PATH
Hypoglycemia is the most frequent acute complication in type 1 diabetes.
Predisposing factors:
I- Increase glucose utilization:(excess exercise,high insulin dose,alcohol intake). II- Decrease glucose supply:(missed or delayed meal).
Clinical manifestations of hypoglycemia:
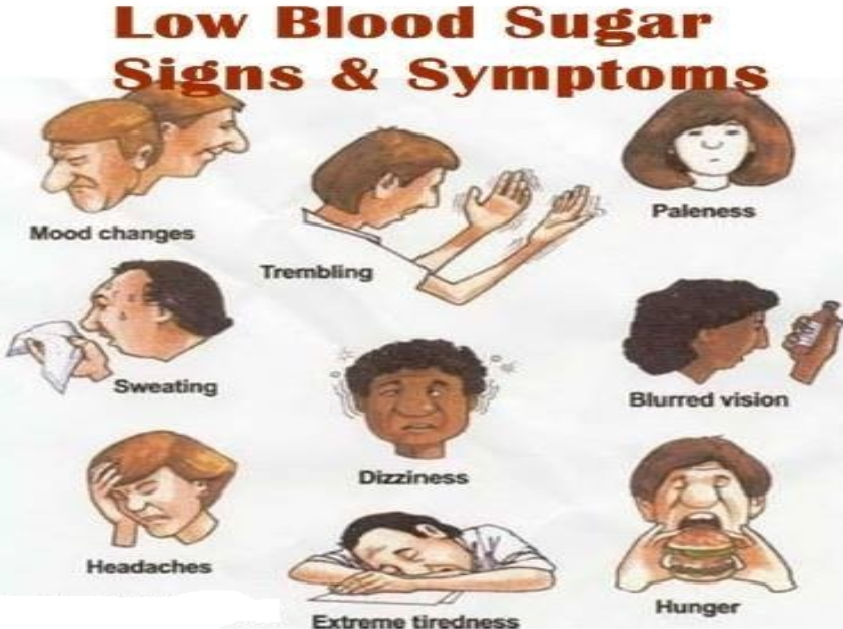
1- At first adrenergic manifestation (if glucose level less than 70mg/dl : Hunger,Tremor,Palpitation,Anxiety,Pallor, Sweating. 2- Then Neurologic manifestations(if glucose level less than 45mg/dl) : Impaired thinking,Change of mood, Irritability ,headache,Convulsion,Coma.
Treatment of hypoglycemia:
- In mild cases :oral rapidly absorbed carbohydrate.
- In sever cases :(comatose patient) I.V hypertonic glucose 25% or 50% concentration & glucagon injection.
THERA
Causes:
- Large dose of insulin or sulfonylurea.
- Missed meal while taking insulin or sulfonylureas.
- Vigorous muscular exercise without dietary adjustment.
Manifestations:
They are first discerned at a plasma level of 60 to 80 mg/DL and include:
-
Sympathetic overactivity: tremors, cold sweating, mydriasis, tachycardia anxirety.
-
parasympathetic overactivity(hunger pain , nausea), mental confusion, convulsions, and finally coma.
-
They are also named neuroglycopenic symptoms (headache, mental confusion, weakness, dizziness, blurred vision, drowsiness, bizarre behavior, convulsions and coma).
-
Severe hypoglycemia (seizure/coma) (BG < 40 mg/dL)
-
Therapy
- Conscious patients: oral glucose
- Unconscious patients: IV glucose (25-50 %) or glucagon IM 1mg I.M