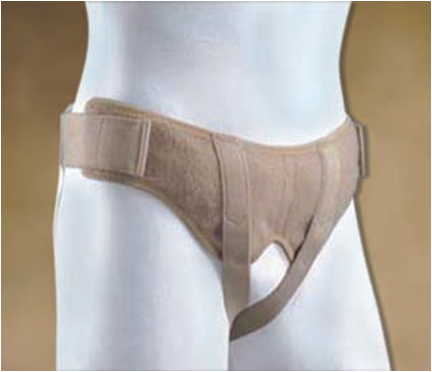
C. Truss : is not curative for hernia.
- It is a special belt devised to keep the hernia reduced at the deep ring or Hesselbach triangle for those who are unfit or unwilling for surgery
- Hernia should be reducible to wear a truss.
- Contraindicated in cases of irreducible hernia, undescended testis, associated huge hydrocele, unintelligent people.
SURGERIES FOR HERNIA
- Indirect Hernia: Adult - Herniotomy + mesh repair, Children- Herniotomy
- Direct Hernia: No sac excision, sac reduced
1. Herniotomy
2. HERNIORRHAPHY
3. Hernioplasty